Updated study available: Updated Impact of Increasing Tariffs on U.S. Fashion Companies’ Sourcing and Businesses (October 2025)
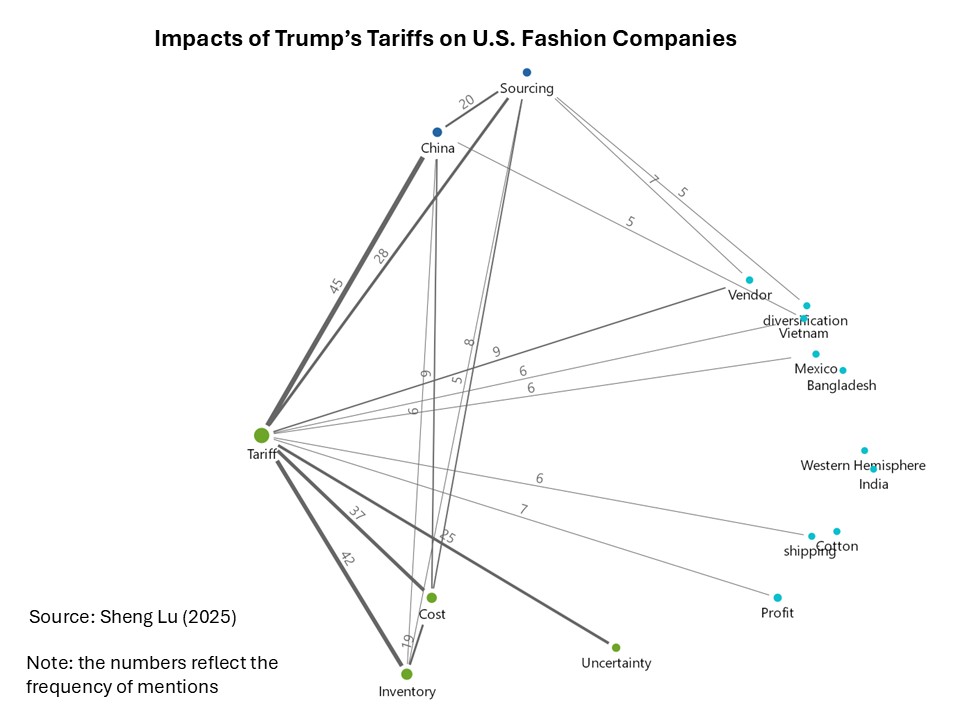
(Note: The figure above shows how frequently the term “tariff” was mentioned alongside other key issues in the earnings calls. A higher frequency indicates a more significant impact and a closer connection between tariffs and a specific theme.)
This study aims to examine the impacts of the Trump administration’s escalating tariffs on U.S. fashion companies’ apparel sourcing practices. Based on data availability, transcripts of the latest earnings calls from approximately 25 leading publicly traded U.S. fashion companies were collected. These earnings calls, held between mid-May and June 2025, covered company performance in the first quarter of 2025. A thematic analysis of the transcripts was conducted using MAXQDA.
Overall, the results indicate that the Trump administration’s escalating tariffs and policy uncertainties have financially hurt U.S. fashion companies and disrupted their apparel sourcing practices. To mitigate these impacts, most companies plan to further reduce their “China exposure,” maintain a geographically diversified sourcing base, and prioritize flexibility in sourcing and shipping. However, there is no clear evidence that the current policy environment has successfully incentivized U.S. companies to expand apparel sourcing from the Western Hemisphere, let alone commit to new long-term investments. Meanwhile, U.S. fashion companies have adopted a strategic pricing approach by not passing the entire cost increase to consumers through widespread retail price hikes.
A few key findings:
First, far from surprising, many leading U.S. fashion companies expressed concerns that the Trump administration’s escalating tariffs have resulted in higher sourcing costs and cut companies’ profit margins. For example:
- Company G (specialty store): if current tariffs of 30% on most imports from China and 10% on most imports from other countries remain for the balance of the year, we estimate a gross incremental cost of approximately $250 million to $300 million.
- Company O (a parent company of several leading apparel brands): We expect that gross margin will contract approximately 200 basis points for the year. This contraction includes $40 million in additional tariff costs.
- Company V1 (underwear brand): gross tariff impact of approximately $120 million, which assumes 30% China tariffs and 10% non-China, with tariff mitigation of approximately $70 million for a net impact to fiscal year 2025 of approximately $50 million.
Second, with the hiking tariff rate on U.S. apparel imports from China and increasing strategic competition between the two countries, many leading U.S. fashion companies plan to reduce their apparel sourcing from China to a single-digit, if not move out of the country entirely. For example:
- Company A1 (apparel brand): We’re on track to reduce our sourcing exposure to China to under 10% this year with fall and holiday season down to low single digits.
