The following analysis was based on the latest trade statistics from the Office of Textiles and Apparel (OTEXA) under the U.S. Department of Commerce.
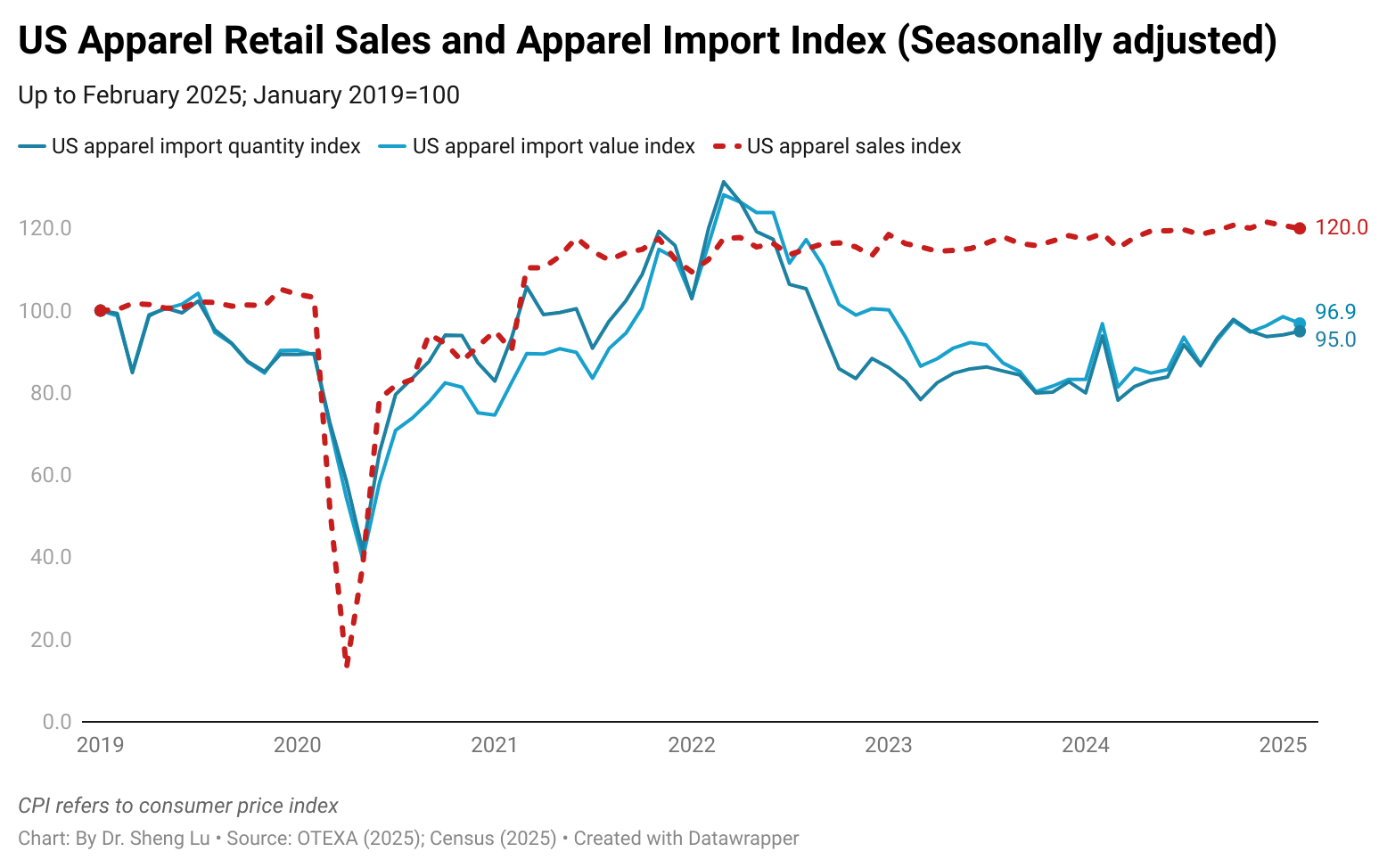
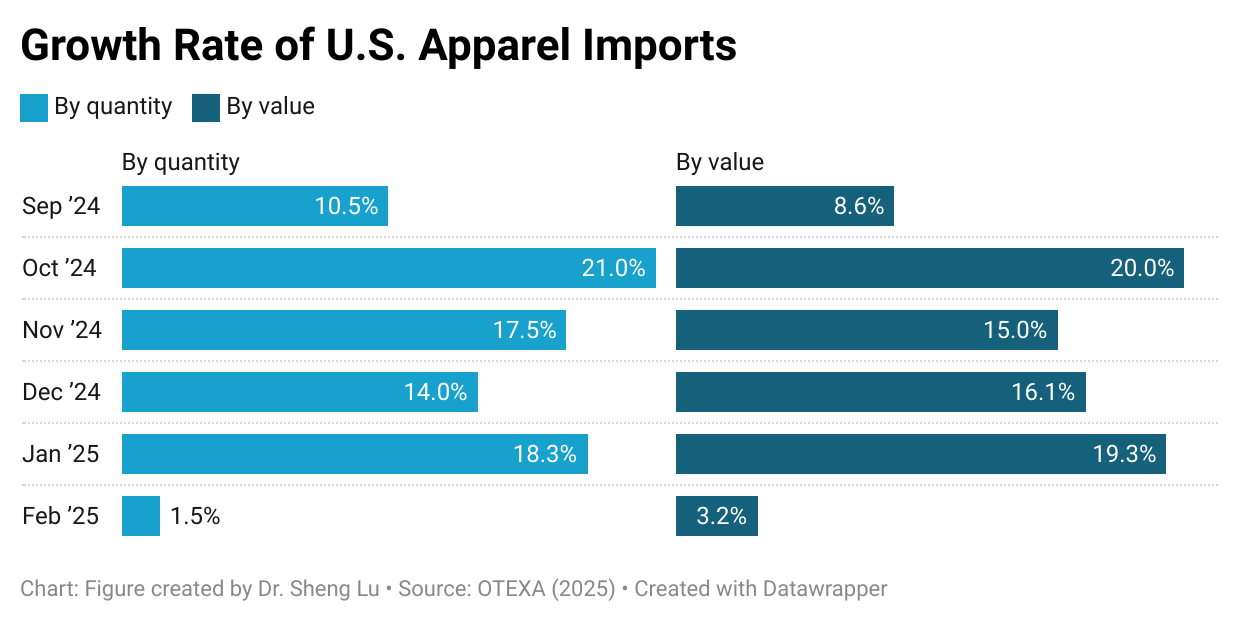
First, the growth of U.S. apparel imports significantly slowed as fashion companies shifted from eagerly piling up stock to the wait-and-see mode. Specifically, in February 2025, U.S. apparel imports moderately went up 3.2% in value and 1.5% in quantity, much lower than the 18-19% increase seen in late 2024 and January 2025. The much-slowed growth confirmed that the earlier U.S. apparel import surge was largely driven by fashion companies’ worries about the upcoming tariff hikes rather than an actual increase in consumer demand.
