[The updated World Textiles and Clothing Trade in 2022 is available]
This article provided a comprehensive review of the world textiles and clothing trade patterns in 2021 based on the newly released data from the World Trade Statistical Review 2022 and the United Nations (UNComtrade). Affected by the ongoing pandemic and companies’ evolving production and sourcing strategies in response to the shifting business environment, the world textiles and clothing trade patterns in 2021 included both continuities and new trends. Specifically:
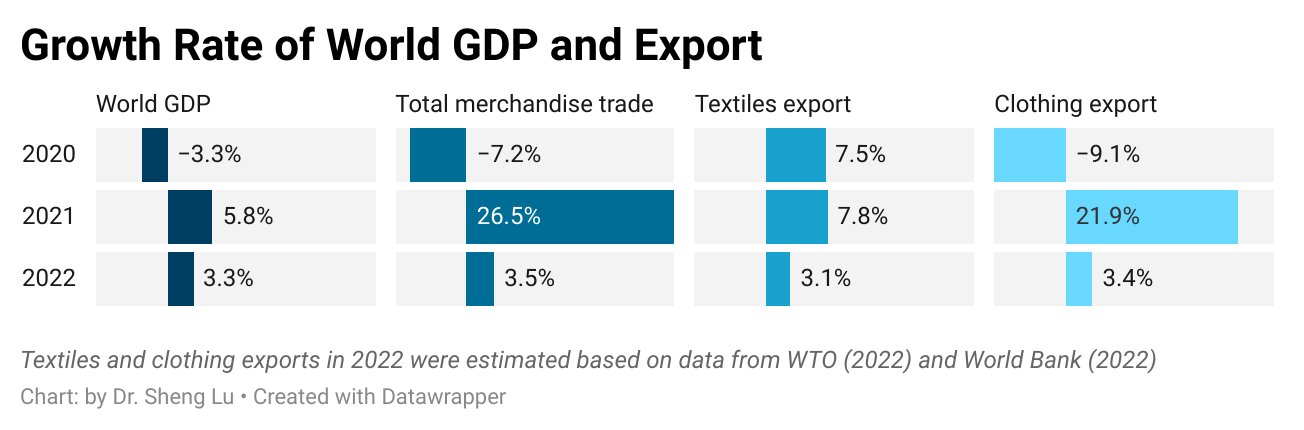
Pattern #1: As the world economy recovered from COVID, the world clothing export boomed in 2021, while the world textile exports grew much slower due to a high trade volume the year before. Specifically, thanks to consumers’ strong demand, world clothing exports in 2021 fully bounced back to the pre-COVID level and exceeded $548.8bn, a substantial increase of 21.9% from 2020. The apparel sector is not alone. With economic activities mostly resumed, the world merchandise trade in 2021 also jumped 26.5% from a year ago, the fastest growth in decades.
In comparison, the value of world textiles exports grew slower at 7.8% in 2021 (i.e., reached $354.2bn), lagging behind most sectors. However, such a pattern was understandable as the textile trade maintained a high level in 2020, driven by high demand for personal protective equipment (PPE) during the pandemic.
Nevertheless, the world textiles and clothing trade could face strong headwinds down the road due to a slowing world economy and consumers’ weakened demand. Notably, amid hiking inflation, high energy costs, and retrenchment of global supply chains, leading international economic agencies, from the World Bank to the International Monetary Fund (IMF), unanimously predict a slowing economy worldwide. Likewise, the World Trade Organization (WTO) forecasts that the growth of world merchandise trade will be cut to 3.5% in 2022 and down further to only 1% in 2023. As a result, the world textiles and clothing trade will likely struggle with stagnant growth or a modest decline over the next two years.
Pattern #2: COVID did NOT fundamentally shift the competitive landscape of textile exports but affected the export product structure. Meanwhile, some long-term structural changes in world textile exports continued in 2021.
