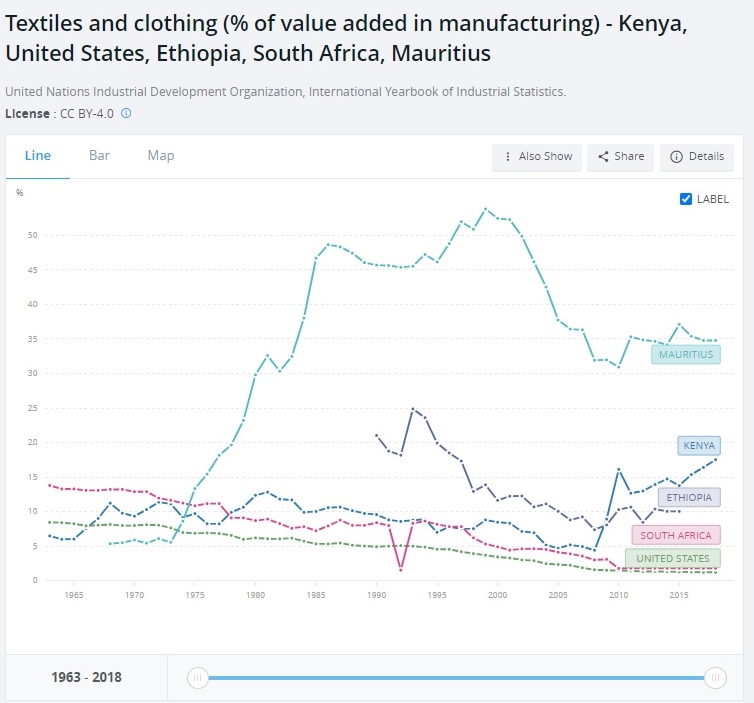
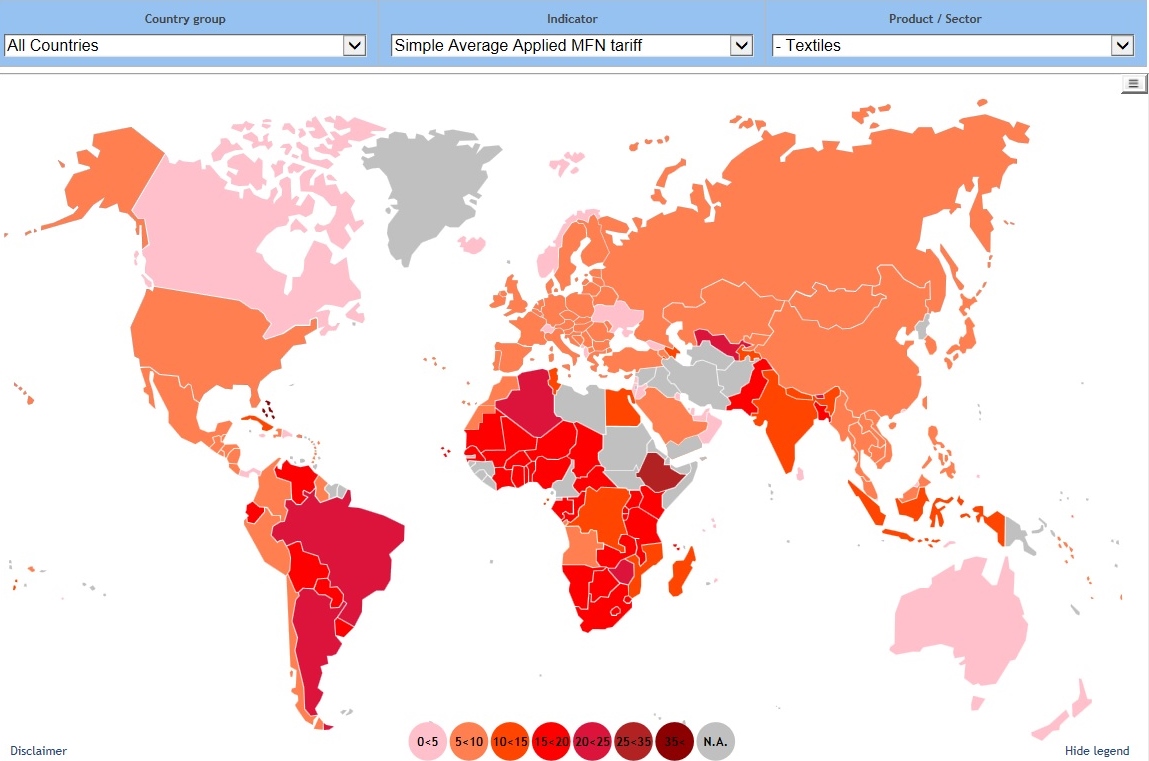
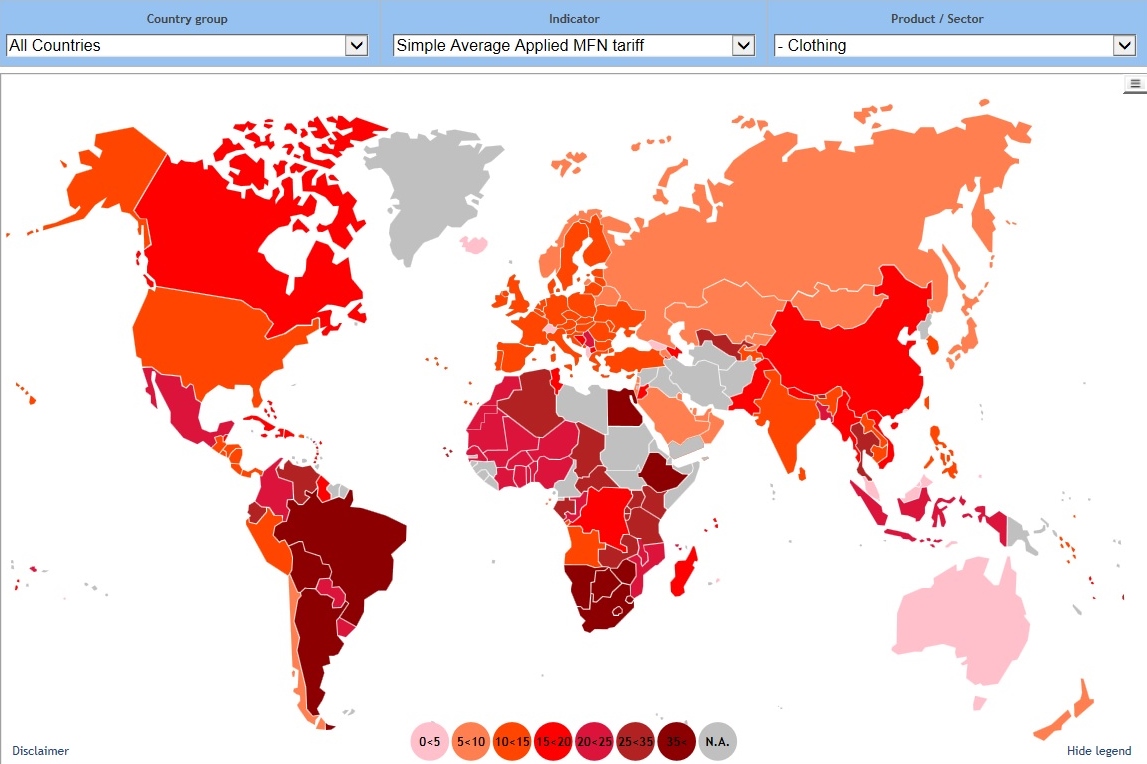
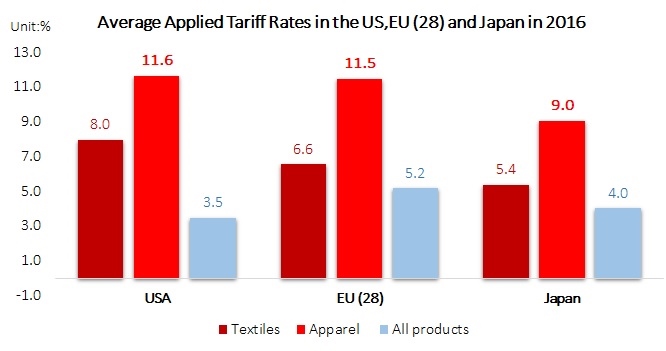
