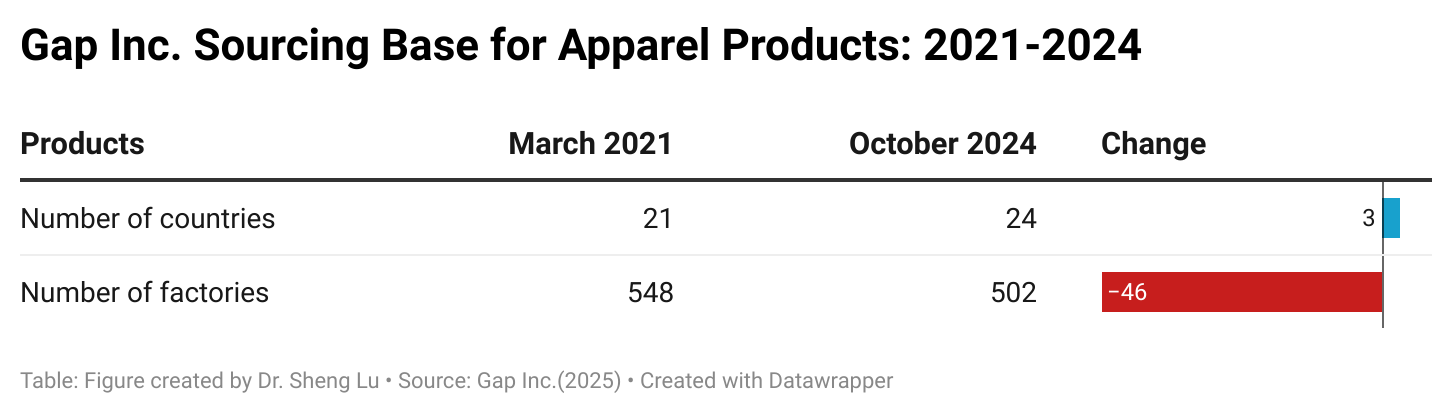
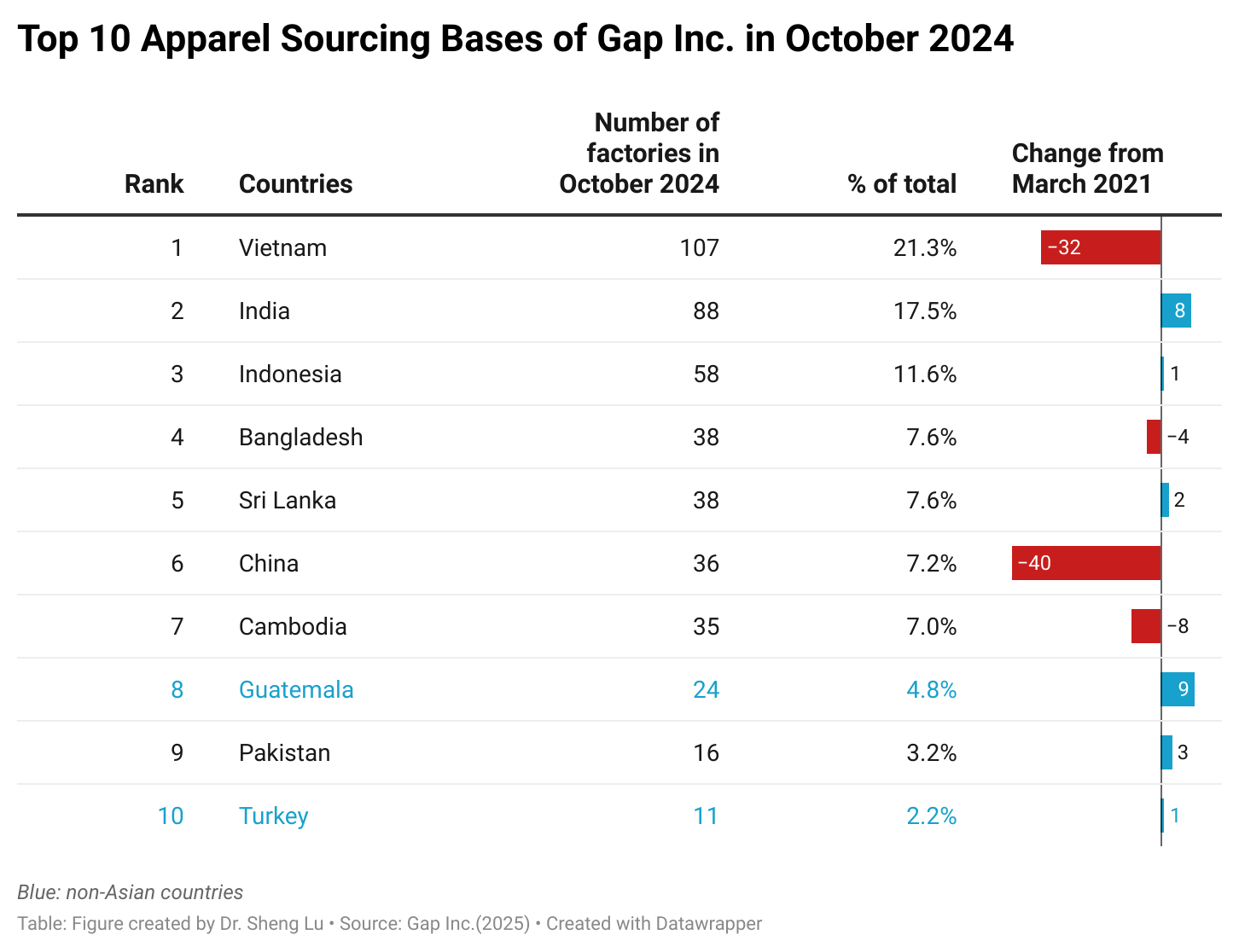
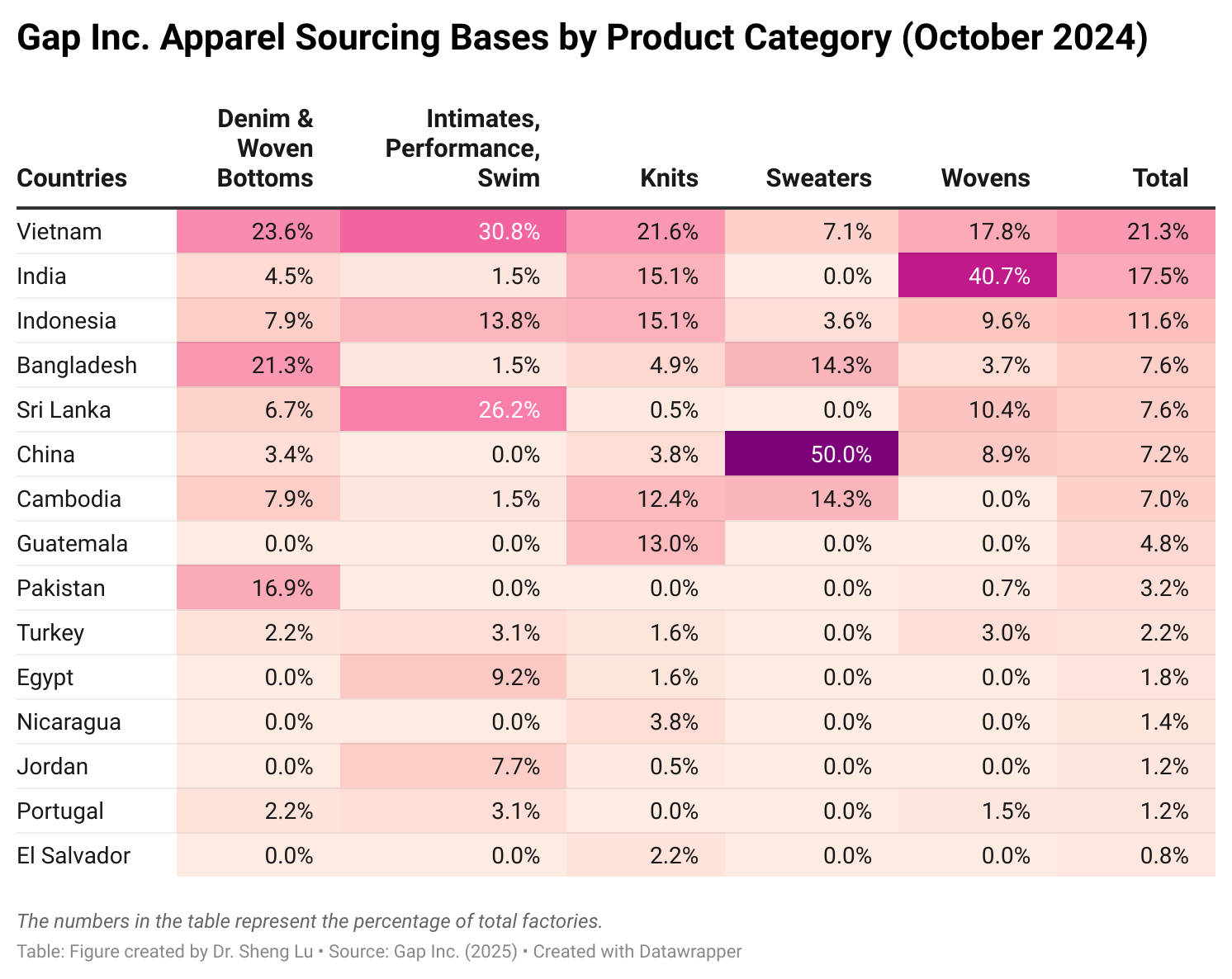
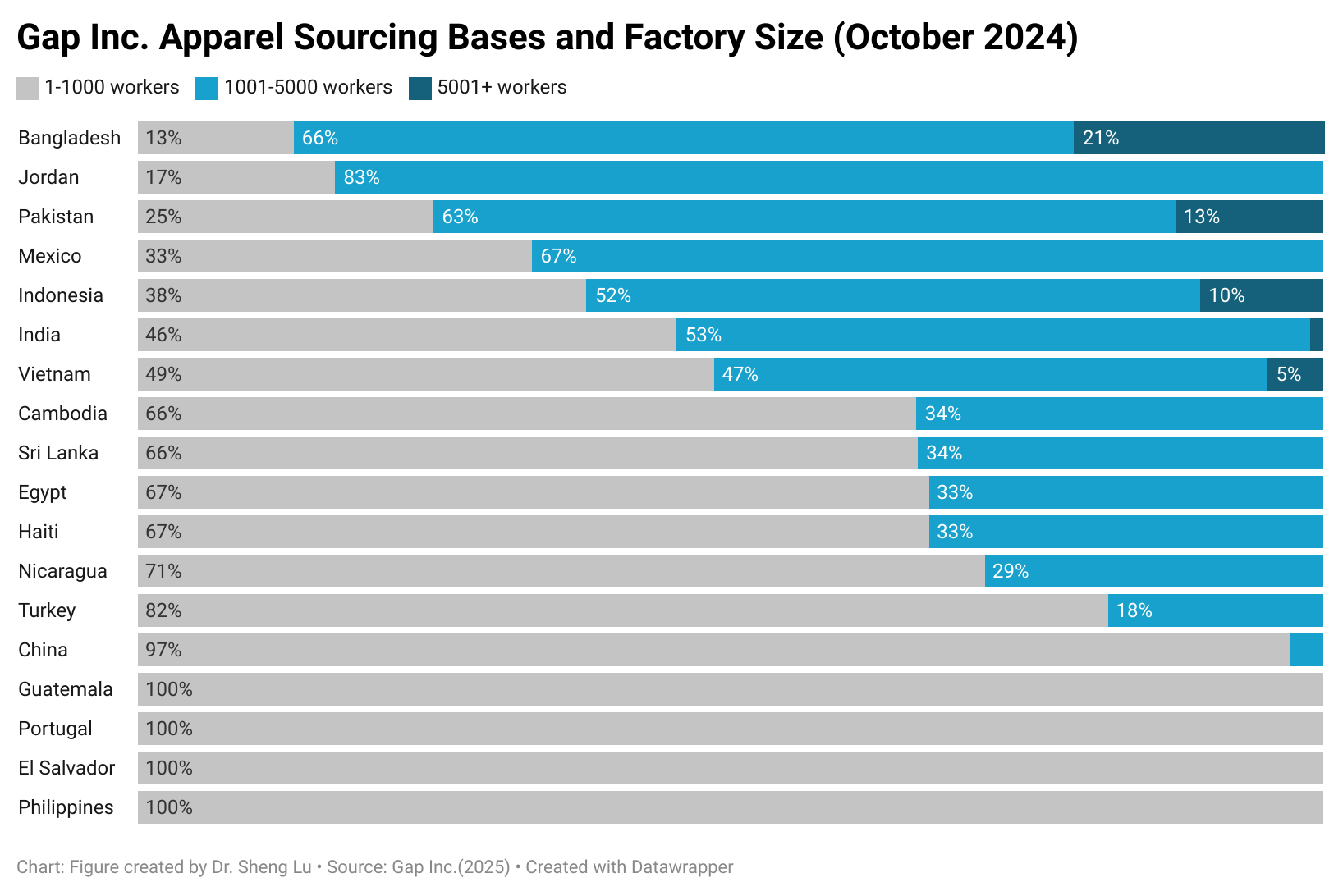
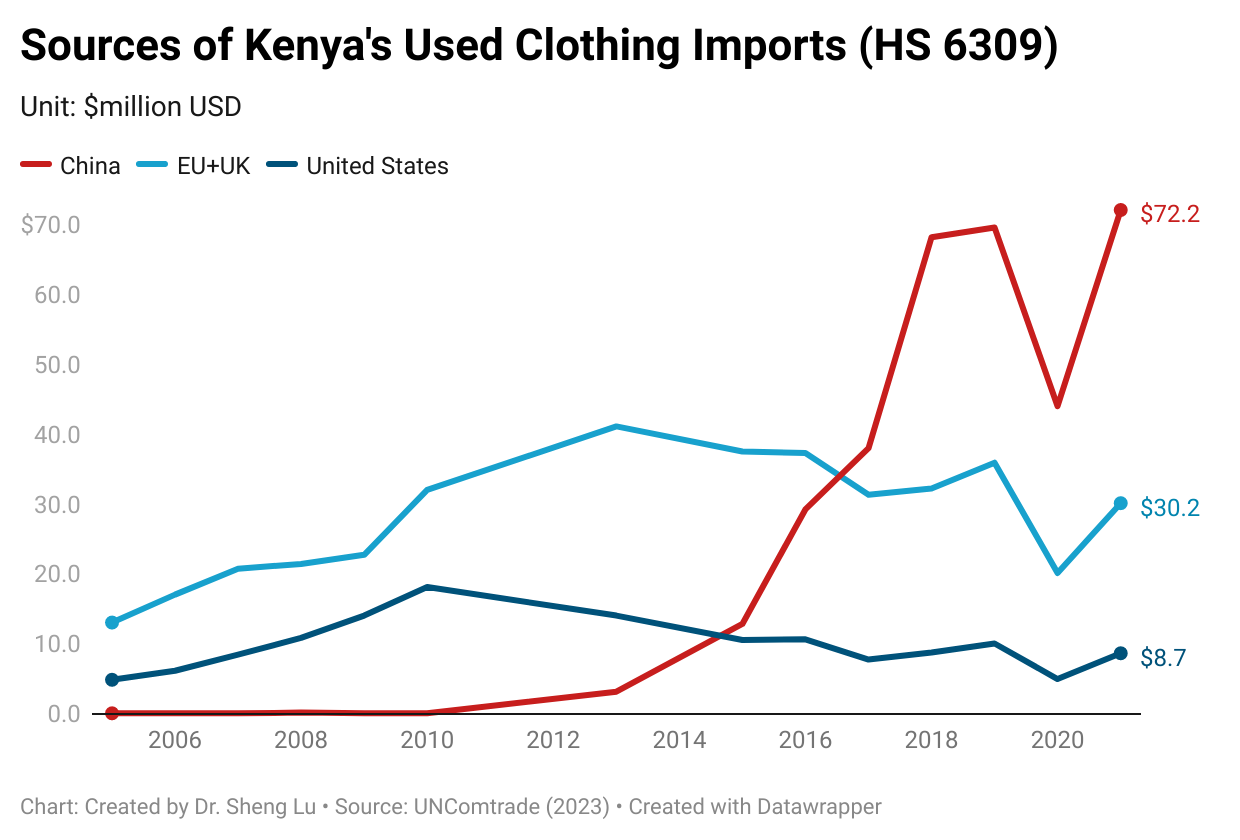
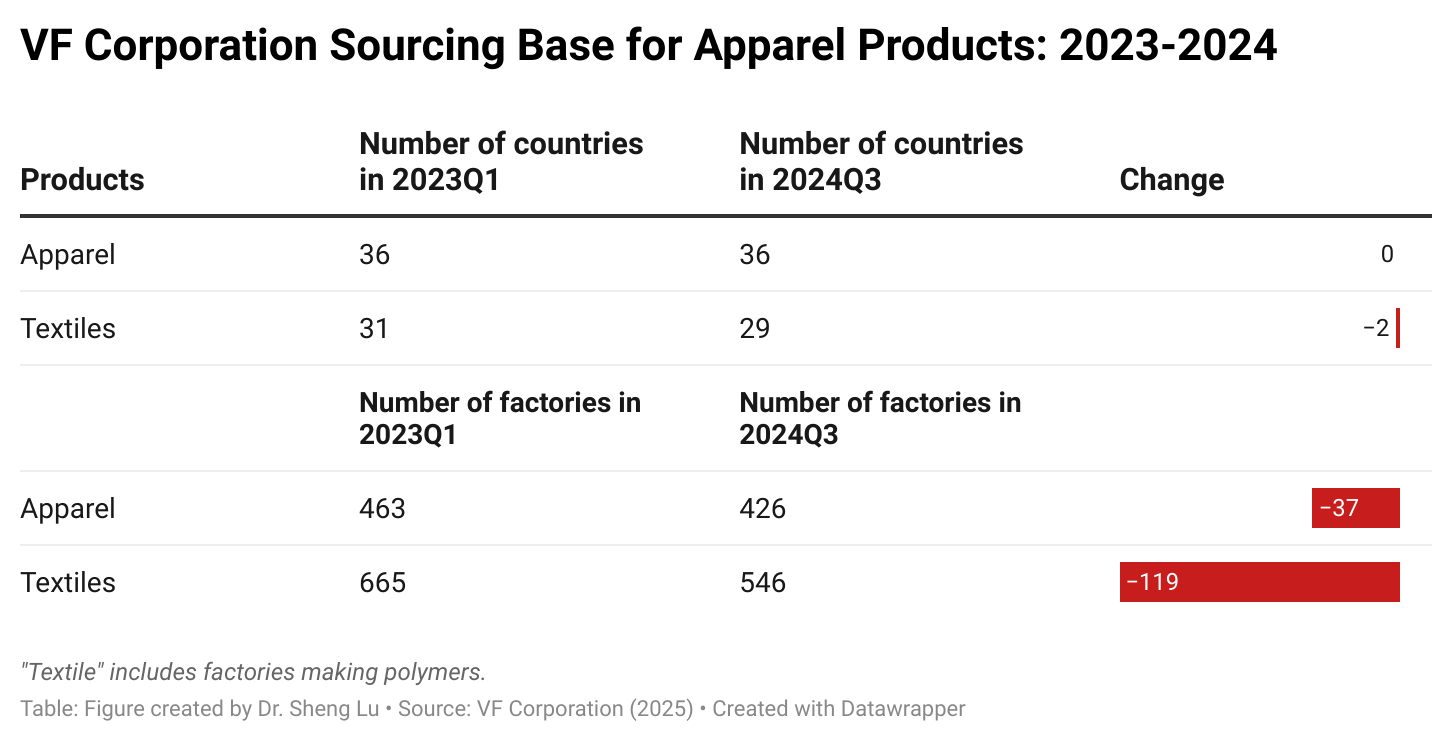