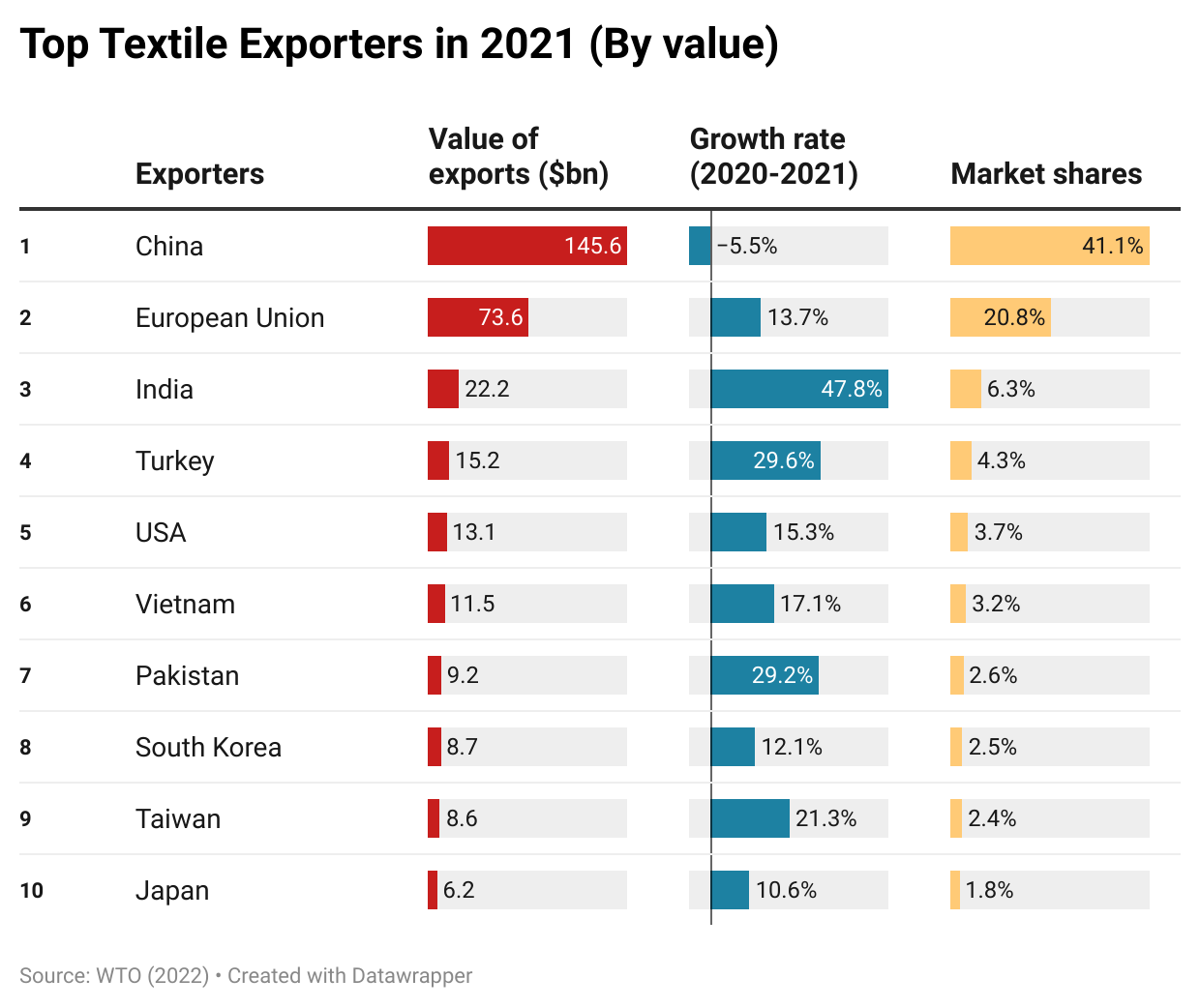
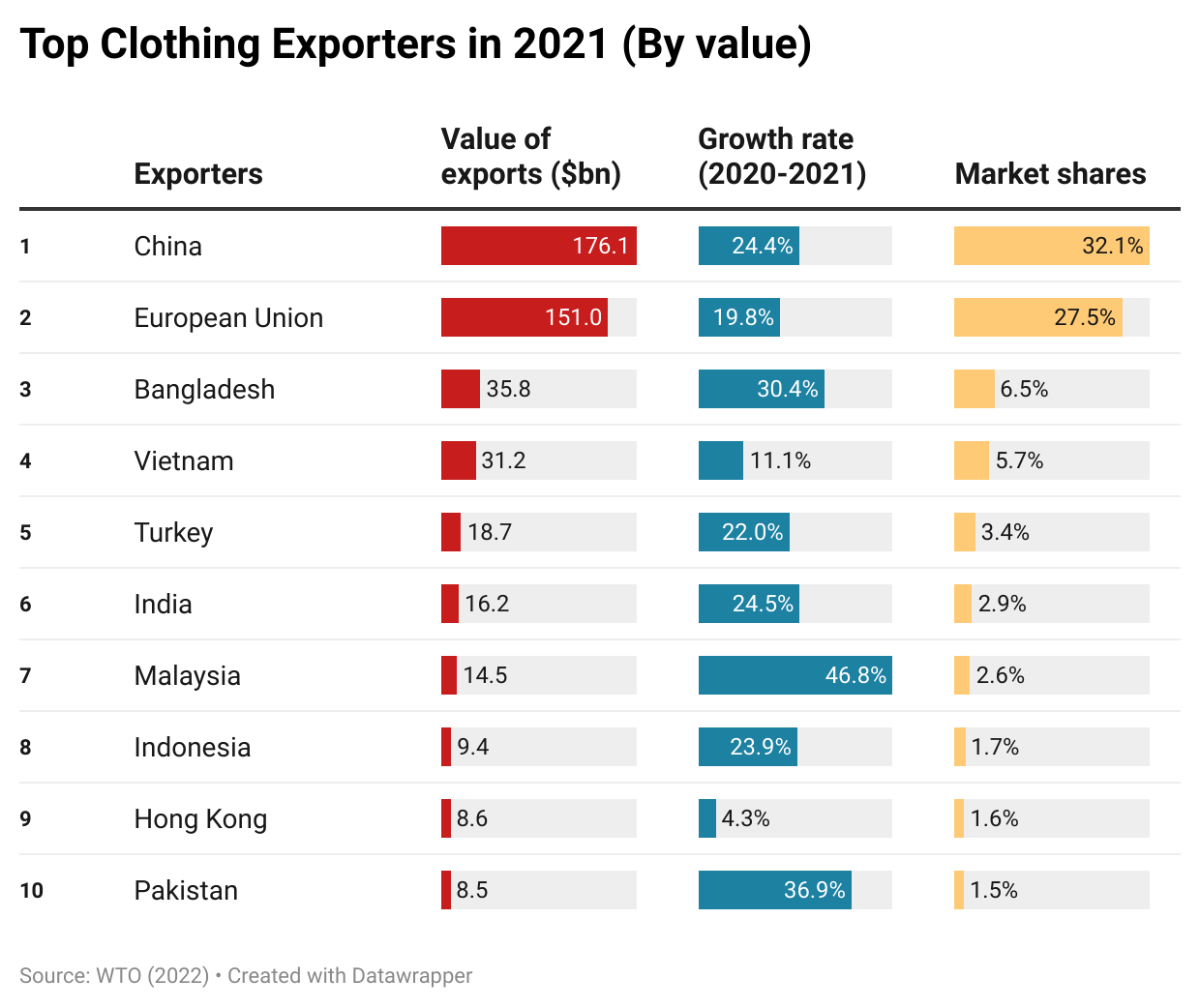
Specifically, China, the European Union (EU), and India remained the world’s three largest textile exporters in 2021, a pattern that has stayed stable for over a decade. Together, these top three accounted for 68% of the world’s textile exports in 2021, similar to 66.9% before the pandemic (2018-2019). Other textile exporters that made it to the top ten list in 2021 were also the same as a year ago and before the pandemic (2018-2019).
Meanwhile, the growth rate of the top ten textile exporters varied significantly in 2021, ranging from -5.5% (China) to 47.8% (India). The demand shift from PPE to apparel-related yarns and fabrics was a critical contributing factor behind the phenomenon. For example, China’s PPE-related textile exports decreased by more than $33bn (or down 43%) in 2021. In contrast, the world knit fabric exports (SITC code 655) surged by more than 30% in 2021, led by India (up 74%) and Pakistan (up 72%). Nevertheless, as consumers’ lifestyles almost reached a “new normal,” we could expect the textile export product structure to stabilize soon.
