Julia K. Hughes is President of the United States Fashion Industry Association (USFIA), which represents textile and apparel brands, retailers, importers, and wholesalers based in the United States and doing business globally. Founded in 1989 as the United States Association of Importers of Textiles & Apparel with the goal of eliminating the global apparel quota system, USFIA now works to eliminate tariff and non-tariff barriers that impede the industry’s ability to trade freely and create economic opportunities in the United States and abroad. Ms. Hughes represents the fashion industry in front of the U.S. government and international governments and stakeholders.
Ms. Hughes has testified before Congress and the Executive Branch on textile trade issues. She is recognized as an expert in textile and apparel issues and frequently speaks at international conferences including the Apparel Sourcing Show, MAGIC, Foreign Service Institute, National Association of Manufacturers, Cotton Sourcing Summit, International Textiles and Clothing Bureau, Young Presidents’ Organization, World Trade Organization Beijing International Forum, and others.
Ms. Hughes served as the first President of the Organization of Women in International Trade (OWIT) and is one of the founders of the Washington Chapter of Women in International Trade (WIIT) and WIIT Charitable Trust. In 1992, she received the Outstanding Woman in International Trade award and in 2008, the WIIT Lifetime Achievement Award.
Ms. Hughes has an M.A. in International Studies from the Johns Hopkins School of Advanced International Studies and a B.S. in Foreign Service from Georgetown University.
Special thanks to Samantha Sault, Vice President of Communication for the U.S. Fashion Industry Association for facilitating and supporting this exclusive interview. Ms. Sault is responsible for the development and execution of the association’s communications strategy, including public relations, policy research and messaging, and social media. Prior to joining the association, Ms. Sault honed her communications expertise at DCI Group, a global public affairs communications firm headquartered in Washington, D.C. Previously, she worked in media as a web editor and fact checker at The Weekly Standard and an editorial assistant at Policy Review, the journal of the Hoover Institution. She began her career in the apparel industry at 17 at abercrombie kids in Bethesda, Maryland.
Interview Part
Sheng Lu: Our students are interested in knowing who the members of the U.S. Fashion Industry Association (USFIA) are. Can you name a few of your member companies?
Julia Hughes: Our members range from major global brands and fast-fashion retailers, to small importers and wholesalers. While all of our members must be doing business in the United States, our membership roster also includes some international companies with a retail presence in the United States. Some of our most actively engaged members include iconic brands and retailers like Ralph Lauren, Macy’s, Levi Strauss & Co., JCPenney, Urban Outfitters, PVH Corp., and American Eagle Outfitters. We also represent small and medium-size importers, wholesalers, and manufacturers that you might not know by name, but supply to many of your favorite brands and retailers—companies like Michar, MGF Sourcing, and Golden Touch Imports, to name a few.
Sheng Lu: The USFIA is an advocate for trade liberalization and removal of trade barriers. Can you talk with us about the benefits of free trade, especially for the fashion industry both in the United States and globally?
Julia Hughes: As you know, USFIA was originally founded in 1989 (then known as the United States Association of Importers of Textiles and Apparel) with the mission to eliminate the global quota system. We were successful! But of course, as you also know, that work is not over. The quotas may have gone away, but there still are import barriers that are unique to the apparel industry. USFIA member companies continue to face some of the United States’ highest tariffs. Textiles and apparel, combined with footwear, still account for some of the highest peaks in the U.S. tariff schedule, with many double-digit tariffs and a high of 32 percent.
Not only are these tariffs higher than on other products, but these tariffs also are a regressive tax. We believe it is simply wrong for a single mom to pay a 32 percent import tax for her baby’s onesies and a 16 percent tariff for her baby’s booties, while the wealthy pay a 1.2 percent tariff for their silk scarves. In total, apparel tariffs take more than $10 billion out of the pockets of hard-working Americans annually. So eliminating these tariffs would be an immediate benefit to American consumers and to American families.
But even removing these tariffs would not mean that there is “free trade.” For example, the fact that the United States maintains these peak textile and apparel tariffs creates problems for new policy initiatives to expand export markets for U.S. products. Market access for American brands and exports is hindered by prohibitively high tariffs in attractive third country markets such as India and Brazil. Our own peak tariffs only encourage other governments to maintain their own high apparel and textile tariffs to “protect” their domestic industries. American brands such as Levi’s and Polo are among the most recognized brands in the world. American yarn spinners and fabric makers operate highly efficient operations that make them among the world’s most competitive producers. For all of these companies, we need every opportunity to remove barriers to trade.
There is a great opportunity to create high-paying jobs here in the United States, too. Fashion brands and retailers offer quality design, product development, logistics, sourcing, and service jobs in the United States, along with manufacturing jobs. These jobs are supported by global value chains, and will be on track to grow IF free trade agreements contain rules of origin and market access provisions that will decrease the cost of those fashion products. This would not only help the brands and retailers grow and create more jobs, but also help consumers by providing access to affordable, high quality apparel.