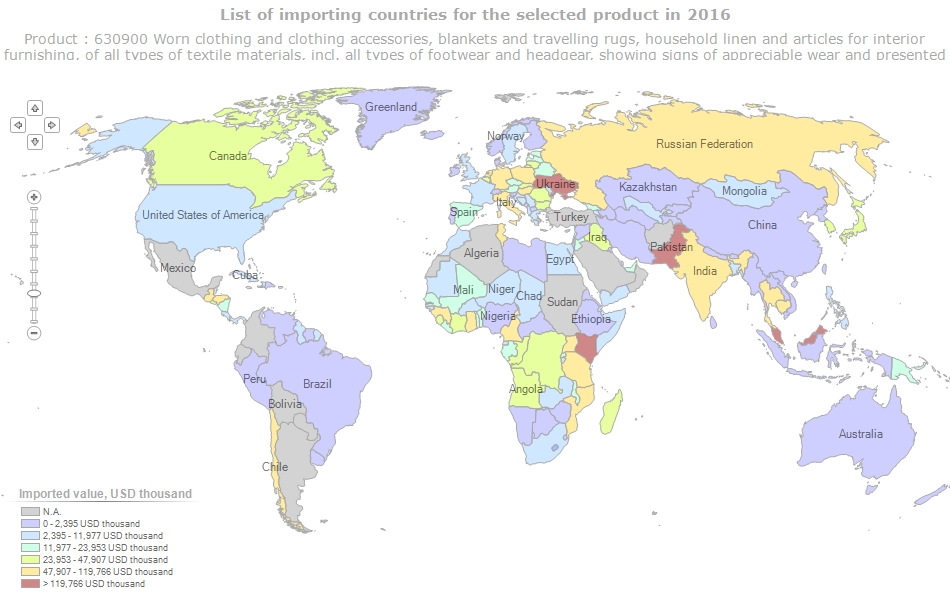
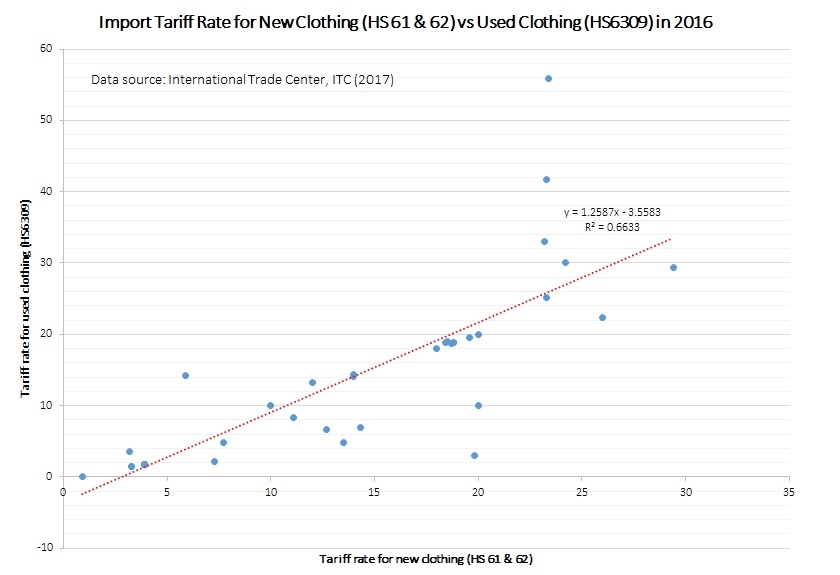
A new study by the Changing Markets Foundation suggests severe negative environmental and social, economic impacts of used clothing exports to Kenya. However, the Textile Recycling Association, based in the UK, argues strongly in favor of the benefits of the used clothing trade.