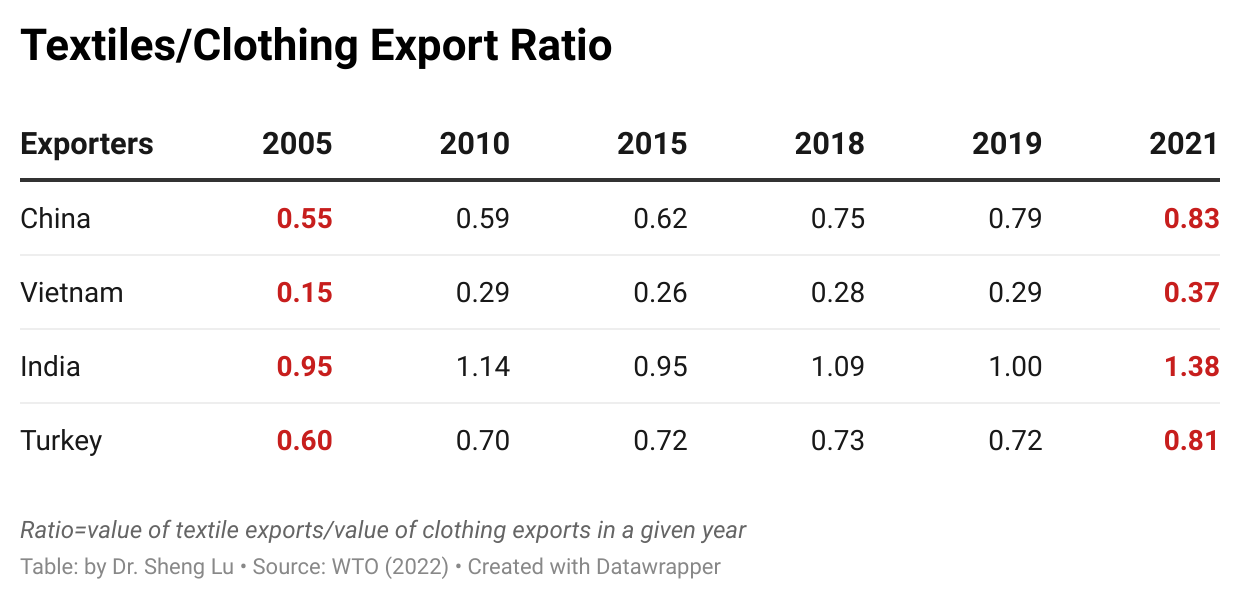
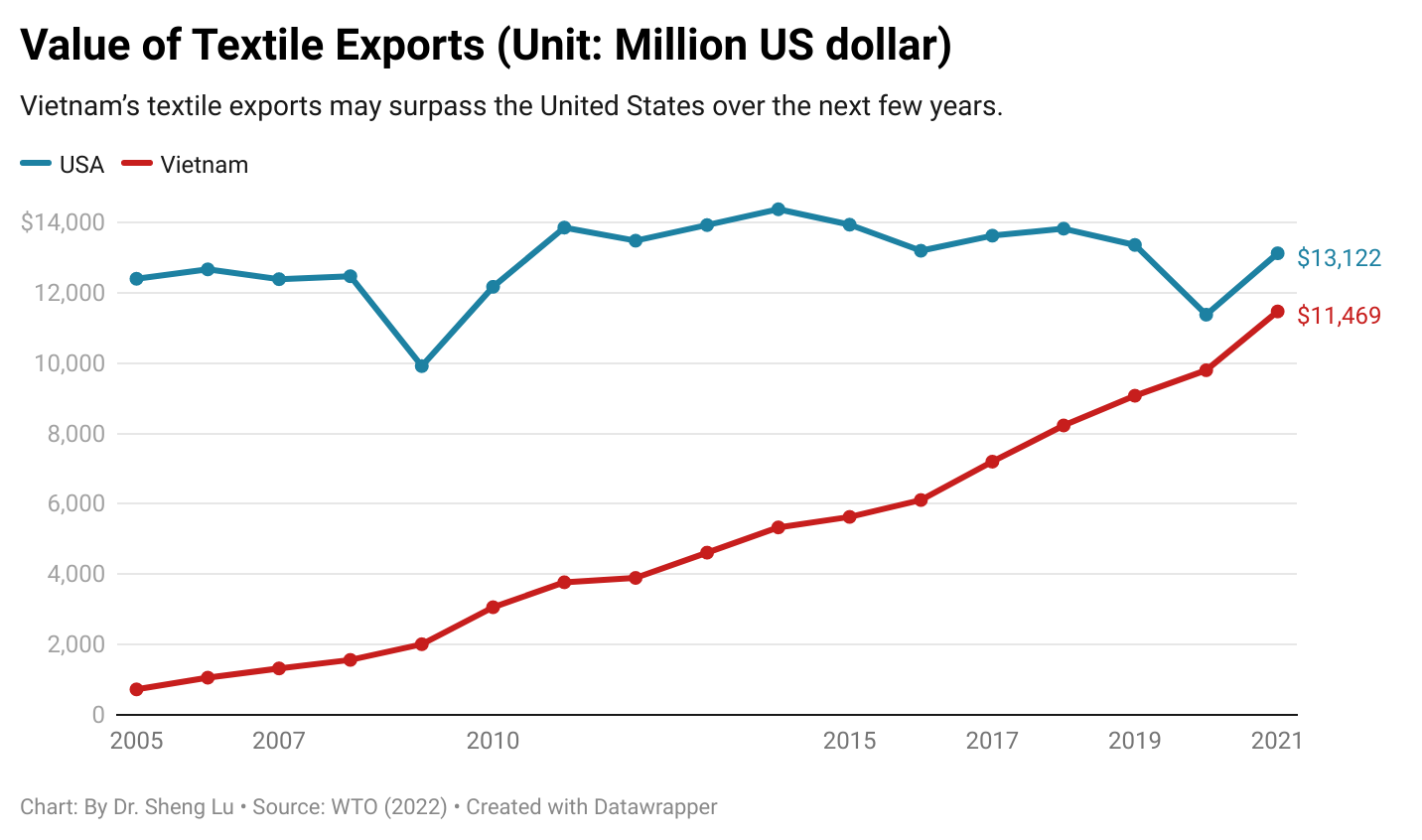
On the other hand, as a trend already emerged before the pandemic, middle-income developing countries continued to play a more significant role in textile exports, whereas developed countries lost market shares. For example, the United States, Germany, and Italy led the world’s textile exports in the 2000s, accounting for more than 20% of the market shares. However, these three countries’ shares fell to 12.8% in 2019 and hit a new low of 11.3% in 2021. In comparison, middle-income developing countries like China, Vietnam, Turkey, and India have entered the development stage of expanding textile manufacturing. As a result, their market share in the world’s textile exports rose steadily. These countries also achieved a more balanced textiles/clothing export ratio over the years, meaning more textile raw materials like yarns and fabrics can be locally produced instead of relying on imports. For example, Vietnam, known for its competitive clothing products, achieved a new high of $11.5bn in textile exports in 2021 and ranked sixth globally. Vietnam’s textiles/clothing ratio also doubled from 0.15 in 2005 to 0.37 in 2021. It is not unlikely that Vietnam’s textile exports may surpass the United States over the next few years.
Pattern #3: Countries with large-scale production capacity stood out in world clothing exports in 2021. Meanwhile, clothing exporters compete to become China’s alternatives, but there seems to be no clear winner yet.
Consumers’ surging demand and COVID-related supply chain disruptions significantly impacted the world’s clothing export patterns in 2021. As fashion brands and retailers were eager to find sourcing capacity, countries with large-scale production capacity and relatively stable supply enjoyed the fastest growth in clothing exports. For example, except for Vietnam, which suffered several months of COVID lockdowns, all other top five clothing exporters enjoyed a more than 20% growth of their exports in 2021, such as China (up 24%), Bangladesh (up 30%), Turkey (up 22%), and India (up 24%).