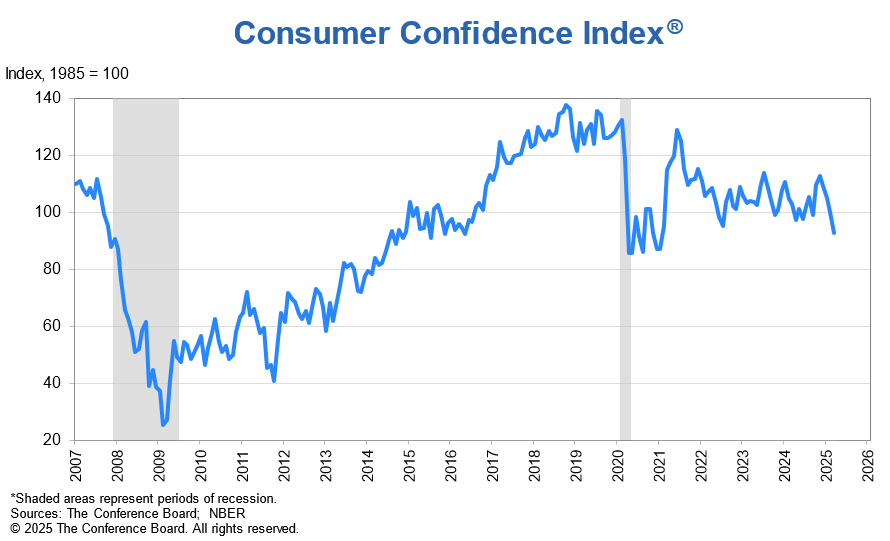
Adding to the concern, U.S. consumer confidence fell sharply, which could lead to a steep drop in U.S. apparel imports ahead. For example, the Consumer Confidence Index dropped to a two-year low of 92.9 in March 2025, down from 100.1 the previous month (1985=100). Similarly, the Expectations Index—which measures consumers’ short-term outlook for income, business, and labor market conditions—plunged to 65.2, marking its lowest level in 12 years. With the announcement of reciprocal tariffs and the growing likelihood of an economic recession, U.S. consumer demand for clothing may decline significantly, potentially leading to the cancellation of many sourcing orders.