Concerns about the used clothing exports to Kenya (viewpoints from the Changing Markets Foundation)
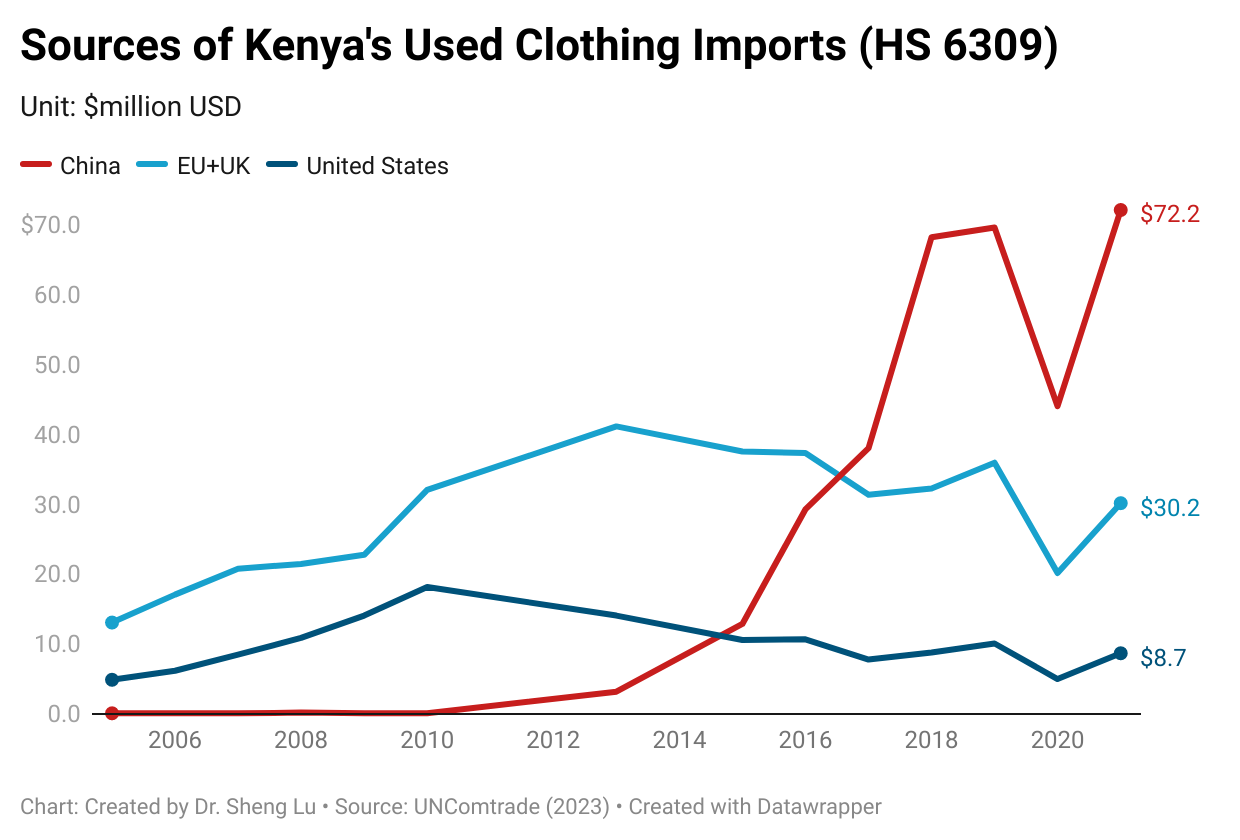
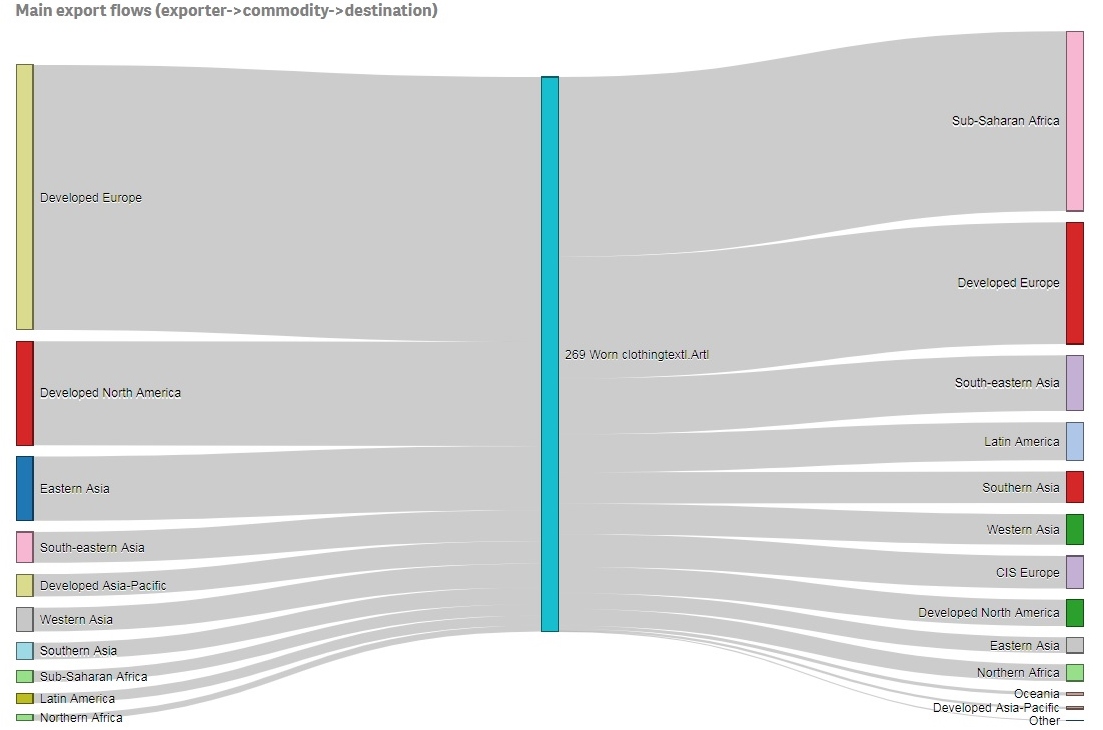
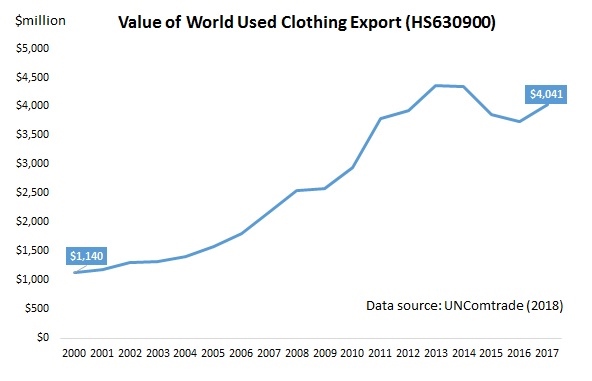
- Data from the United Nations (UNComtrade) shows that Kenya’s used clothing imports surged by over 500% from 2005 ($27 million) to 2021 ($172 million).
- An overwhelming volume of used clothing shipped to Kenya is waste synthetic clothing, a toxic influx creating devastating consequences for the environment and communities. It is estimated that over 300 million items of damaged or unsellable clothing made of synthetic or plastic fibers are exported to Kenya each year, where they end up dumped, landfilled, or burned, exacerbating the plastic pollution crisis.
- Interviews with used clothing traders in Kenya show that 20–50% of the used clothing in bales they purchased was unsellable due to being damaged, too small, unfit for the climate or local styles, and sometimes even with clothing that is covered in vomit, stains or otherwise damaged beyond repair.
- European sorting companies often skimmed off high-quality used clothing for resale in the local EU market. They exported the lower-quality and lower-graded ones to developing countries like Kenya.