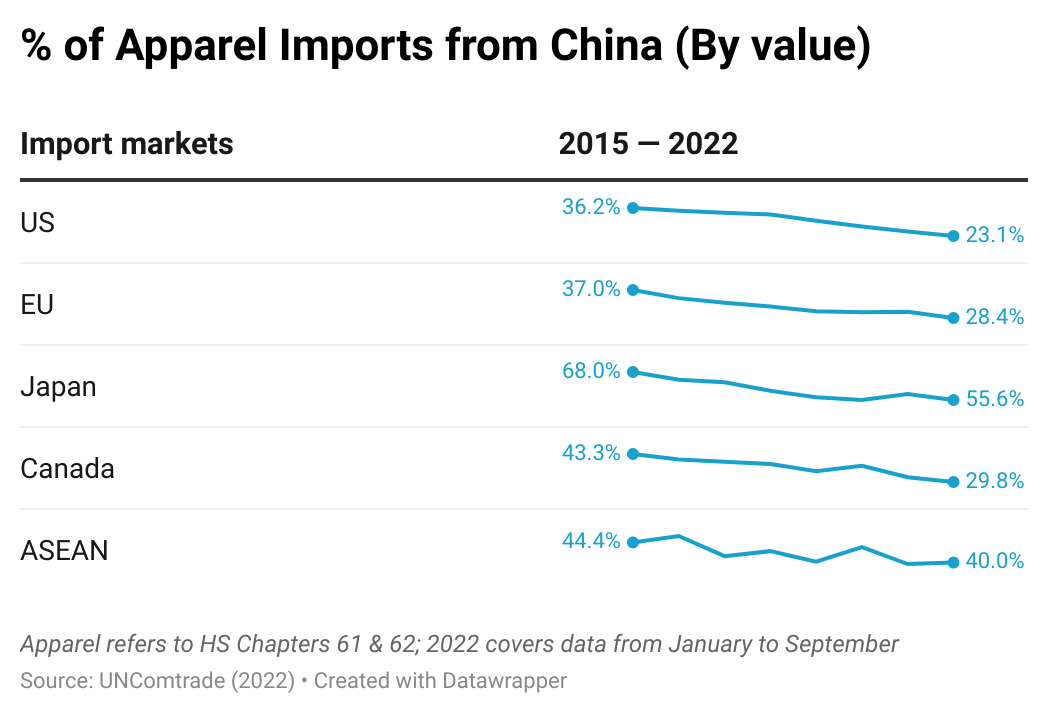
As another critical trend, many international fashion brands and retailers have been trying to reduce their apparel sourcing from China, driven by various economic and non-economic factors, from cost considerations and trade tensions to geopolitics. Notably, despite its strong performance in 2021, China accounted for only 23.1% of US apparel imports in 2022 (January to September), much lower than 36.2% in 2015. Likewise, China’s market shares in the EU, Japanese, and Canadian clothing import markets also fell over the same period, suggesting this was a worldwide phenomenon.
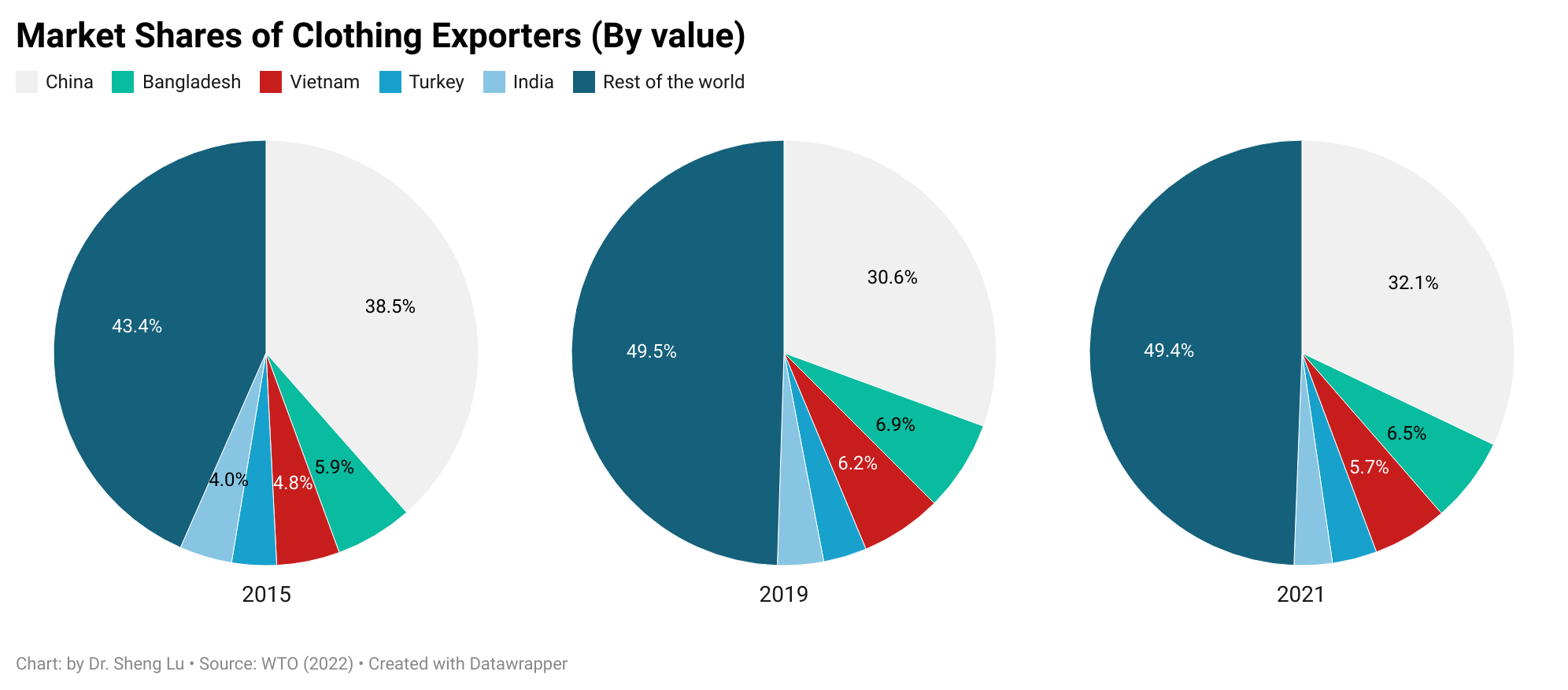
With reduced apparel sourcing from China, fashion companies have actively sought alternative sourcing destinations, but the latest trade data suggests no clear winner yet. For example, Vietnam and Bangladesh, the two most popular candidates for “Next China,” accounted for 6.5% and 5.7% shares in the world’s clothing export in 2021, still far behind China (32.1%). Interestingly, from 2015 to 2021, the world’s top four largest clothing exporters next to China (i.e., Bangladesh, Vietnam, Turkey, and India) did not substantially gain new market shares. Instead, China’s lost market was filled by “the rest of the world.”
Additionally, recent studies show that many fashion companies have switched back to the sourcing diversification strategy in 2022 as managing risks and improving sourcing flexibility become more urgent priorities. In other words, the world’s clothing export market could turn more “crowded” and competitive in the coming years.
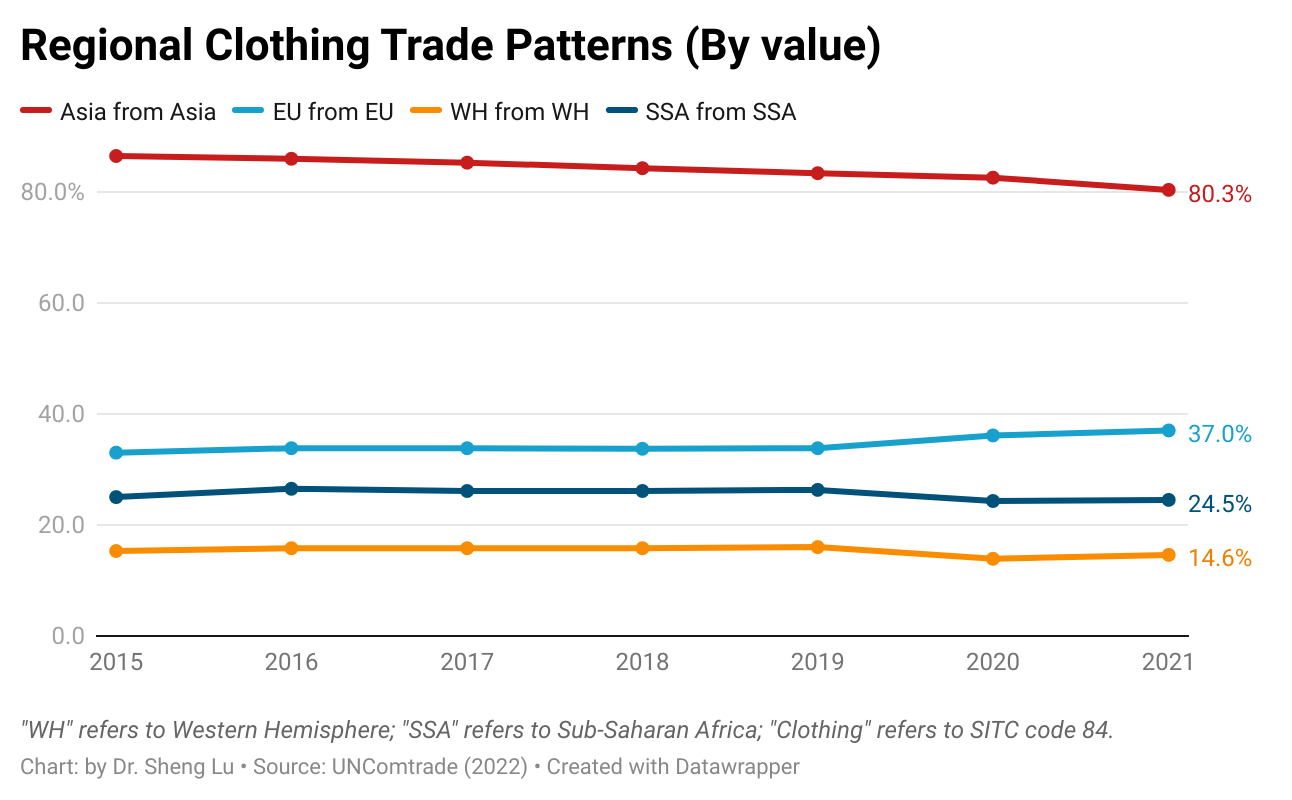
Pattern #4: Regional supply chains remain critical features of the world textiles and clothing trade. Several factors support and shape the regional textiles and clothing trade patterns. First, as clothing production often needs to be close to where textile materials are available, many developing clothing-producing countries rely heavily on imported textile materials, primarily from more advanced economies in the same region. Second, through lowered trade barriers, regional free trade agreements also financially encouraged garment producers, particularly in Asia, the EU, and Western Hemisphere (WH), to use locally or regionally made textile materials. Further, fashion companies’ interest in “near-shoring” supported the regional supply chain, and related textiles and clothing trade flows between neighboring countries.
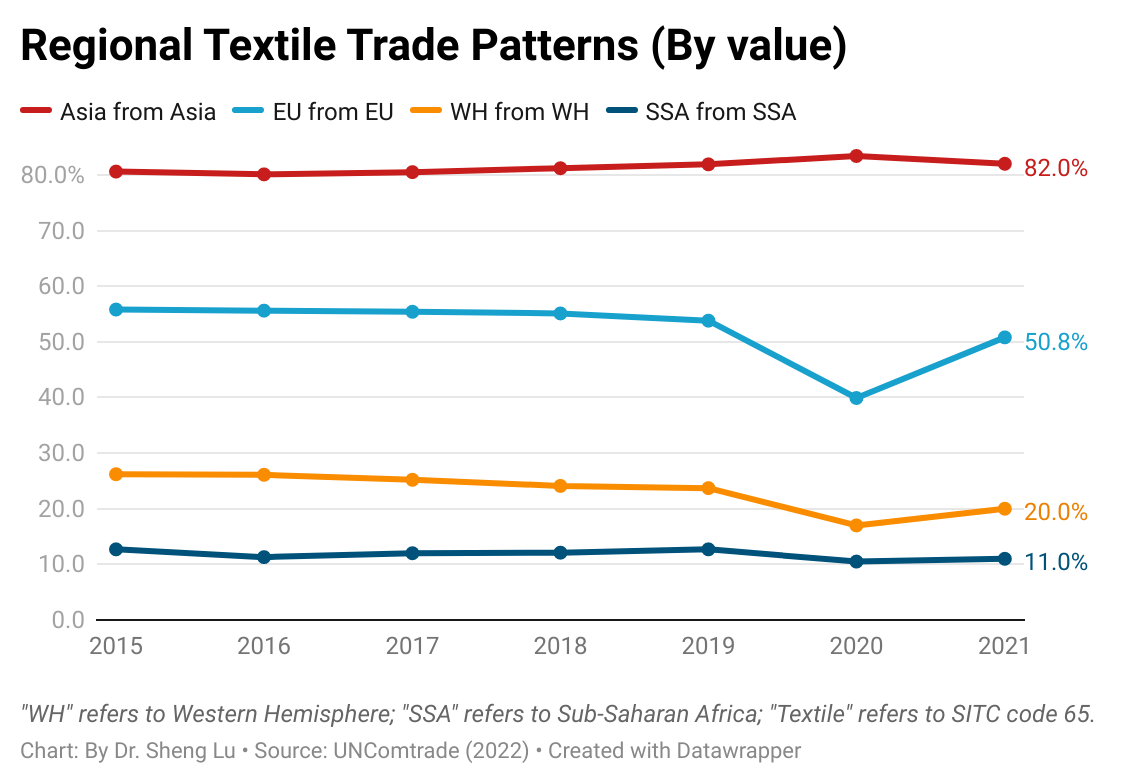
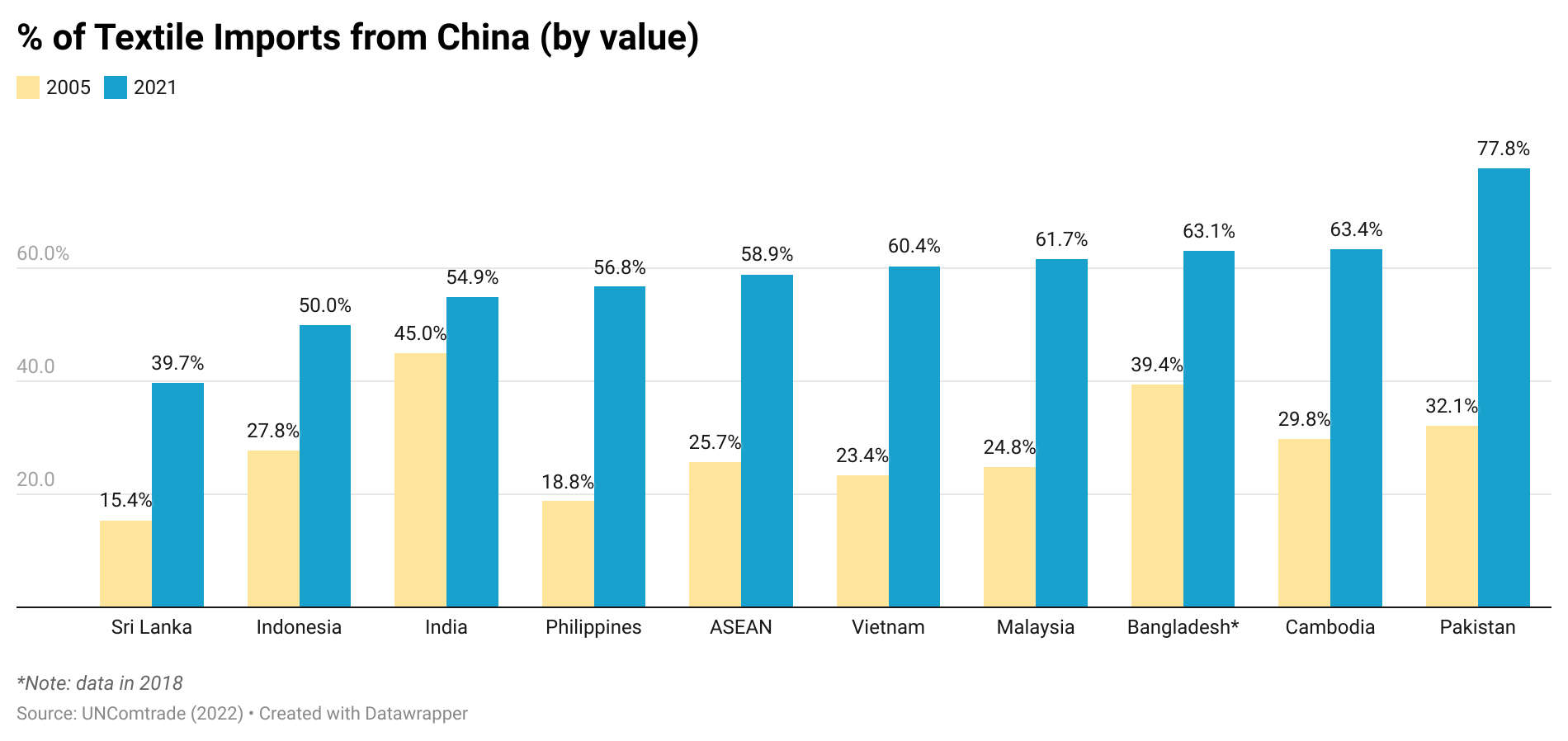
The latest trade data indicated that Asia’s regional textiles and clothing trade patterns strengthened further despite supply chain chaos during the pandemic. Specifically, in 2021, as many as 82% of Asian countries’ textile imports came from within Asia, up from 80% in 2015. China, in particular, has played a more prominent role as a leading textile supplier for other Asian clothing-exporting countries. For example, more than 60% of Vietnam’s textile imports came from China in 2021, a substantial increase from 23% in 2005. The same pattern applied to Pakistan, Cambodia, Bangladesh, and the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) members.
In January 2022, the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP), a mega free trade agreement involving all major economies in Asia, entered into force. The tariff cut and very liberal rules of origin of the agreement will hopefully drive Asia’s booming regional textiles and clothing trade and further deepen its regional economic integration.
Besides Asia, the regional textiles and clothing trade pattern in the EU (or the so-called Intra-EU trade) was also in good shape. In 2021, 50.8% of EU countries’ textile imports and 37% of clothing imports came from other EU members. This pattern has changed little over the past decade, thanks to many EU countries’ commitment to maintaining local textiles and clothing production rather than outsourcing.