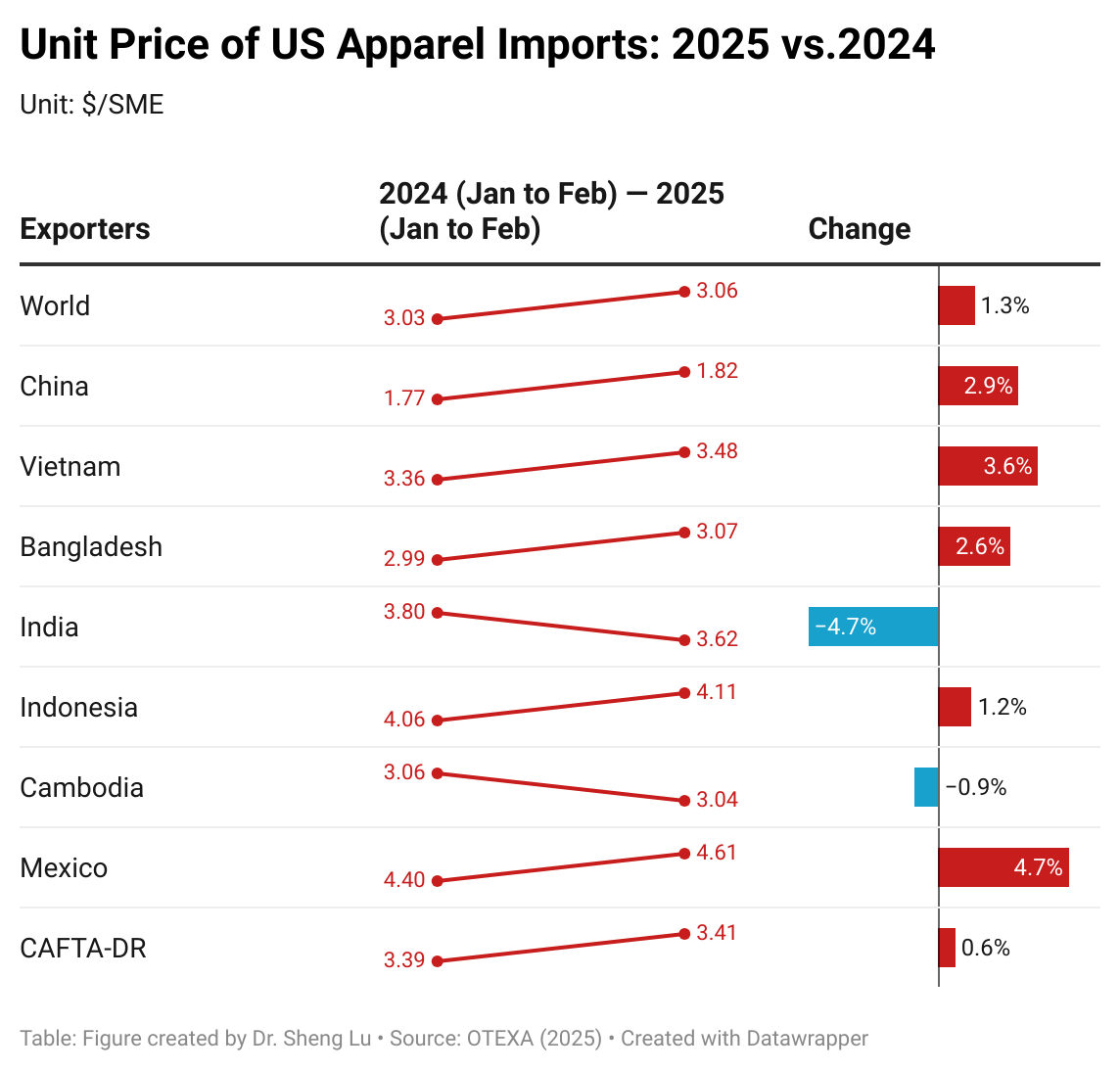
Second, apparel imports have become more expensive. Measured in dollars per square meters equivalent (SME), the unit price of U.S. apparel imports averaged $3.06/SME in the first two months of 2025, up from $3.03/SME a year ago (or a 1.3% increase). The unit price of U.S. apparel imports from many leading Asian countries rose at a notably higher rate, including China (up 2.9%), Vietnam (up 3.6%), and Bangladesh (up 2.6%), as well as those from Mexico (up 4.7%) and CAFTA-DR (up 0.6%). This result reflected the growing pressure of sourcing and production costs facing U.S. fashion companies and their suppliers, driven by rising labor costs and raw material prices among other factors. Indeed, if Trump’s reciprocal tariffs ultimately take effect, import prices could increase even more significantly.
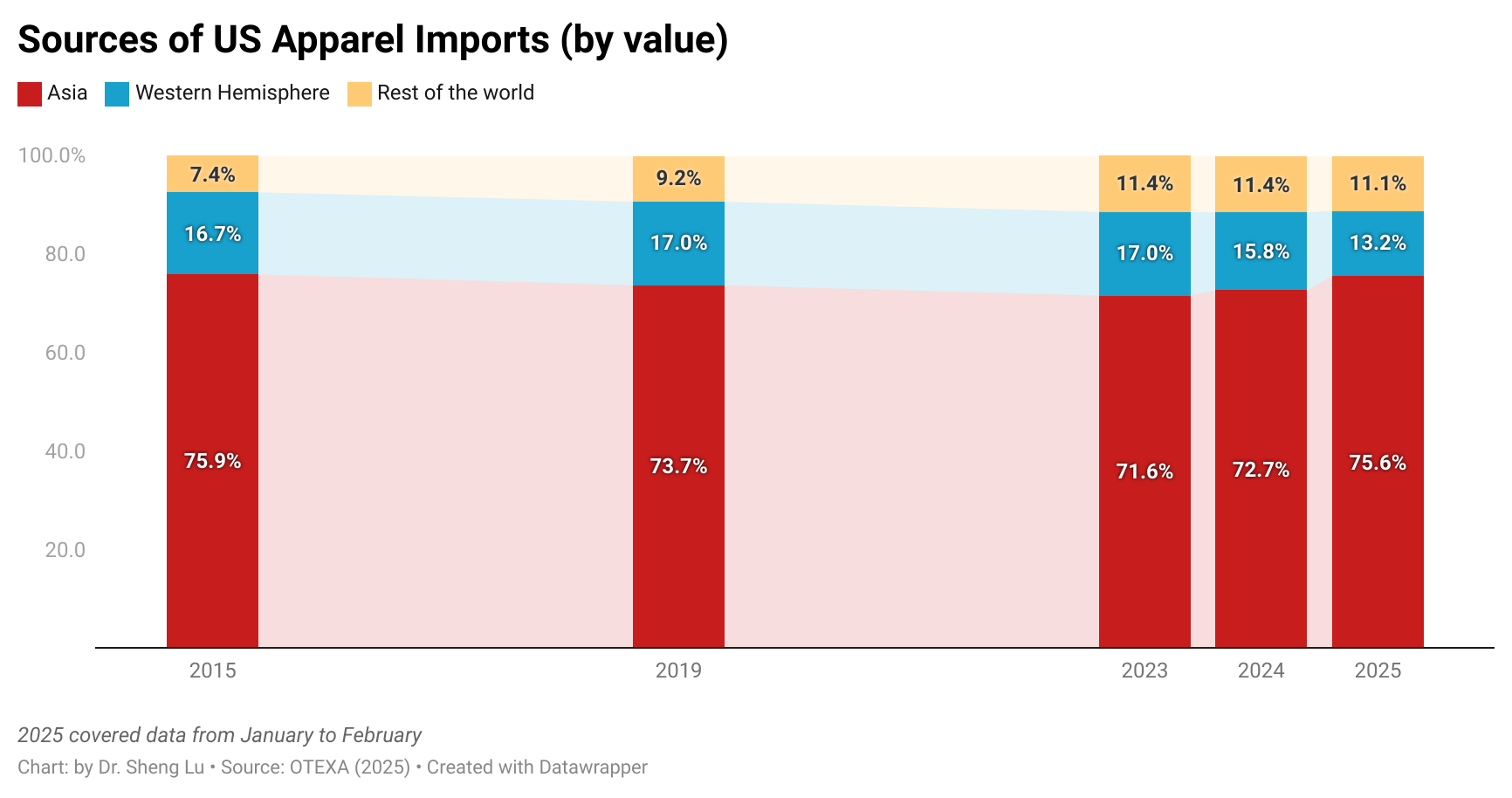
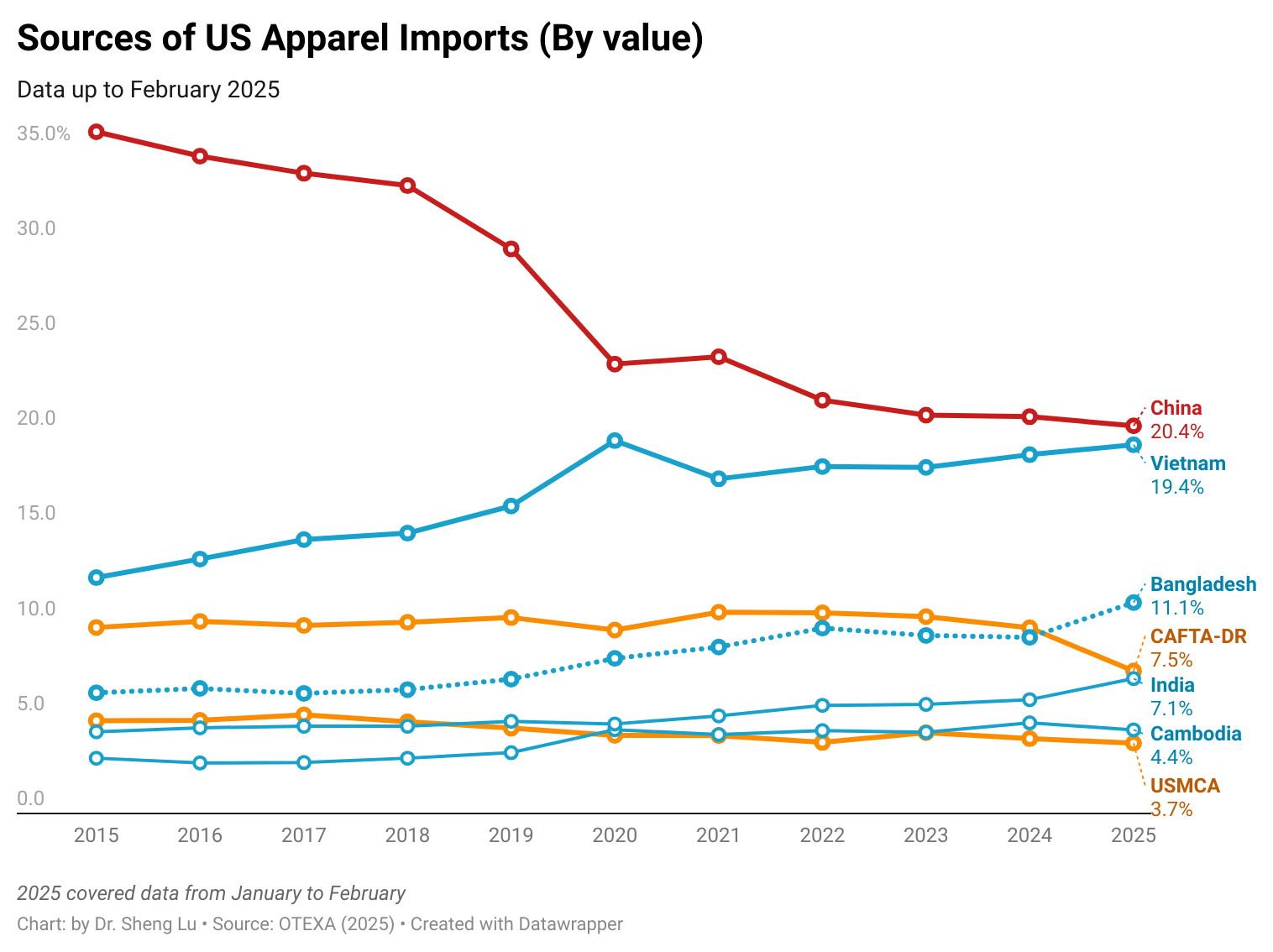
Third, U.S. fashion companies’ sourcing diversification efforts appeared to slow amid rising uncertainty. In February 2025, Asian countries collectively accounted for 71.5% of the total value of U.S. apparel imports—unchanged from a year earlier. Similarly, in the first two months of 2025, the top five suppliers (China, Vietnam, Bangladesh, Cambodia, and India) made up 63.7% of total apparel imports by value, up from 59.7% during the same period in 2024. Even China’s market share remained largely stable at 18.4% in value and 32% in quantity, compared to a year ago.
These figures suggest that U.S. fashion companies somehow have become more hesitant to adjust their sourcing base in response to the universal tariffs imposed by the Trump administration, which target nearly all U.S. trading partners. As a result, U.S. fashion companies may find the sourcing diversification strategies no longer as effective as in the past in effectively mitigating their sourcing risks.
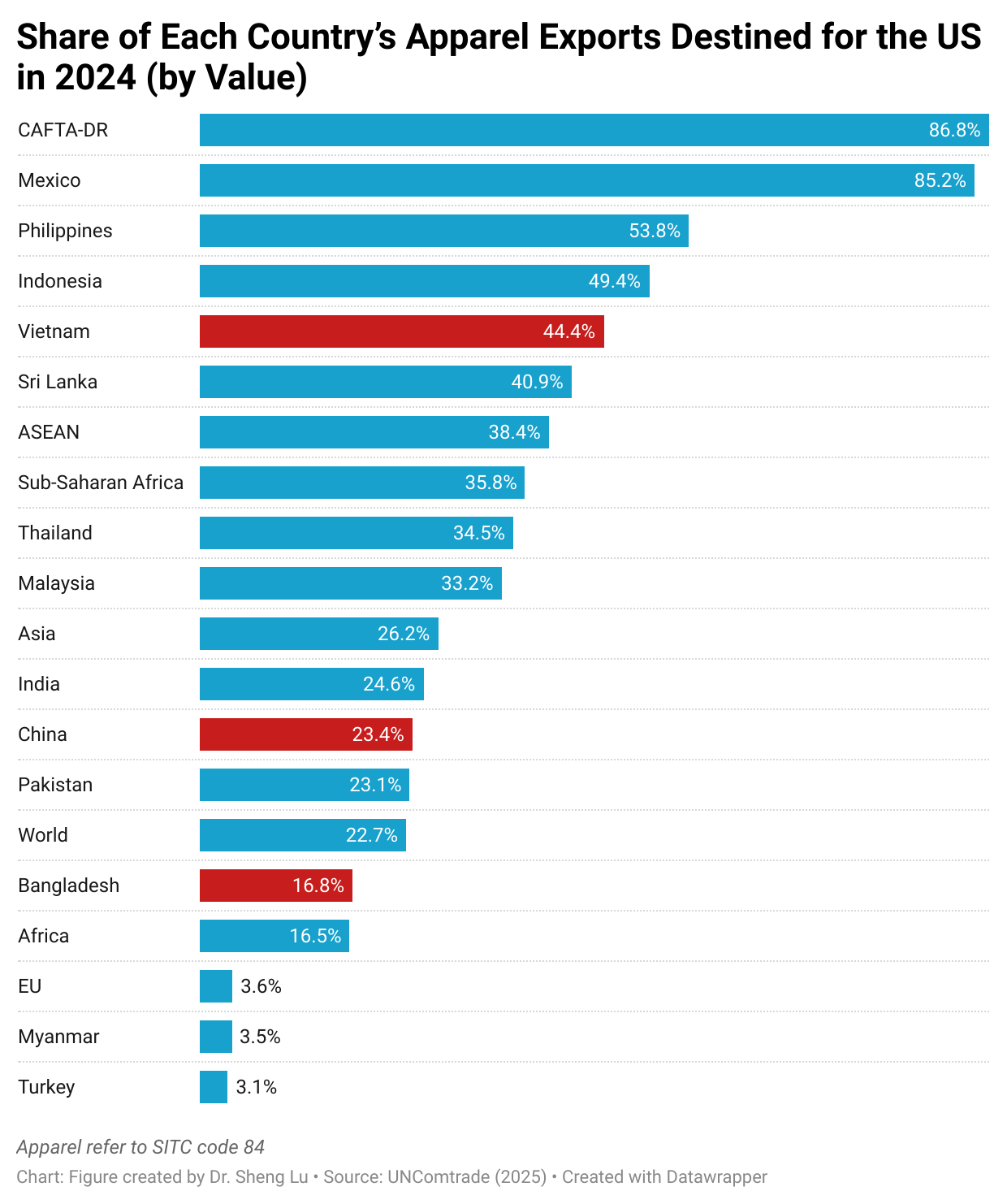
Meanwhile, data from the United Nations (UN Comtrade) show that Asian countries’ dependence on the U.S. market for apparel exports varied. In 2024, Vietnam, Sri Lanka, and ASEAN members exported about 40% of their apparel to the U.S., whereas the U.S. accounted for only about 20% of China’s and Bangladesh’s total apparel exports to the world. At the same time, the U.S. remained the single largest export market for Mexico and CAFTA-DR members, due to the integrated Western Hemisphere textile and apparel supply chain.
Fourth, no evidence shows that the current trading environment has benefited from near-shoring from the Western Hemisphere. On the contrary, measured in quantity, in February 2025, only 7.6% of U.S. apparel imports came from CAFTA-DR members, a notable drop from 9.6% a year ago. Similarly, Mexico accounted for 2.3% of U.S. apparel imports in February 2025, also lower than 2.4% a year earlier.
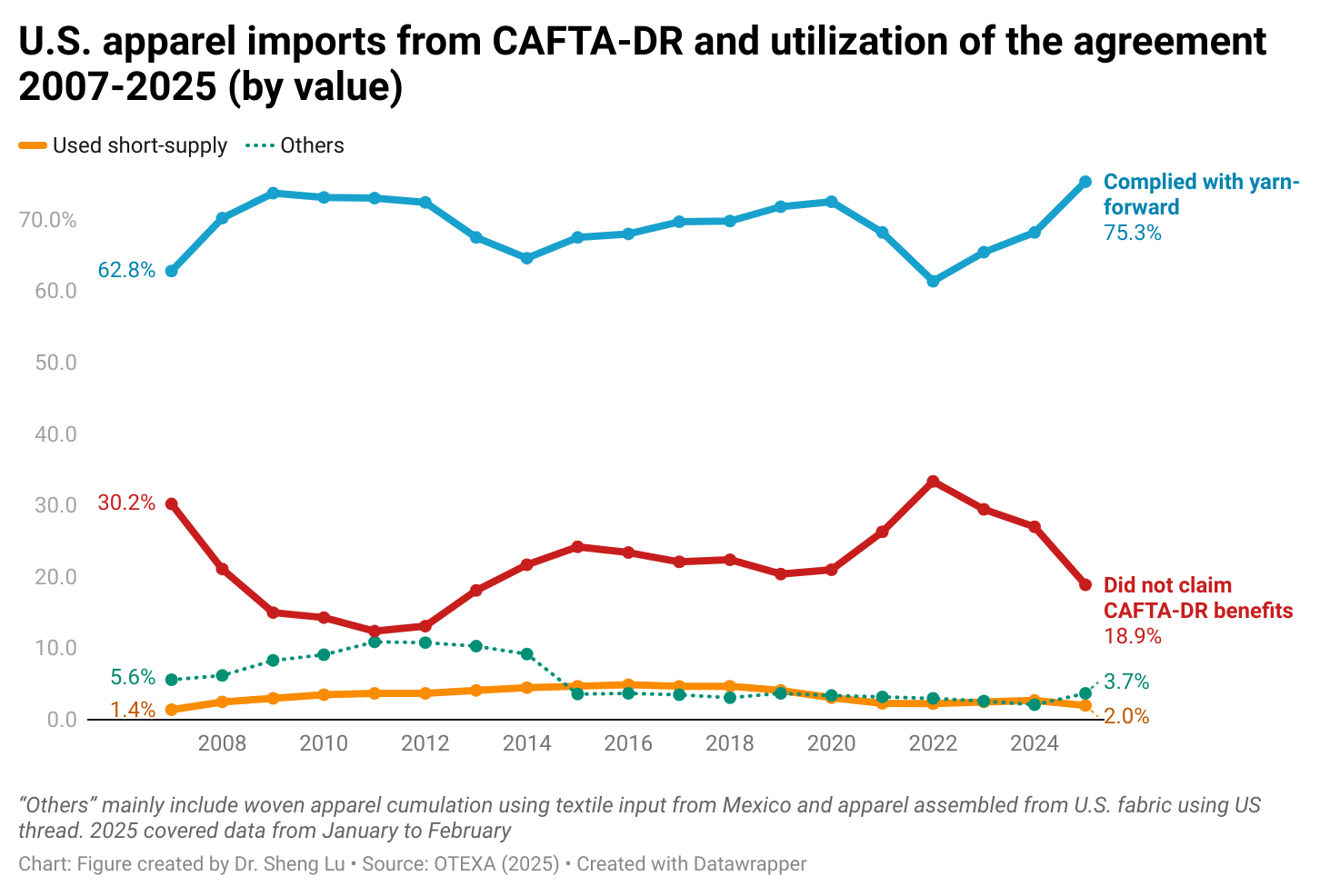
As a silver lining, the utilization rate of CAFTA-DR reached 81.1% in 2025 (January to February), much higher than 73.8% over the same period in 2024. About 75.3% of U.S. apparel imports from CAFTA-DR in 2025 (January to February) complied with the yarn-forward rules of origin compared to 67.4% a year ago. However, the use of “short-supply” remained low–only about 2.0% in 2025 so far.
by Dr. Sheng Lu
Related analysis: Lu, S. (2025). Patterns of U.S. Apparel Imports in 2024. Global Textile Academy, International Trade Centre, Geneva, Switzerland.
