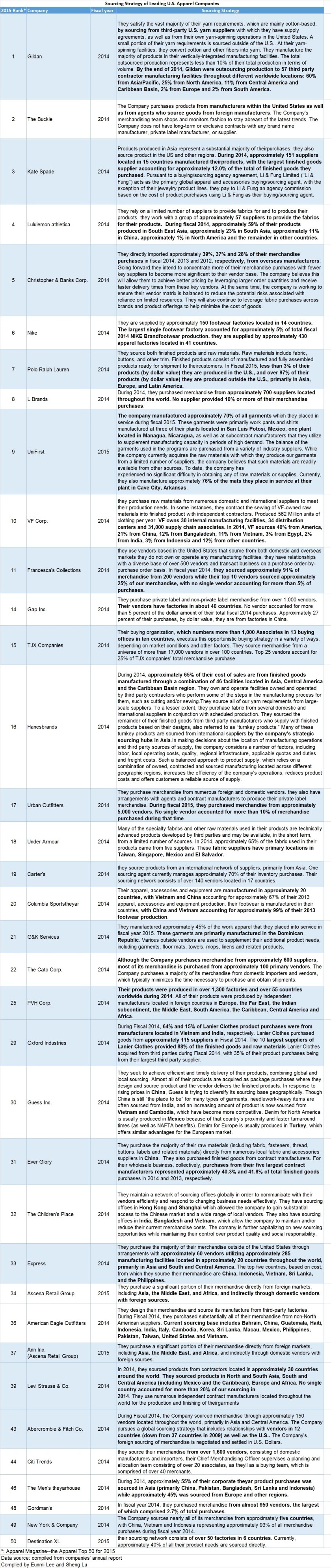
Blog Articles
A Big Picture of International Trade and the U.S. Economy (updated Feb 2016)
1. Trade keeps the US economy growing. Since 1960, trade in the US on average has grown at double the rate of growth of the economy as a whole. Exports of goods and services—produced by businesses employing millions of Americans—are fourteen times what they were six decades ago.
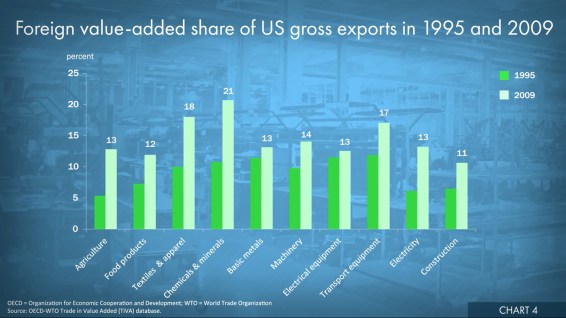
2.Trade pushes countries to produce and export what they are relatively more efficient at making. This is called comparative advantage. The US has abundant skilled-labor and has become one of the world’s leading exporters of high-tech machinery, electrical equipment, vehicles and other capital goods. The same can be said for US exports of business, professional and technical services. The chart shows the trend of higher average earnings in manufacturing industries that export more per worker. More broadly, workers producing US exports are higher paid on average, by 16 to 18 percent more than other workers. And by all metrics, exporting industries are generally more productive than non-exporting industries.
3.Imports are essential to US production and exports! Export competitiveness relies on access to high-quality, low-cost imports. US production processes rely on multiple countries forming parts of the supply chain.
4. U.S. public opinion on trade has long been divided, although in recent years Americans appear to be more persuaded that the potential gains outweigh the costs. The unequal benefits from growing international trade, loss of manufacturing jobs and the downward pressure on wage level remain the top concerns of trade skeptics.
References:
- Council on Foreign Relations (2016) Trading up: U.S. Trade and Investment Policy
- Peterson Institute for International Economics (2015). Why International Trade and Investment Are Good for the US Economy: A Story in Eight Charts
The Global Journey of a Marks and Spencer Wool Suit
An interesting BBC article describes the global journey of a Marks and Spencer (M&S) wool suit:
- The suit was designed by M&S in-house team in UK
- Wool that makes up the suit came from Australia
- Raw wool was shipped from Australia to China for topping.