In comparison, the Western Hemisphere (WH) textile and apparel supply chain (e.g., clothing made in Mexico or Central America using US or regionally made textiles) seemed to struggle in recent years. As of 2021, only 20% of WH countries’ textile imports came from within WH, down from 26% in 2015. Likewise, WH countries (mainly the US and Canada) just imported 14.6% of clothing from WH in 2021, down from 15.3% in 2015 and much lower than their EU counterparts (37% in 2021). It will be interesting to see whether US and Canadian fashion companies’ expressed interest in expanding near-shoring may reverse the course.
Furthermore, the regional textiles and clothing trade patterns in Sub-Saharan Africa (SSA) are also worth watching. Compared with Asia and the EU, SSA clothing producers used much fewer locally-made textiles (i.e., stagnant at around 11% only from 2011 to 2021), reflecting the region’s lack of textile manufacturing capability. Most trade programs with SSA countries, such as the US-led African Growth and Opportunity Act (AGOA) and EU’s Everything But Arms (EBA) program, adopt liberal rules of origin for clothing products, allowing third-party textile input to be used. It can be studied whether such liberal rules of origin somehow disincentivize building SSA’s own textile manufacturing sector or are still essential given the reality of SSA’s limited textile production capacity.
By Sheng Lu
Suggested citation: Lu, Sheng (2022). World Textiles and Clothing Trade in 2021: A Statistical Review. Just-Style. Retrieved from https://www.just-style.com/analysis/world-textiles-and-clothing-trade-in-2021-a-statistical-review/