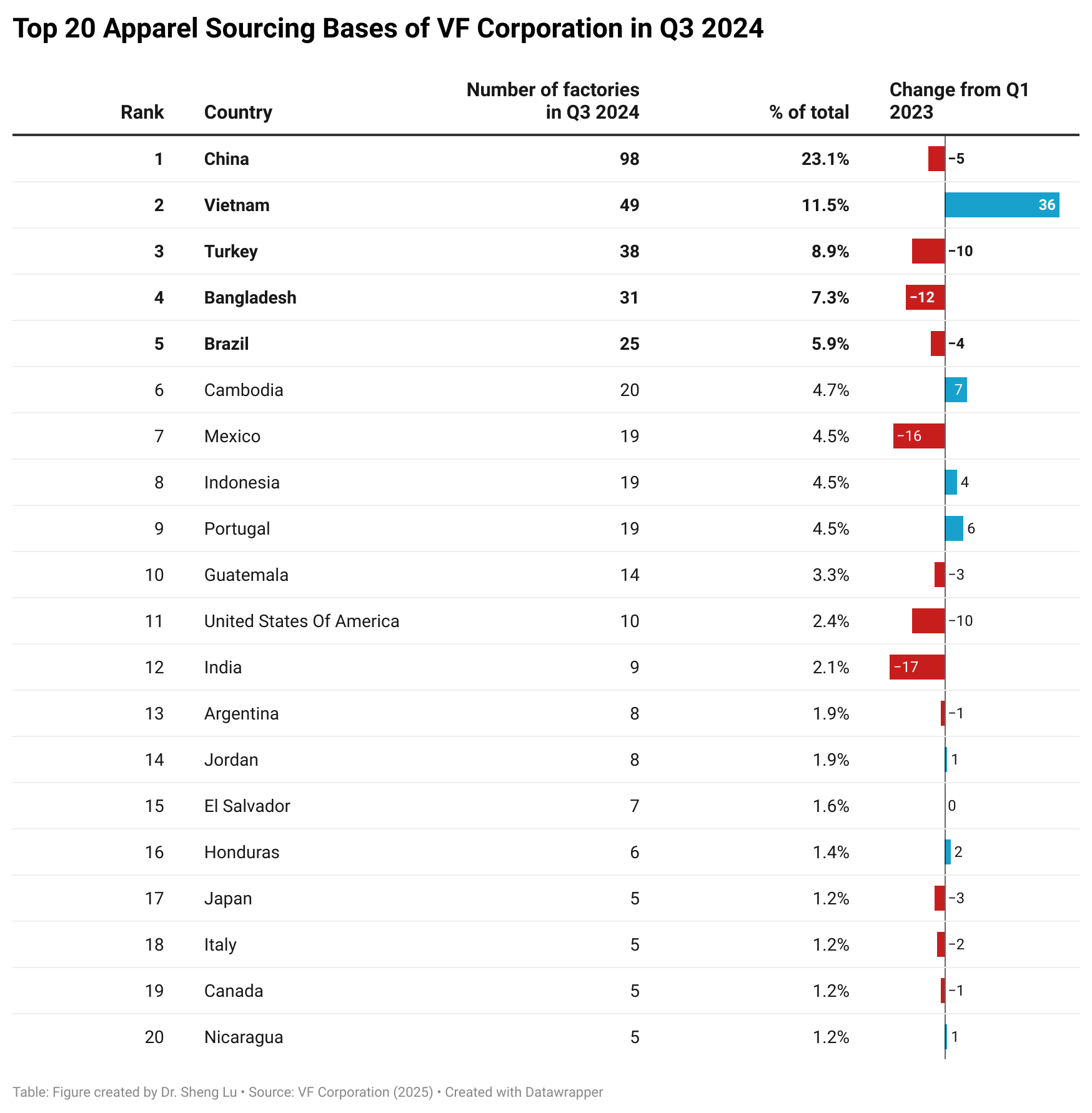
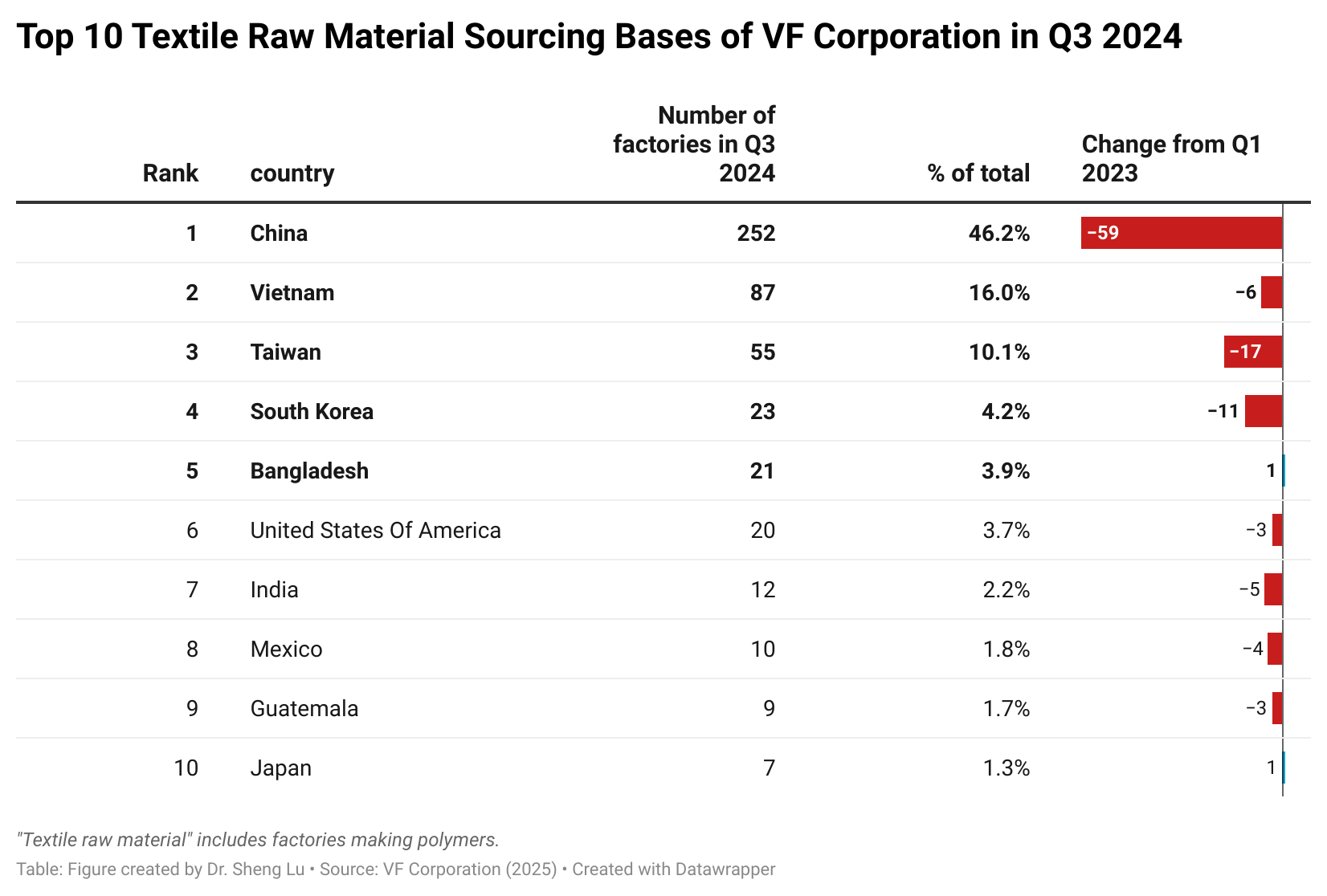
Background: Pursuant to the America First Trade Policy Presidential Memorandum and the Presidential Memorandum on Reciprocal Trade and Tariffs, the Office of the U.S. Trade Representative (USTR) solicited public comments on the proposed “Reciprocal Tariffs” from February to March 2025. Below is a summary of comments submitted by stakeholders in the textile and apparel industry.
The United States Fashion Industry Association (USFIA), whose members include many leading U.S. fashion brands and retailers, opposes raising tariffs and argues for lowering tariffs on textile and apparel products where the U.S. imposes a higher tariff rate than its trading partners. According to USFIA, higher tariffs on apparel and textiles would disproportionately impact lower-income U.S. consumers:
- “A true ‘reciprocal’ trade policy would lower tariffs on the products of trading partners that maintain lower tariffs than the United States.”
- “We recommend that the most successful policy to achieve trade reciprocity would be for the United States to lower the tariff rates of products for which our trading partners apply lower tariff rates. For consumer products such as textiles and apparel, this would help combat inflation and assist consumers who struggle to afford basic necessities.”