- Wool top was shipped from China to Italy for dying
- Dyed wool was shipped from Italy to Romania to be spun into yarn
- Yarn was shipped to Yorkshire, UK to be woven into cloth
- Cloth was shipped from Yorkshire, UK to Cambodia to be made into finished suit
- Finished suit was shipped back to UK to be sold at M&S retail stores
As noted by the article, such a global-based production model for M&S’s suit is increasingly typical in UK. What makes the issue controversial, however is that, the suit is labeled as “100% British cloth”. As “defined” by M&S, “British cloth means it is woven, dyed and finished in the UK”.
Similar debates also exist in the United States. In the past, even if a garment was cut and sewn in California but made of imported items, the tag still had to say, “Made in USA of imported fabric, zippers, buttons and thread.” But a new law which takes into effect on January 1, 2016 allows California manufacturers to attach the “Made in USA” label as long as no more than 5 percent of the wholesale value of the garment is made of imported materials.
Discussion questions:
- What are the driving forces behind apparel companies’ global-based production model?
- Is the clothing label “Made in ___” outdated in the 21st century?
- Do you support the new law which allows apparel labeled “Made in USA” to contain certain value of imported material? Why? Do we need such a regulation at all? Why or why not?
Clothing Label Reveals the Global Nature of the Textile and Apparel Industry
While shopping in SoHo (NYC), Nicole Farese, a student from FASH455, found the label of a Splendid sweater reads “Made of Italian Yarn” and “Made in China”. Splendid is a casual wear store which is known for their high-quality clothing sold at a premium price.
Do you find any example of globalization from your clothing label or closet? Please feel free to leave your comment or send your pictures to shenglu@udel.edu (selected pictures will be shared through the blog).
Changes in the Final Text of TPP Regarding Textile and Apparel Rules of Origin

The final text of the Trans-Pacific Partnership (TPP) released by the New Zealand Foreign Affairs & Trade in January 2016 has made a few changes to the textiles and apparel specific rules of origin compared with the USTR version released in November 2015:
- “5407.94” is replaced by “5403.49”
- “or heading 54.08″ is replaced by ” or heading 54.04 through 54.08″
- Minor wording changes are made regarding 55.03 and 55.06-55.11
- TPP originating input of “54.04 through 54.07” is now required for 54.08 (Woven fabrics of artificial filament yarn, including woven fabrics obtained from materials of heading 5405)
- Rules of origin for HS96.19 (Sanitary towels (pads) and tampons, diapers and diaper liners for babies and similar articles, of any material are newly added.
Details of the changes can be downloaded from HERE
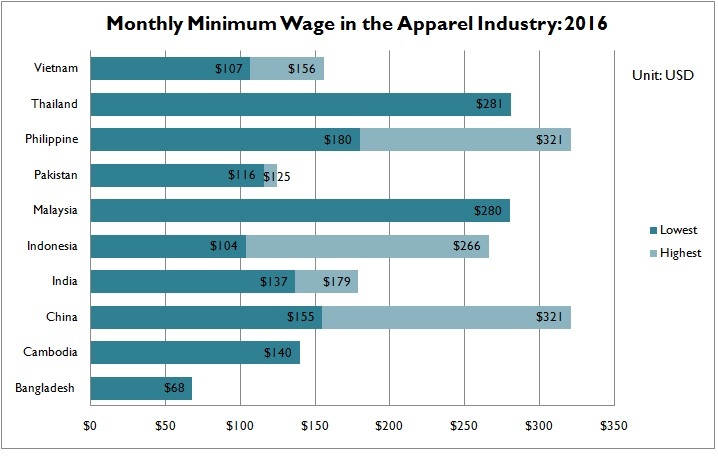
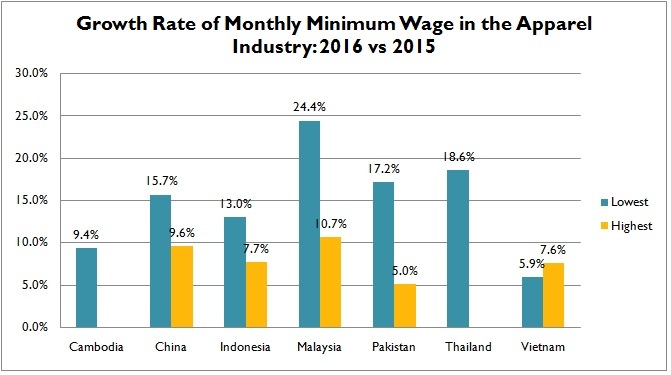
Minimum Wage in the Apparel Industry Continues to Rise in Most Asian Countries in 2016
Apparel producers across Asia may face a more than 5% minimum wage increase in 2016, according to an industry source. India, Malaysia, Thailand and Pakistan may see the biggest increase of minimum wage (up more than 15%) among the leading Asian apparel producers, whereas minimum wage in Bangladesh and Philippine may remain roughly unchanged from last year.
