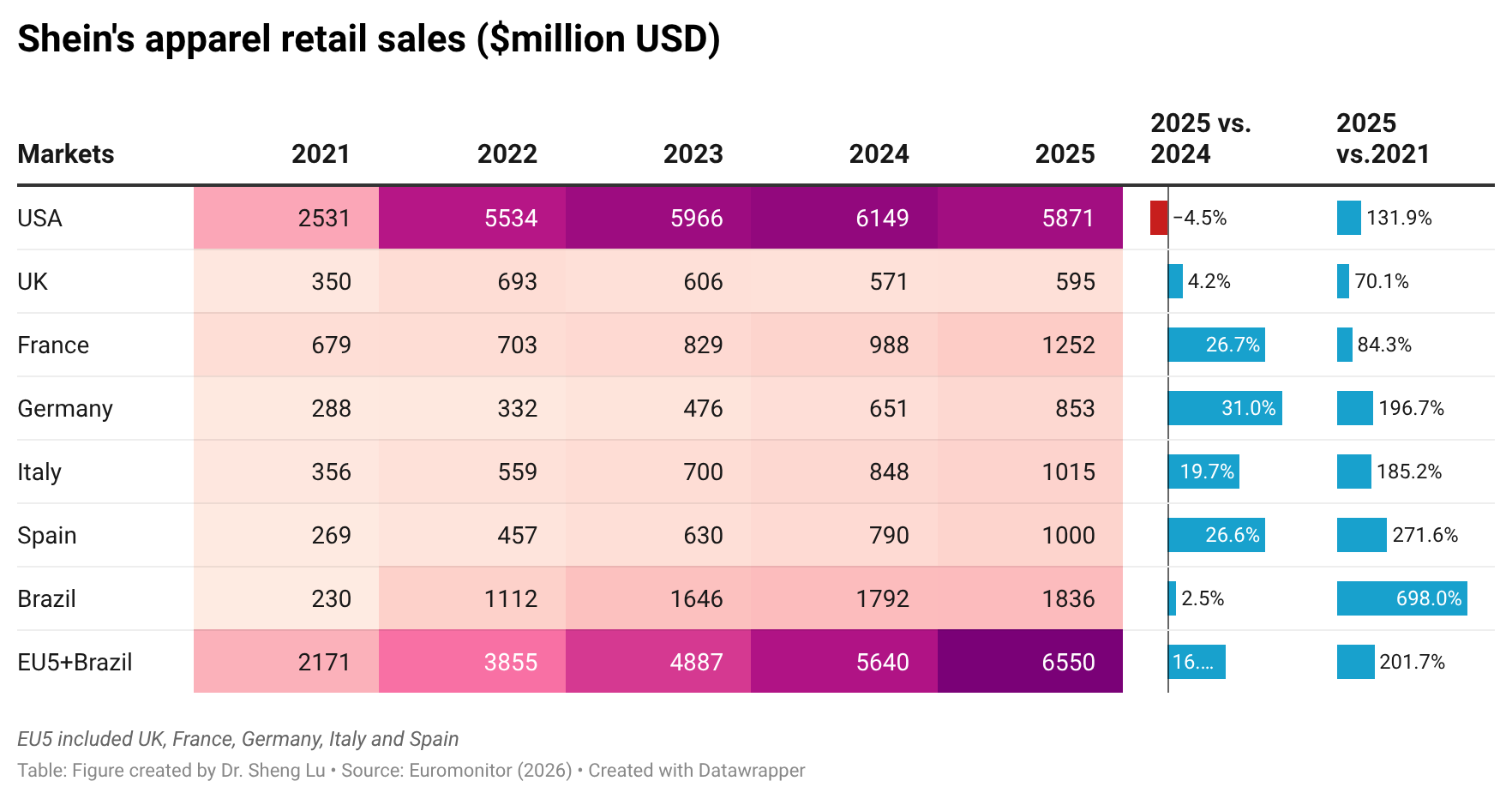
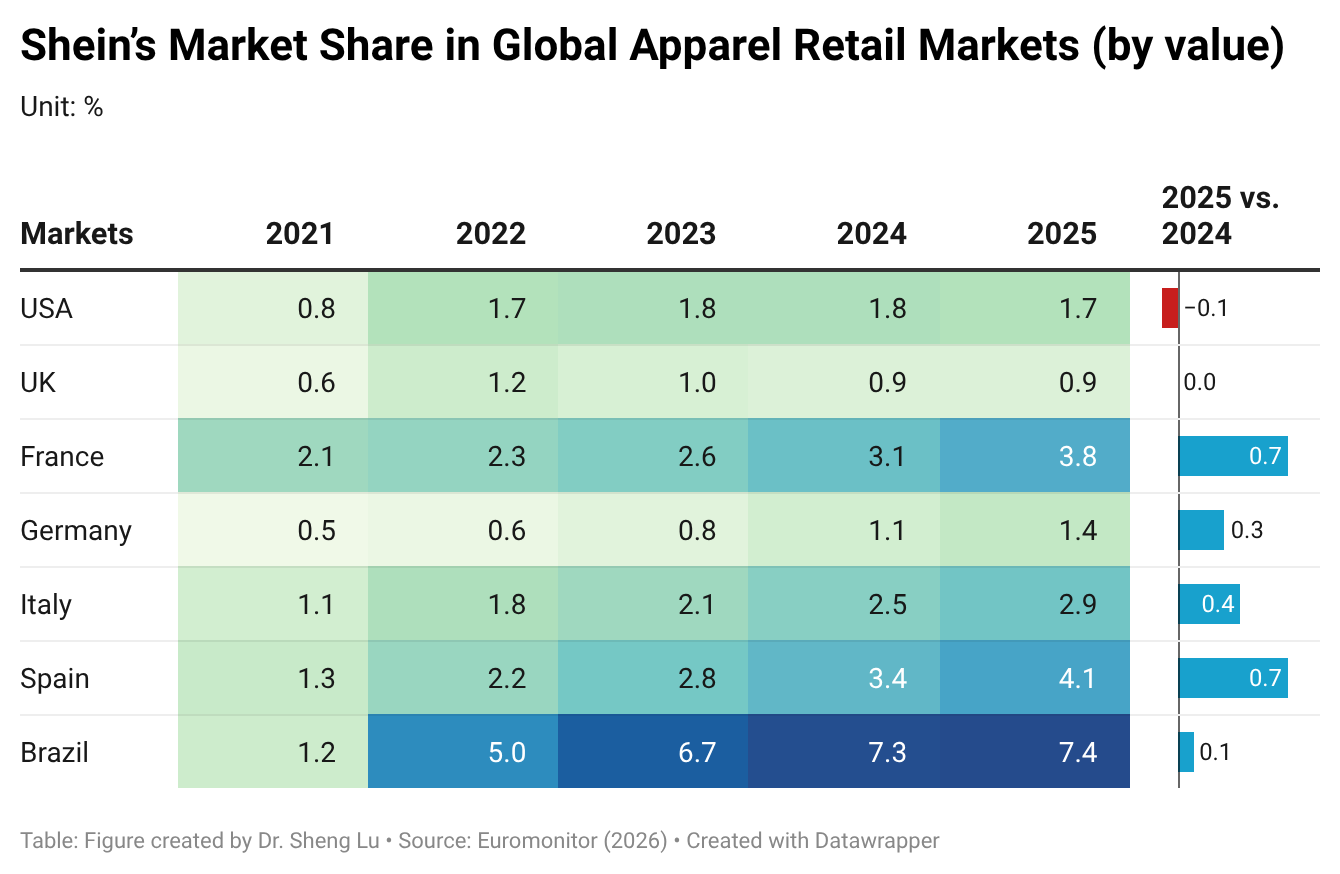
Latest Data from Euromonitor shows that while the United States remained Shein’s largest apparel sales market in 2025, the value of sales declined by 4.5%, affected by factors such as higher tariffs on Chinese products, the elimination of the “de minimis” rules, and young U.S. consumers’ growing concern about sustainability. Based on the value of sales, Shein’s market share in the U.S. also dropped from 1.8% in 2024 to 1.7% in 2025, the first time since 2021.
Shein’s business outlook in the U.S. is expected to remain challenging in 2026 due to ongoing high tariffs affecting imports from China, tighter regulations and enforcement on cross-border e-commerce shipping, and consumers’ increasing demand for sustainable apparel products and supply chain transparency.
Amid headwinds in the US, Shein is diversifying its sales markets in the rest of the world. For example, Shein achieved more apparel retail sales in key EU markets in 2025, including the UK (up 4.2%), France (up 26.7%), Germany (up 31%), Italy (up 19.7%), and Spain (up 26.6%). Likewise, Shein’s sales in Brazil increased by over 698% between 2021 and 2025, much higher than 131% in the US.
As of 2025, Shein’s total apparel sales in the UK, France, Germany, Italy, Spain, and Brazil (around 6.5 billion USD) already surpass the sales in the US (around 5.9 billion). It is likely that emerging markets like Brazil will become increasingly important to Shein’s future global expansion due to the price competitiveness of Shein’s products in local markets, the relatively relaxed regulatory environment, and the attractiveness of Shein’s commitment to investing in production there.
Additional reading: Inside the Chinese factories of fast-fashion giant Shein (by FRANCE 24 English | February 2026)