Finally, free trade isn’t just about tariffs – but also non-tariff barriers like regulations, certifications, and testing requirements all represent non-tariff barriers to trade. And since today’s global brands are selling everywhere from the United States to the UK to Japan to Dubai, we are working to eliminate these barriers, too.
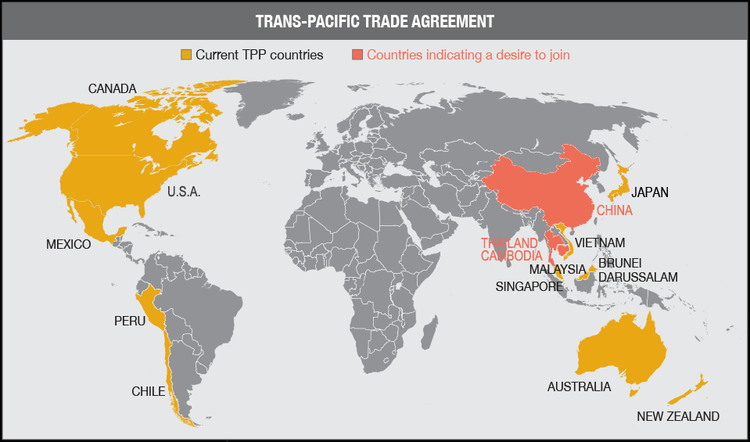
Sheng Lu: The Trans-Pacific Partnership (TPP) is a buzzword for the fashion industry, with Vietnam and China at the core of the discussion. Many people see Vietnam as an alternative sourcing destination to China for labor-intensive apparel and footwear products. You’ve visited both Vietnam and China recently. What’s your first-hand observation? How competitive is “Made in Vietnam” compared with “Made in China”?
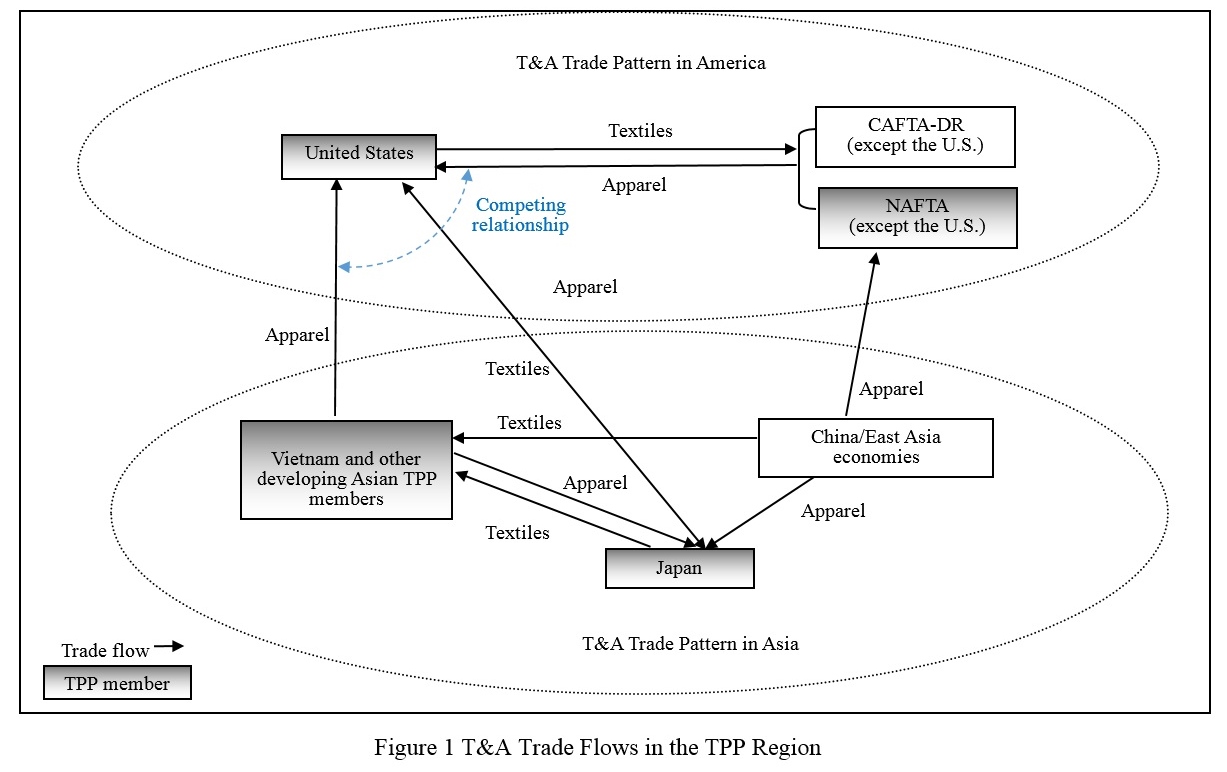
Julia Hughes: The TPP is a top priority for USFIA and for our member companies. But unlike some, we do not see the TPP as creating an either/or scenario for sourcing apparel and footwear. China remains the top supplier to the U.S. market, and we do not see that changing any time soon. The breadth of manufacturing operations in China, combined with the state-of-the-art infrastructure and logistics operations, mean that sourcing executives are comfortable with placing orders and knowing that they will get the quality product that they want delivered on time.
However, you are correct that Vietnam is seen as an alternative sourcing destination.—not just by U.S. sourcing executives, but also for Chinese companies. Both the TPP and the EU-Vietnam Free Trade Agreement make Vietnam an especially attractive destination for making apparel and for investments in manufacturing yarns and fabrics. But Vietnam is not necessarily the destination for companies searching for lower prices.
Sheng Lu: In the 2015 USFIA Benchmarking Study, around one-third of respondents report sourcing from 6-10 different countries and another one-third report sourcing from 11-20 different countries. What are some of the reasons that U.S. fashion companies today would choose to have such a diversified sourcing base?
Julia Hughes: There are a couple reasons why companies have such diversified sourcing bases. First, it is a holdover from the quota era, because companies were pretty much forced to diversify their sourcing since they couldn’t import everything from China. Following the elimination of the quotas in 2005, companies had cultivated trusted suppliers all over the world in countries as diverse as Vietnam, Sri Lanka, Mexico, and Colombia, so there was no reason to leave these good suppliers after they had spent the time and resources developing their supply chain. Second, diversification is a method of risk management. There are lots of risks that could impact your supply chain—from natural disasters to labor strife to terrorist attacks. The last thing a company wants is to have all of their production in one place—because when disaster strikes, you won’t be able to get your product to your customers. By keeping a diverse supply chain, you can ensure that you’ll always have products moving to the shelves. Finally, different countries have different specialties—and truthfully, no one country can do it all. Companies don’t necessarily prefer to source fabric, yarn, zippers, and buttons from four different countries and ship to a fifth for cutting and sewing, but sometimes, that’s the way it must be done in order to produce the best product at the best price for your target customer.
Sheng Lu: We know that the African Growth and Opportunity Act (AGOA) has been extended for another 10 years. How has the U.S. fashion industry reacted to the AGOA extension? Are U.S. consumers going to see more “Made in Africa” apparel in the retail stores?
Julia Hughes: USFIA member companies are definitely looking at sourcing opportunities in Africa after the extension of AGOA. Today a little more than 1 percent of U.S. apparel imports come from Sub-Saharan Africa—and there are only a few countries that ship apparel to the U.S. market. Kenya, Lesotho, Mauritius, and Madagascar are the major producers of apparel today – representing 87% of the U.S. imports. The ten-year extension of AGOA is allowing companies to take a fresh look at what is available to source in Africa today, as well as to plan to long-term growth. Both PVH and VF, for example, have been very public about their commitment to develop a vertically integrated industry in Ethiopia.
What is exciting is that new sourcing supply chains are opening up in Africa. While the level of U.S. imports remains low there are some growing suppliers. For example, during March 2016–a month when the overall U.S. apparel imports plunged by -21 percent compared to March 2015—there were a few Sub-Saharan African suppliers that bucked the trend. U.S. imports from Madagascar jumped by 160 percent, from Ethiopia by 83 percent, and from Ghana by 371 percent!
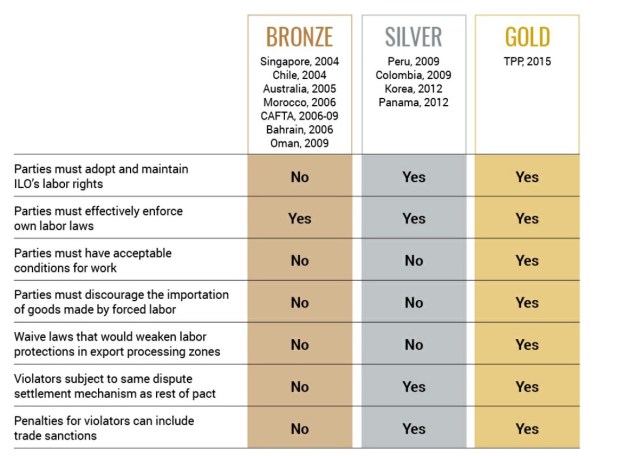
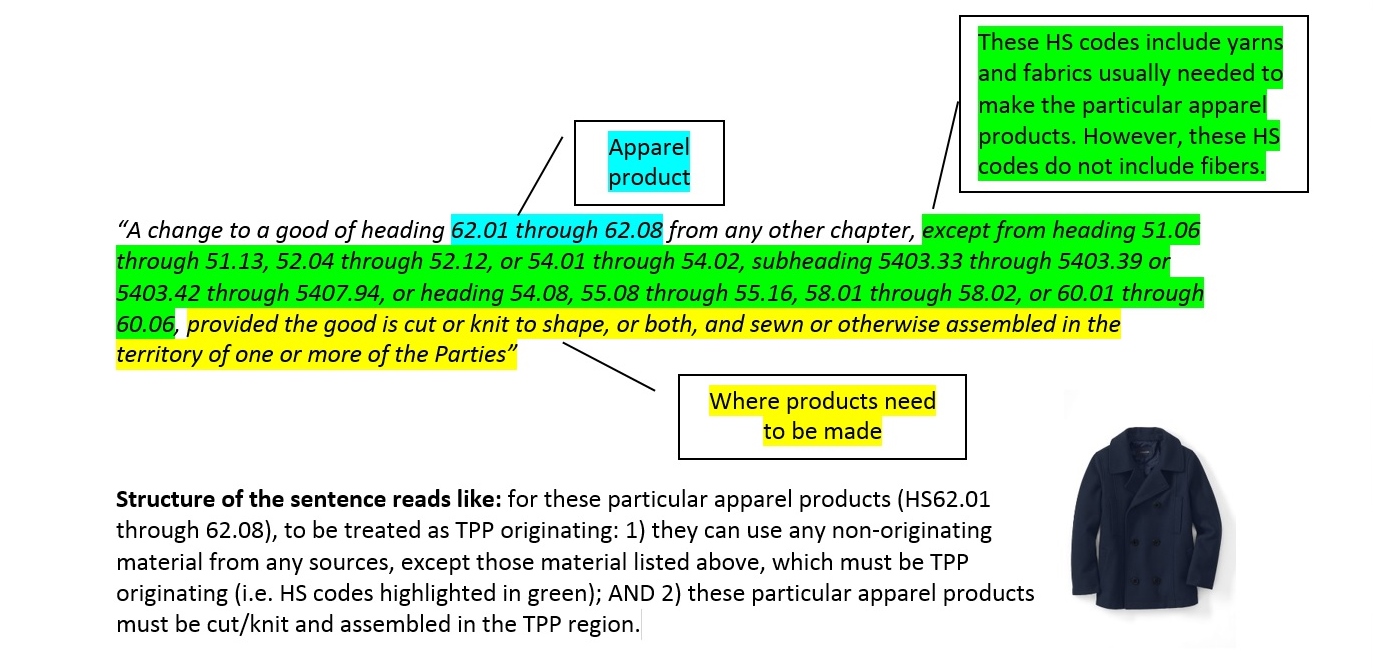
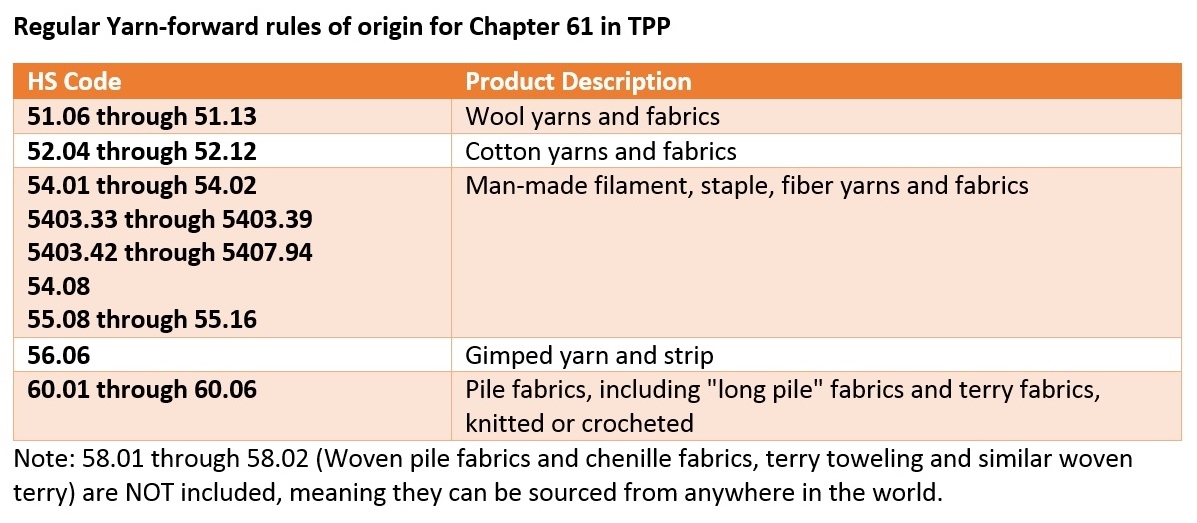
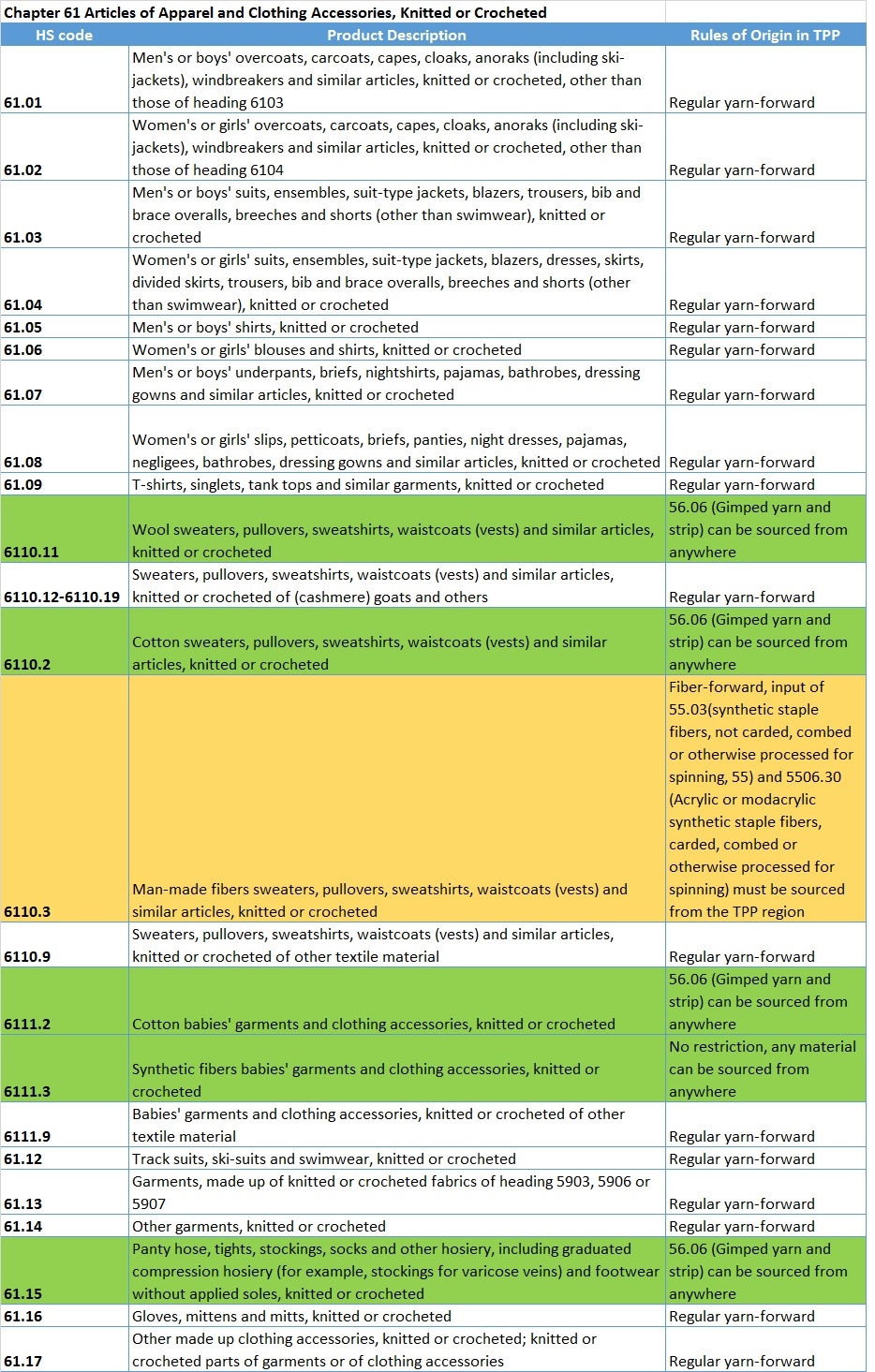
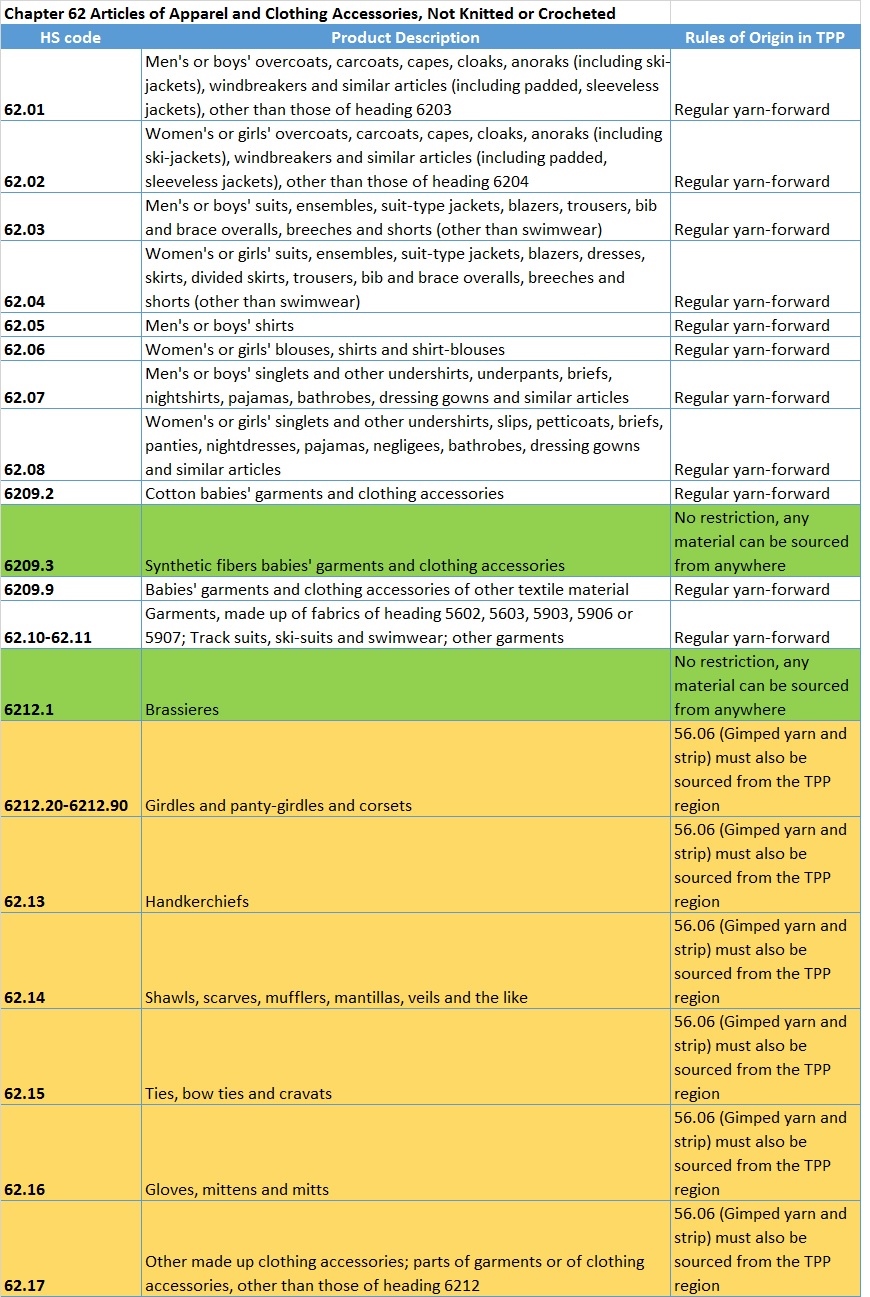
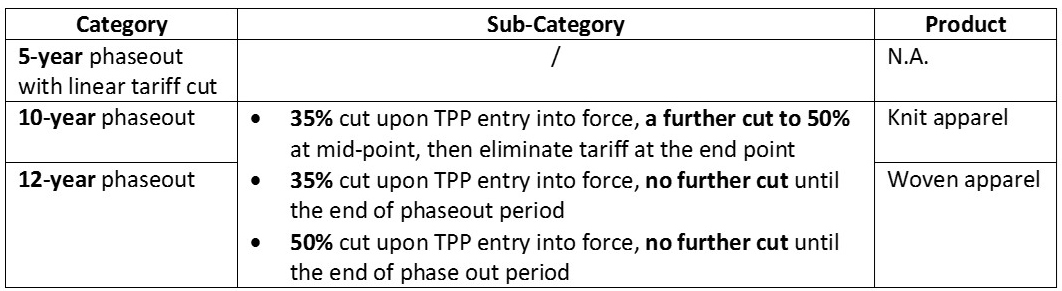
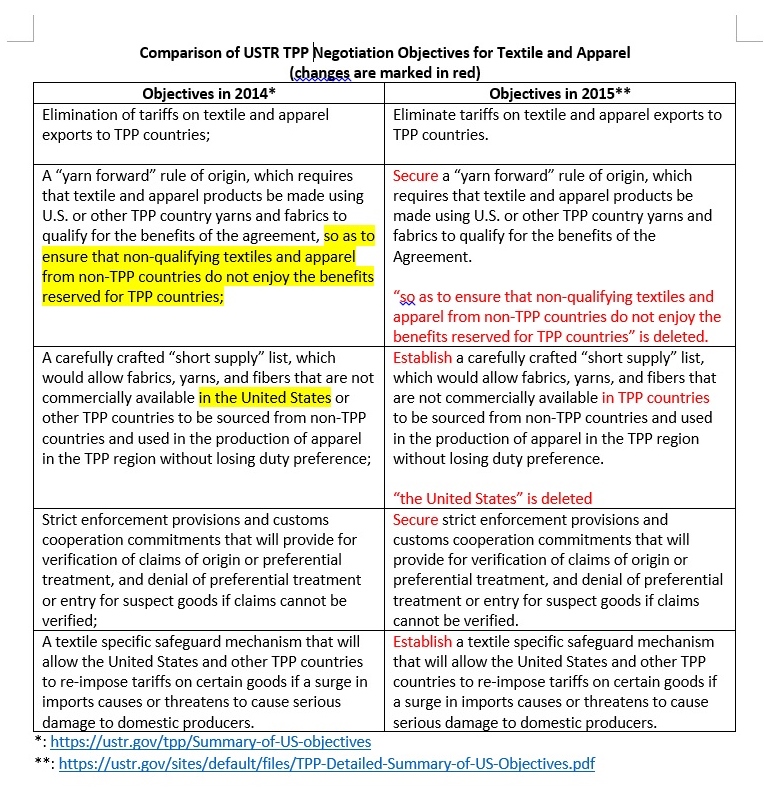
Sheng Lu: Textile and apparel trade policy is always one of the most challenging topics for students in FASH455. Many students wonder why the rules governing the global textile and apparel trade are always far more complicated than most other sectors. For example, in the past, students had to learn about the quota system, from the Short-term Arrangement (STA) to the Multi-Fiber Arrangement (MFA). The quota system is gone, but it seems students now have to know even more “terms”: the yarn-forward rules of origin, short supply list, third country fabric provision, trade preference level (TPL) and earned import allowance… What makes the textile and apparel trade so unique in terms of trade regulations?
Julia Hughes: This is a great question–and one that does not have an easy answer. Absolutely, when I first started working with the industry, it was a revelation to understand about quotas and labeling requirements classification issues. Today, the industry is even more complicated. I think that a lot of the complexity today is due to protectionism. Negotiators looked for ways to limit the market opening impact of trade agreements, and to try to protect their domestic industry. This isn’t just an issue for the United States. Starting with NAFTA in the 1990’s, the rules are more complicated in every free trade agreement—and none of the free trade agreements exactly matches the others. But the complexity isn’t just for FTAs, of course. Today, we also face more regulations, different labeling requirements for different countries (and unfortunately sometimes even different labels are required in different states!), and more testing and certification requirements.
Sheng Lu: Looking ahead in 2016, what important sourcing trends and trade patterns shall we expect in the U.S. fashion industry? What are the policy priorities for the USFIA this year?
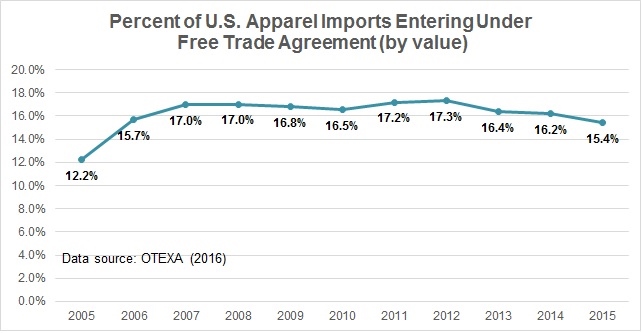
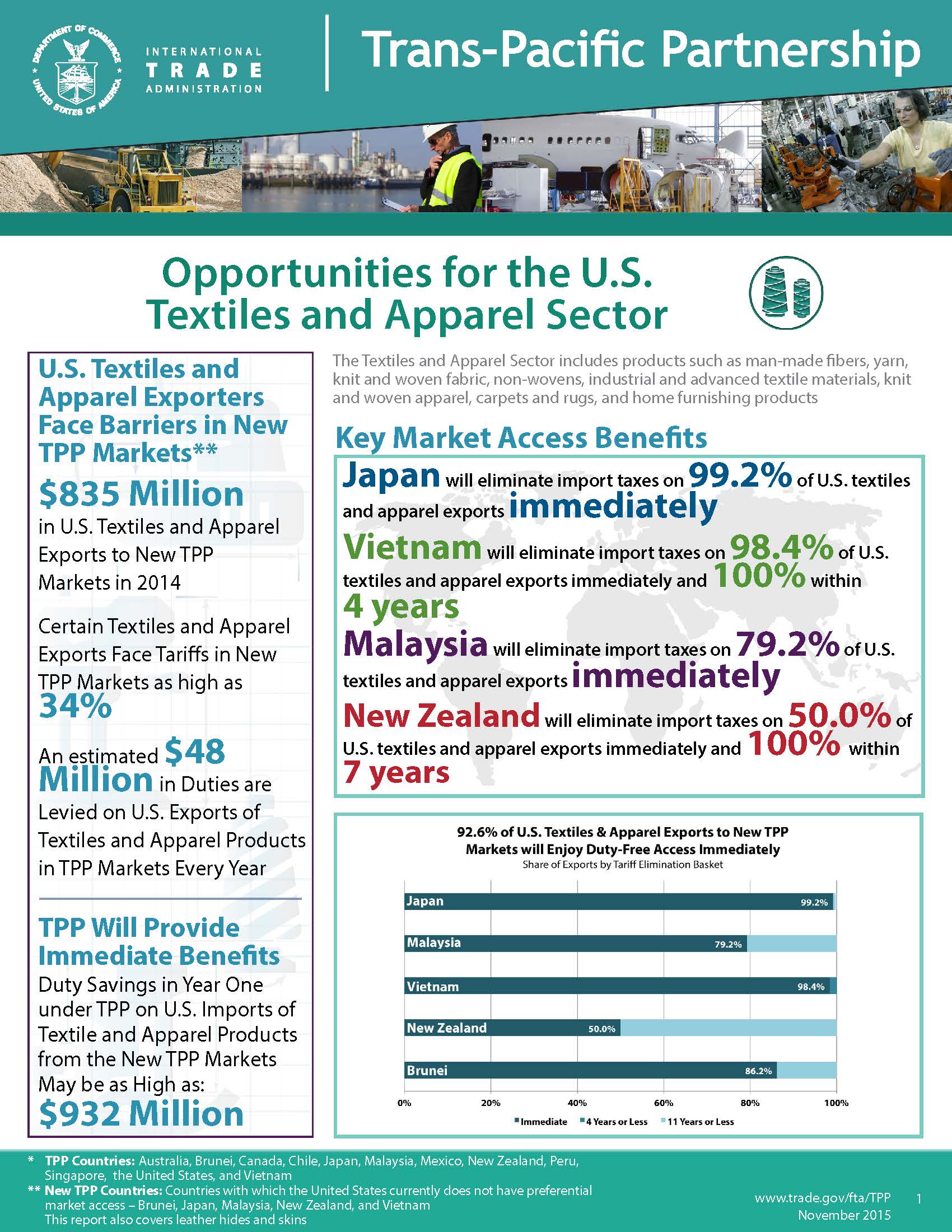
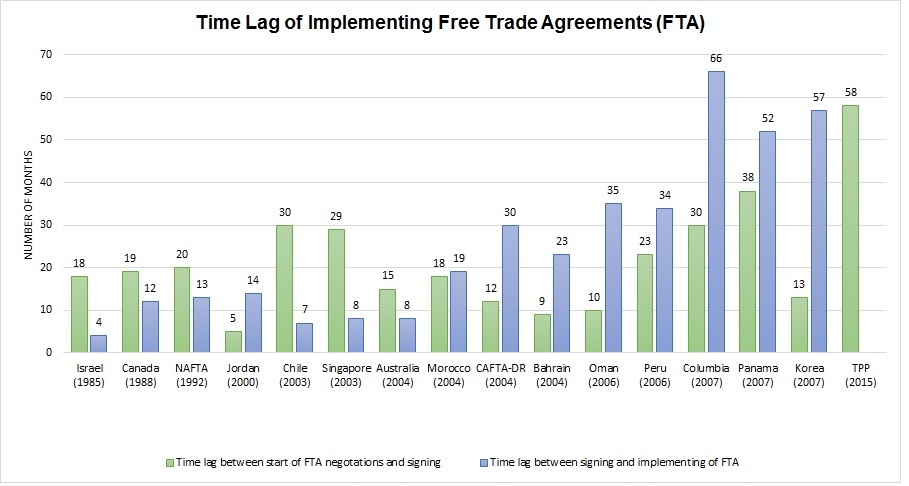
Julia Hughes: The implementation of the Trans-Pacific Partnership (TPP) remains at the top of our list of policy priorities. But implementation is still a long way off, especially since the U.S. Congress is unlikely to vote on the agreement before the November elections. We don’t expect to see a huge shift to sourcing in Vietnam, Malaysia, and the other TPP partners in 2016-2017, since duty-free treatment is a long way off, but we do expect to see companies taking a closer look at opportunities there—and it helps that Vietnam is already the #2 supplier to the United States, so many companies are already sourcing there. We’re also prioritizing completion of the Transatlantic Trade & Investment Partnership (T-TIP) between the United States and European Union. The EU is a great source for luxury brands and companies manufacturing leather goods, but this agreement has an even greater potential in terms of regulatory harmonization, making it easier for many of our members to break into the retail markets in Europe. We’re also focused on enhancing the African Growth & Opportunity Act (AGOA), cumulation of free trade agreements, and customs and ethical sourcing issues, too. As far as future trends, we’re looking forward to seeing the results of our third-annual Fashion Industry Benchmarking Study, which will give us a lot of insight into what brands are thinking about sourcing and expansion!
Sheng Lu: Last but not least, our students wonder what makes you and your staff personally interested in the fashion industry. Particularly, through your daily work, how do you see the impact of the fashion industry in the 21st century global economy?
Julia Hughes: My path to the world of fashion is from the policy side. I was always interested in international policy and after graduating from Georgetown University and SAIS, I was fortunate to hear about an opportunity to be the Washington Representative for Associated Merchandising Corporation (AMC). It was a terrific opportunity to be engaged in policy discussions, but also to spend time with the buyers, with the sourcing teams, and also with the overseas offices and vendors to understand the impact on trade policy on the clothes we wear. Let’s face it, it is a shock to realize the way that Congressional actions, and negotiations, can determine whether a jacket is made with down, or synthetic fibers, or cotton–or maybe it is manufactured to qualify as a shirt instead of a jacket. It also is inspiring to work with industry executives who are committed to fashion as well as doing good for the global economy. Textiles and apparel has always been an industry that can be a gateway for economic development–and I have seen the positive impact by creating jobs where there were none before–as well as expanding U.S. jobs in design, product development and compliance.
Samantha Sault: I have always loved fashion—in fact, my very first job in high school was folding clothes and working the register at abercrombie kids at the mall in my hometown!—but I never thought about fashion as a career until I had been working for a few years after college. I started my career in political media in D.C., and eventually started covering the intersection of fashion and politics for various publications, including exciting events like New York Fashion Week and President Obama’s first inauguration (and the First Lady’s fabulous dresses). After five years in media and public affairs, I found my way to USFIA and the business and policy side of the fashion industry. The most inspiring part about working in fashion has been getting to know our contacts at our member companies, and seeing how committed they are not only to their brands, but also to ethical sourcing and compliance. These are not just buzzwords—I’ve learned firsthand that many of the individuals at our member companies are deeply committed to ensuring that they are doing the right thing in their supply chains from the factory floor (especially for women) to the retail store, and it has made me appreciate these brands even more than I already did.
–The End–