As noted by the industry source, this year’s minimum wage increase comes from various reasons. In Cambodia, the increase is mostly pushed by local labor unions. Indonesian government raises the wage aiming to shorten the gap between minimum and living wage in under-developed regions. Additionally, countries such as India adjust their minimum wages more based on economic factors such as inflation rate, GDP growth rate and consumers’ price index.
Data further shows that the gap in minimum wage between Asian apparel producers somehow is widening. For example, monthly minimum wage in some parts of China has reached $321 USD in 2016, which is $253 USD higher than in Bangladesh ($68 USD/month), up from $225 USD in 2015. A wide gap in minimum wage is also found within some Asian countries. For example, in Philippine, Indonesia and China, the highest minimum wage could be almost twice as high as the lowest minimum wage in the country.
Despite the increase, minimum wage in Asia remains a fraction of the level in the developed countries. For example, minimum wage in the United States was $7.5/hour in 2015, meaning a worker’s monthly minimum wage shall no less than $1,200 (assume working 40 hours/week, 4 weeks/month).
State of China’s Textile and Apparel (T&A) Industry (Updated in January 2016)

How to deal with China as a sourcing destination remains a tough and controversial issue facing U.S. apparel retailers and fashion brands in 2016. Although companies are of grave concerns about China’s continuous rising production cost (especially labor cost), few other lower-wage countries can beat China in terms of industry integration, supply chain efficiency, and reliability.This blog post intends to add to the discussion by taking a look at the supply side, i.e. what is happening in the China textile and apparel (T&A) industry.
First, China’s production capacity remains unparalleled in the world. In 2014, the latest statistics available, textile fiber production in China exceeded 50 million tons, accounting for 54.36 percent of world share. By 2013, as much as 64.2 percent of the world’s chemical fibers, 64.1 percent of synthetic fibers and 26.2 percent of cotton were produced in China (see the table blew). On the other hand, apparel production in China reached 29.9 billion units in 2014, up 10.4 percent from 2013. Given China’s vast production capacity, very likely it will remain the top apparel sourcing destination for most EU and US fashion apparel companies for many years to come. For example, Vietnam’s apparel production in 2015 totaled 2.85 billion units, which was only around 10 percentage of China’s production scale in 2014.
Second, China’s T&A industry is growing slower. Specifically, output of China’s T&A industry (measured by value added) grew only 7.0 percent between 2013-2014, a significant drop from 10.3 percent between 2009-2010. Other major economic indicators in the industry, from sales revenue, net profit to investment, followed a similar pattern (see the figure below). Additionally, for the first time since the 2008 financial crisis, China’s T&A exports suffered a 3.9 percent decline in 2015 (-1.3% for textiles and -5.4% for apparel). Given the downward pressure on China’s economy and uncertainties in the world marketplace, such a slow-growth pattern is likely to continue in the years ahead.


Third, China’s T&A industry is undergoing important structural adjustment. Within the total industry output, the ratio of apparel, home textiles and industrial textiles has turned from 51:29:20 in 2010 to 46.8: 28.6: 24.6 in 2014, reflecting China’s efforts to move towards making more value-added and technology-intensive textile products. This ratio is expected to become 40:27:33 by the end of 2020 (i.e. the end of China’s 13th five-year plan). In order to overcome the pressure of rising labor and production cost, China’s T&A manufacturing base is gradually moving from the east coast to the western and central part of the country (accounting for 22.5 percent of China’s T&A production in 2014, up from 16.8 percent in 2010; this share may further increase to 28 percent by 2020). Additionally, T&A companies in China are encouraged to increase spending on research and development (R&D), which on average had accounted for 0.47 percent of T&A companies’ sales revenue in 2013, up from 0.43 percent in 2011.
Fourth, T&A companies in China are actively seeking business opportunities in the domestic retail market. Apparel retail sales in China reached 893.6 billion yuan in 2014 (around $137.5 billion), among which 30.77 percent were sold online (up from 14.54 percent in 2011). Apparel retail price on average rose 2.6 percent between 2013-2014, compared with 2.0 percent increase of China’s overall CPI over that period. However, it shall be noted that apparel retail sales in China’s tier 1 and tier 2 cities achieved almost zero growth in 2014, partially reflecting the negative impact of retail price increase on consumers’ demand. In comparison, apparel retail sales in China’s tier 3 & 4 cities as well as rural areas remain robust and strong. Additionally, financial performance of T&A companies in China is becoming more polarized. Companies that follow the traditional business model of manufacturing and exporting are facing their most difficult time since the 2008 financial crisis. However, there are also many success stories of apparel companies that focus on function upgrading, i.e. moving from simply “manufacturing” products to “serving” the market needs.
Sheng Lu
Recommended reading: China’s 13th five-year plan for its textile and apparel industry: Key numbers
Top 10 Most Read FASH455 Blog Posts in 2015

1. Potential Impact of TPP on the Textile and Apparel Sector: A Summary of Recent Studies
2. 2014 World Textile Industry Labor Cost Comparison
3. Global Trade of Used Clothing (Updated: October 2015)
4. Market Size of the Global Textile and Apparel Industry: 2014 to 2018
5. When Will TPP Take Effect? Let’s look at the History
6. China to Become the World’s Largest Apparel Market in 2019
7. Are US Textile and Apparel Imports Using Free Trade Agreements?
8. 2015 US Fashion Industry Benchmarking Study Released
9. Exclusive Interview with Erin Ennis, Vice President, US-China Business Council
10. US Tariff Phaseout Schedule for Textile and Apparel in TPP by OTEXA Code
Textile and Apparel (T&A)-Specific Rules of Origin in TPP—Apparel Products
Textile and apparel (T&A)-specific rules of origin (RoO) for most apparel articles under TPP are known as the nickname “yarn forward”. “Yarn-forward “means preferential treatment under TPP will be allowed if the component determining classification meet BOTH the following two criteria:
- knit or woven in TPP countries FROM yarn spun or extruded in TPP countries;
- apparel is cut or knit to shape or both + sewn or otherwise assembled in TPP countries
In other words, “yarn forward” RoO not only requires the activity of apparel manufacturing must happen in one or more TPP countries, but also requires certain textile material used to make the apparel products must come from the TPP region.
The following is an example of how TPP describes “yarn-forward” rules of origin:
“A good is an originating good if it is produced entirely in one or more TPP countries by one or more producers using non-originating materials and each of the non-originating materials used in the production of the good satisfies any production process requirement, any applicable change in tariff classification requirement or any other requirement specified.”
The followings are details of T&A-specific RoO for apparel products in TPP compiled based on released TPP text. “Regular yarn-forward” means all textile material listed in the table must be TPP originating. Overall, TPP allows much fewer exceptions to “yarn-forward” rules than most existing free trade agreements in the United States (such as NAFTA, CAFTA-DR, and Columbia Free Trade Agreement).