- Company A2 (specialty store): For China specifically, we have worked for some time now to relocate the supply resources, and this year’s sourcing volume from China will be in the low single digits.
- Company L (apparel brand): Less than 8% of our purchase order dollars last fiscal year were utilized on buys of China.
- Company O (a parent company of several leading apparel brands): By the second half of 2026, we currently plan to be substantially out of China.
- Company V2 (a parent company of several leading apparel brands): over the past several years we’ve strategically diversified our supply chain and proactively reduced our US finished goods sourced from China to less than 2%.
- Company K2 (a parent company of several leading apparel brands): China for us is de minimis.
Third, maintaining a geographically diverse sourcing base remains a popular strategy for U.S. fashion companies to mitigate the impacts of increasing tariffs and ongoing policy uncertainties. Companies particularly intend to avoid “putting too many eggs in one basket” and limiting the reliance on any single supplying country. For example:
- Company K1 (retailer): our talented and experienced global sourcing team has done an incredible job diversifying our countries of production to ensure that we are not overly reliant on any one country. Although tariffs remain a fluid and uncertain situation, the teams continue to work to reduce our exposure to high tariff countries by leveraging our diverse factory network to move production, adjusting orders based on pricing elasticity analysis.
- Company G (specialty store): Most other countries represent less than 10%, Vietnam and Indonesia represented 27%, and 19% of our sourcing last year, respectively, and our goal is for no country to account for more than 25% by the end of 2026.
- Company R (apparel brand): While tariffs will primarily impact our gross margins… we have a proven toolkit to manage cost inflation headwinds. This includes first, significant supply chain diversification…No single country accounts for more than 20% of our production volumes, with most countries representing a single-digit percentage.
- Company U (retailer): The remaining third is strategically diversified across a number of other countries, each representing a low to mid-single-digit percentage. This deliberate diversification creates a well-balanced portfolio, reducing reliance on any single market and enhancing our ability to navigate geopolitical, costs and supply chain complexities from a position of strength.
Notably, while a limited few companies specifically mentioned the possibility of expanding sourcing from the Western Hemisphere amid the current business environment, most did not. For example:
- Company L (apparel brand): We intentionally drove significant change in our supply chain as we accelerated production in the Western Hemisphere, giving us both speed and additional avenues to mitigate tariffs and provide resiliency.
- Company G (specialty store): Diversification also means near-shoring as well as domestic investment.
Fourth, U.S. fashion companies have leveraged shipping timing, piled up inventory, and delayed or cancelled existing orders to mitigate the tariff impacts as much as possible. For example:
- Company C (sportswear): For products that are impacted by the reciprocal tariffs, we are accelerating shipments to the extent possible in order to receive products during the 90-day tariff.
- Company K1 (retailer): Inventory was up 1.7% compared to last year, driven by inventory strategies implemented to navigate the tariff pressure, including the pull forward of receipts and pack in holding seasonal inventory to be sold in the back half of the year.
- Company B (off-price retailer): Our reserve inventory was 48% of our total inventory versus 40% of our inventory last year. In dollar terms, our reserve inventory was up 31% compared to last year, reflecting the great deals we were able to make to get ahead of tariffs.
- Company M (retailer): With the recent announcement of these tariffs, we’ve renegotiated orders with suppliers, and we’ve canceled or delayed orders where the value proposition is just not where it needs to be.
It should be noted, however, that adjusting shipping and inventory could incur additional costs. For example:
- Company V1 (underwear brand): More than half of the gross margin rate pressure in the quarter was due to a combination of elevated and expected airfreight rates, some tariff-related order adjustments…
Fifth, despite higher sourcing costs and increasing financial pressures, many U.S. fashion companies have avoided widespread price hikes but have implemented selective increases in less price-sensitive apparel categories. For example:
- Company V1 (underwear brand): [price increase driven by higher tariffs] And so we are going to sort of play in the middle where we see value. So and it won’t be across all categories. As we think about our business, it’s really that strategic case by case, category by category look that we’re taking.
- Company U (retailer): gently and sparingly raising some prices. Please note that any price increases will be very strategic, protecting opening price points and only targeting areas where we believe we could raise prices without affecting the overall customer experience.
- Company A2 (specialty store): we are not planning broad-based ticket increases. As we’ve done season after season, our goal is to deliver high-quality product and align inventory and promotions with our customers’ value perception.
- Company P (a parent company of several leading apparel brands): We will evaluate strategic discounts to mitigate the potential tariff impact. While we are focused on delivering price value for the consumer, we are also ready to take calibrated targeted pricing actions where we have pricing power.
by Sheng Lu
Additional reading: Tariffs Upend Fashion Sourcing and Disrupt Cash Flow Amid Widening Trade Gap (Sourcing Journal, June 27, 2025)