- It remains challenging to recycle synthetic clothing as it often contains harmful additives or other materials that make the recycling process difficult or impossible. Additionally, the quality of the recycled synthetic fibers is typically lower than that of the original fabric (i.e., using virgin fiber).
Defend the used clothing exports to Kenya (viewpoints from the Textile Recycling Association, TRA)
- Sorting, trading and selling used clothing “directly employs two million people in Kenya alone , with tens of millions employed globally and supporting many more employment positions in ancillary sectors.”
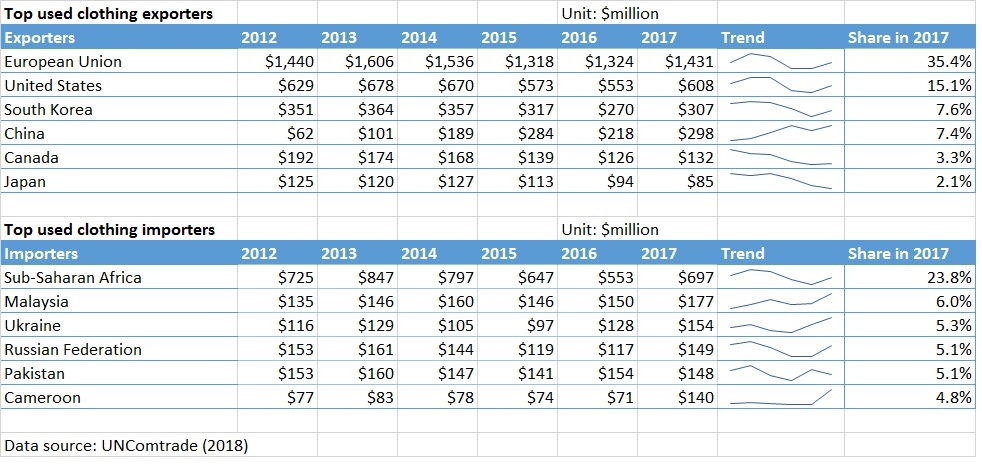
- “Used clothing and textiles collected in the UK, should go through a detailed sorting process and can be sorted typically into 130 plus re-use and recycling grades and sometimes this can be more than 200 grades. In the sorting process each garment is picked up and individually assessed by highly trained experts*. The good quality re-useable products are segregated from the recycling grades.” [*According to Changing Markets Foundation’s report, about 36 million pieces of used clothing were exported from the UK to Kenya in 2021; All EU countries exported about 112 million pieces to Kenya]
- “It is the buyers in these countries (note: countries like Kenya) that dictate the flows of (used clothing) textiles and which import the goods into their countries.”
- “TRA members are required to ensure that only good quality re-usable clothing products are sold onto countries in Africa and other non-OECD countries. Recycling grades and other non-textile/clothing items have to be removed… However, the majority of countries are not subject to the same tight restrictions on trading as the UK.. This is to the extent that some countries allow unsorted used textiles containing a complete mix of re-usable items, recycling grades, and waste to be sold into African countries as a product.” “The qualities of (used clothing) items originating from different countries is likely to vary significantly.”
- “Kenyan’s buy more than 10 times as much used clothing from China than they do from the UK.”
For FASH455: the blog comment assignment can address the following questions:
- What is your stance on the used clothing trade? Should the government impose more export or import trade restrictions on used clothing?
- As we learned in class, developing countries like Kenya are supposed to rely on making and exporting labor-intensive garments to develop their economies. Can importing used clothing lead to similar economic growth? Any evidence that can support the argument?
- What are the ethical issues involved in the used clothing trade? Should government policies play a role in regulating these ethical concerns?
- Could restricting the used clothing trade discourage fast fashion and reduce textile waste generation? Why or why not?
- Should developed countries like the U.S. voluntarily restrict used clothing exports to lessen the economic and environmental pressures on developing countries like Kenya? What are the potential benefits and drawbacks of such a policy?
- Based on the reading, what critical questions remain unanswered, and what further studies could be conducted to gather valuable information for informed decision-making on regulating the used clothing trade?
Additional reading: