On June 15, 2018, the Trump Administration announced to impose a 25% punitive tariff on a list of Chinese goods based on the results of its Section 301 investigation, which targeted against China’s unfair trade practices related to the forced transfer of American technology and intellectual property. The additional duty will first apply to 818 lines of products on July 6, 2018, which cover approximately $34 billion worth of imports from China. Office of the U.S. Trade Representative (USTR) said it would issue a final determination on the second set of 284 proposed tariff lines, which cover approximately $16 billion worth of imports from China shortly. The total 1,102 tariff lines targeted by USTR generally focuses on products from industrial sectors that contribute to or benefit from the “Made in China 2025” industrial policy, which include industries such as aerospace, information and communications technology, robotics, industrial machinery, new materials, and automobiles.
In response to the U.S. action, China’s Ministry of Commerce (MOFCOM) quickly announced its proposed countermeasures, including a 25% punitive tariff on approximately $34 billion worth of U.S. soybean, autos, and fruits effective July 6, 2018. China is also ready to impose the punitive tariff on another list of products, which cover approximately $16 billion worth of medical device, chemicals and energy imports from the United States.
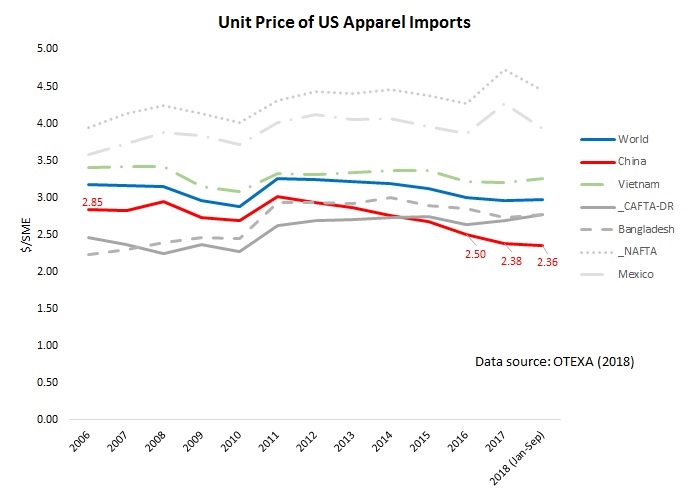
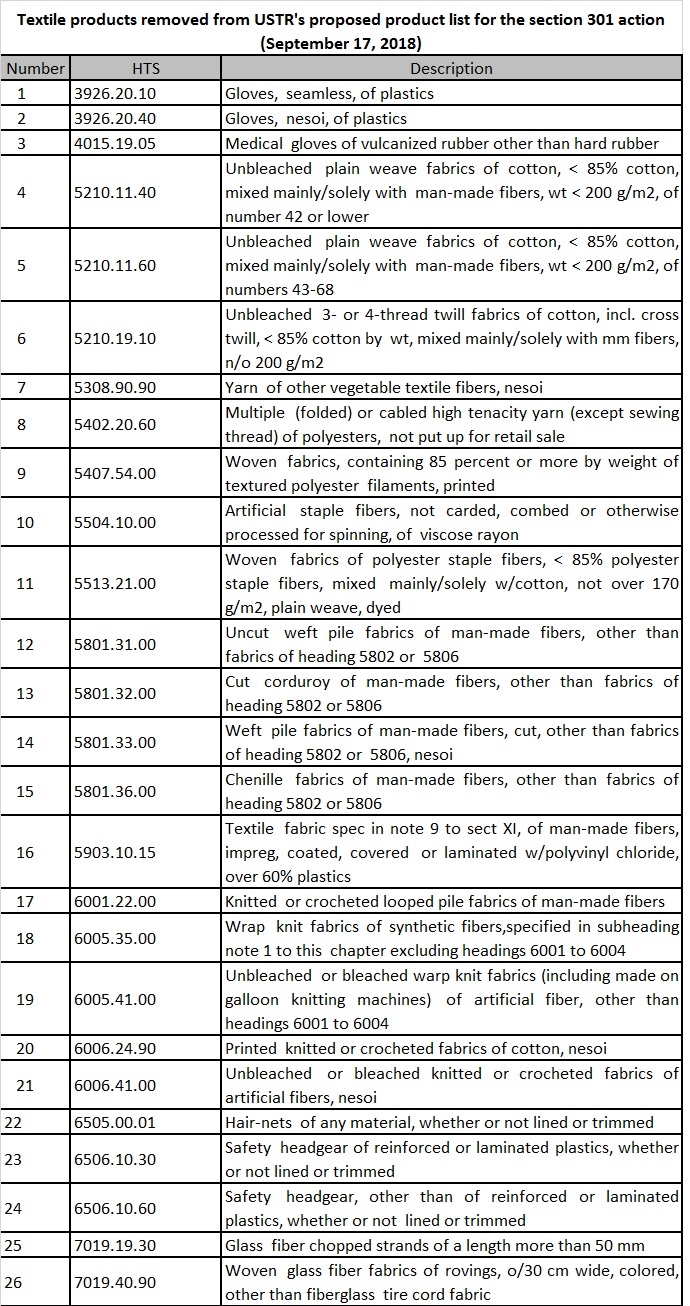
The U.S. textile and apparel industry keeps a close watch on the U.S.-China trade dispute since as much as 36% of U.S. textile and apparel imports come from China. In an announcement released on June 16, 2018, the American Apparel and Footwear Association (AAFA) called a victory that no textile and apparel products are subject to the punitive tariff proposed by USTR. The June 15 USTR list also removes the majority of the textile machinery initially on the retaliation product list back in April 2018. However, U.S. fashion brands and apparel retailers remain deeply concerned about Trump’s tariff action and its potential negative economic impacts on the apparel sector.