The American Apparel and Footwear Association (AAFA), representing U.S.-based “apparel, footwear and other sewn products companies”, opposes broad tariffs on apparel, footwear, and textiles. It is of concern to AAFA that the apparel and footwear sector already faces some of the highest tariffs in the U.S., and tariffs are a “hidden, regressive tax that falls harder on lower-income Americans.” Even worse, AAFA worries that higher tariffs would benefit “Illicit traders” and tariff threats would undermine the regional textile and apparel supply chain in the Western Hemisphere:
- “Illicit traders are better positioned to escape paying proper duties or any duties at all. Higher tariffs end up maximizing the profit and market access they can gain at the expense of legitimate shippers.”
- “Recent tariff threats particularly on our neighbors, Canada and Mexico, are especially concerning as the U.S.-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA) review is about to begin. Canada is a key export market for U.S. made apparel and footwear while Mexico is a major source of a wide variety of apparel, including denim imports. Not only does the threat of tariffs cast uncertainty but it also undermines future investment and nearshoring opportunities.”
National Council of Textile Organizations (NCTO), representing U.S. textile mills, supports targeted tariffs against “unfair trade” but opposes penalties on Western Hemisphere trading partners:
- “We strongly recommend that the Trump administration take a targeted approach to raise tariffs on specific countries that disrupt markets through the use of blatantly unfair and often illegal trade practices, while simultaneously operating in home markets that remain mostly closed to our products.”
- “We must preserve and strengthen existing trade relationships with U.S. free trade agreement (FTA) countries in the Western Hemisphere that offer valuable markets for U.S.-made textiles.”
- “We strongly believe that reciprocity should not mean a race to the bottom with lower tariffs on imports from other countries into our market. Rather, reciprocity should hold bad actors accountable for systemic unfair trade practices that have hurt domestic manufacturers.”
- “We urge the Trump administration to take several actions immediately to make textile and apparel trade more reciprocal and to support the domestic industry…Aggressively raise tariffs on imports of textile and apparel products from China and other trade predators in Asia…Close the de minimis loophole for all countries…”
SMART (Secondary Materials and Recycled Textiles Association), representing businesses engaged in the collection, reuse, conversion, and recycling of textiles and other secondary materials, advocates for addressing trade barriers that affect U.S. secondhand clothing exports. SMART also opposes CAFTA-DR members using the “yarn-forward” rules of origin for imports of secondhand clothing (HTS 6309) from the U.S. under the agreement.
National Retail Federation (NRF), generally representing all types of U.S. retailers, opposes broad-based tariffs, arguing that they increase consumer costs, disrupt supply chains, and hurt retailers. NRF supports targeted measures against unfair trade practices but warns against policies that could lead to unnecessary retaliation from U.S. trading partners.
- “We believe that high, across-the-board tariffs will undermine the economic growth signaled by the other features of the president’s agenda and have lasting negative consequences for consumers and workers. If the goal of reciprocal tariffs is to enter into negotiations to remove barriers to trade, this will unlock economic growth and reduce prices for consumers. However, if the goal is primarily to raise tariffs, then the opposite is true.”
- “There are plenty of areas where U.S. tariffs are actually much higher than our trading partners, for example, especially when you look at U.S. tariffs on low value apparel and footwear. These regressive tariffs hurt low- and middle-income consumers the most.”
- “The administration should also consider the potential for retaliation from our trading partners on any reciprocal tariffs that are established. We are already witnessing our trading partners respond to strong tariff actions by the administration. This will further impact our farmers and manufacturers who are looking to gain access to those foreign markets.”
- “We need to focus on key high-priority sectors where it makes sense to return manufacturing home or areas where there is strategic competition. High tariffs on everyday household goods, which could raise consumer prices, should not be the focus of such a policy.”
Parkdale Mills, a leading producer of spun yarns based in North Carolina, expressed concerns about “unfair trade practices” from its Asian competitors. Parkadel also calls for closing the “De minimis” loophole.
- “Each week millions of pounds of product move through our free trade agreement partner countries illegally causing significant damage to the domestic textile industry. Non qualifying goods are shipped using false HTS codes, False Certificates of Origin, and illegal inputs to circumvent the required duty for US entry.”
- “Section 321 De Minimis (imports)…are shipped into the US each day without inspection or any type of customs enforcement causing millions in lost revenue and again, thousands of lost jobs. This loophole must be closed.”