In contrast, the U.S. textile industry, represented by the National Council of Textile Organizations (NCTO) praised the Trump administration’s tariff announcement. NCTO also called on the Trump administration to include finished textile and apparel products on any future lists of imports from China to be made subject to Section 301 tariffs. Not surprisingly, NCTO’s proposal is opposed strongly by AAFA and the U.S. Fashion Industry Association, representing U.S. fashion brands and apparel retailers. As argued by USFIA, the U.S. tariff rates on apparel and fashion products are already the highest among manufactured goods, reaching 32 percent for man-made fiber apparel and 67 percent for footwear. Any additional tariff would constitute a huge, regressive tax increase and have a negative impact on the American jobs.
Appendix: Timeline of U.S. Section 301 Investigation against China
June 15, 2018: The Trump Administration announced to impose a 25% punitive tariff on a list of Chinese goods based on the results of its section 301 investigation
June 4, 2018: Secretary of Commerce Wilbur Ross concluded his two-day trade negotiation with China in Beijing. A White House statement said “the meetings focused on reducing the United States’ trade deficit by facilitating the supply of agricultural and energy products to meet China’s growing consumption needs, which will help support growth and employment in the United States. The United States officials conveyed President Donald J. Trump’s clear goal for achieving a fair trading relationship with China.” While the announcement didn’t mention the next round, it says that the delegation will “receive guidance on the path forward.”
May 29, 2018: President Trump suddenly announced that the United States will impose a 25 percent tariff on $50 billion of goods imported from China containing industrially significant technology, including those related to the “Made in China 2025” program. The final list of covered imports will be announced by June 15, 2018. The announcement also said that the U.S. Trade Representative Office (USTR) will continue WTO dispute settlement against China originally initiated in March to address China’s discriminatory technology licensing requirements. Additionally, the United States will implement specific investment restrictions and enhanced export controls for Chinese persons and entities related to the acquisition of industrially significant technology. The list of restrictions and controls will be announced by June 30, 2018.
May 19, 2018: A joint statement released by the White House said that the United States and China had led to an agreement for China to buy more goods and services, including “meaningful increases in U.S. agriculture and energy exports.” The statement also said that both sides attach importance to intellectual property protections, agreed to encourage two-way investment and to strive to create a fair, level playing field for competition, and agreed to engage at high levels on trade and investment issues. Additionally, the statement said that the United States would send a team to China to work out the details of the agreement. However, the statement did not contain a specific target for reducing the $375 billion trade deficits.
April 5, 2018: President Trump announced that he has instructed the Office of the U.S. Trade Representative (USTR) to consider $100 billion additional retaliatory tariffs on China, in response to China’s own retaliation against the Section 301 tariffs announced in late March. In a statement released the next day, USTR confirms the proposed new measures. USTR also says that any additional tariffs proposed will be subject to a similar public comment process as the proposed tariffs announced on April 3, 2018. No tariffs will go into effect until the respective process is complete.
April 3, 2018: USTR released the proposed list of Chinese products to be subject to the retaliatory tariff under the Section 301 action. The proposed list covers approximately 1,300 separate tariff lines and will undergo further review in a public notice and comment process, including a hearing (scheduled at around May 15, 2018). The USTR statement says it will make a final decision on whether to implement the proposed tariff action after the whole process.
March 26, 2018: USTR filed a WTO case against China’s discriminatory technology licensing requirements (DS542). The US claimed that China’s measures appear to be inconsistent with Articles 3, 28.1(a) and (b) and 28.2 of the Trade-Related Intellectual Property Rights Agreement (TRIPS). As of April 8, 2018, the European Union, Japan, Ukraine and Saudi Arabia have requested to join the dispute as third parties. According to the WTO rule, China shall enter into consultation with the US no later than April 26, 2018. If the dispute is not resolved by May 25, 2018 (i.e., 60 days after the request for consultation), the United States may request a WTO panel. As of June 17, 2018, the case is still in consultations.
March 22, 2018: President Trump announced his decisions on the actions the Administration will take in response to China’s unfair trade practices covered in the USTR Section 301 investigation of China’s Acts, Policies, and Practices Related to Technology Transfer, Intellectual Property, and Innovation. U.S. Trade Representative Robert Lighthizer initiated the investigation in August 2017 at the direction of President Trump. In the Memorandum he signed, President Trump directed the US Trade Representative to level tariffs on about $50 billion worth of Chinese imports.
January 2018: the U.S. Trade Representative Office submitted its annual report on China’s WTO Compliance to U.S. Congress. The report says that “It seems clear that the United States erred in supporting China’s entry into the WTO on terms that have proven to be ineffective in securing China’s embrace of an open, market-orientated trade regime.”
August 14, 2017: President Trump issued a memorandum directing the USTR to determine if China’s policies regarding IPR theft and forced technology requirements “may be harming American intellectual property rights, innovation, or technology development,” and thus warrant USTR action under Section 301of the 1974 Trade Act.
Related reading: The Section 301 Investigation against China Divides the U.S. Textile Industry and U.S. Fashion Brands and Retailers