U.S. Department of Commerce Releases Factsheet on TPP and the U.S. Textile and Apparel Industry
According to the factsheet released by the U.S. Department of Commerce, the Trans-Pacific Partnership (TPP) will create exciting new export opportunities for the U.S. textile and apparel (T&A) industry. The report highlights Vietnam and Japan as two promising markets in TPP for certain T&A products “Made in USA”, including:
Vietnam:
- Cotton fiber, yarn, and Cotton woven Fabric (U.S. exported $394 million in 2014 with 16% market share only after China; tariff will be cut from 12% to zero on day one)
- Non-woven fabrics (U.S. exported $23million in 2014, up 951% from 2009; tariff will be cut from 12% to zero on day one)
Japan
- Synthetic fiber, yarn, and fabric (U.S. exported $61 million in 2014, up 61% from 2009; tariff will be cut from 2.7%-10% to zero on day one)
- Industrial and advanced textile fabrics (U.S. exported $91 million in 2014, the fourth largest supplier after China, Taiwan, South Korea; tariff will be cut from 8.2% to zero on day one)
- Men’s and boy’s apparel (U.S. exported $32.6milion in 2014, up 30.9% from 2009; tariff will be cut from 9.8% to zero on day one)
The factsheet also argues that TPP is a “balanced” deal for the U.S. T&A industry: long U.S. tariff phaseout schedule, strict “yarn-forward” rules of origin and textile safeguard mechanism in TPP will serve the interests of those stakeholders that seek protection of U.S. domestic T&A manufacturing, whereas duty savings from import tariff cut and the short supply list will create greater market access opportunities for U.S. fashion brands and retailers.
According to the report, the United States is the fourth largest textile exporter in the world. 54% of total U.S. T&A exports went to TPP markets in 2014. The United States is also the single largest importer of T&A in the world. 372,300 T&A manufacturing jobs remained in the United States in 2014.
The Future of “Made in China”: Robots are taking over China’s Factory Floors
The video echoes one recent Wall Street Journal article about Levi Strauss using automation technologies to revamp their apparel production in China:
“In an apparel factory in Zhongshan, a gritty city of three million stuffed with industrial parks across the Pearl River from Hong Kong, lasers are replacing dozens of workers who scrub Levi’s blue jeans with sandpaper to give them the worn look that American consumers find stylish. Automated sewing machines have cut the number of seamstresses needed to stitch arc designs into back pockets. Digital printers make intricate patterns on jeans that workers used to do with a mesh screen.”
One important factor that gives a push to adopting robots in China’s factory floor is the end of very cheap labor in China. China’s wage level has been rising in double-digit percentages for the past decades. And as a consequence of its “one-child policy”, by 2050, the working-age population in China could decline by 212 million according to estimation from the United Nations.
But Levi executives say they have largely abandoned a strategy of relocating production to one impoverished country after another, known as “chasing the needle,” in favor of other forms of cost-cutting.” “Labor is getting more expensive and technology is getting cheaper,” says Andrew Lo, chief executive of Crystal Group, one of Levi’s major suppliers in China.
“Levi is adapting its laser technology so it can etch different patterns to make one type of denim look like another, reducing costs by buying less fabric. For a new line of women’s wear, Levi said it needed only 12 fabrics, rather than 18. In the past three years, Levi said, it cut the number of its suppliers by 40% and the number of fabrics by 50%.”
“The changes also give Levi greater flexibility, said Ms. O’Neill, the 44-year-old executive who helps oversee the company’s supply chain. If a pair of jeans using a particular fabric is selling well, she says, Levi can use lasers to produce more of the desired look, and pare back designs that are losers. “The idea is to delay decision-making for as long as possible,” said Ms. O’Neill.”
And this is only the beginning! Some technologists think that inventions such as 3-D printing—essentially printers that replicate solid objects like copiers reproduce printed pages—will have a big impact by 2050. In such a world, printers could spew out clothing, food, electronics and other goods ordered online from a nearly limitless selection, with far fewer workers involved in production.
“In 2050, you could potentially have a 3-D printer at home that could produce all the fabrics you want,” said Roger Lee, the chief executive of Hong Kong’s TAL Group, which makes 1 of every 6 dress shirts sold in the U.S. for brands from Banana Republic to Brooks Brothers. “That would make us obsolete.”
Ironically but not surprisingly, automation also keeps wages down. Levi said it expects China production to rise only “modestly” next year; new orders are up for grabs. Apparel InternationaI’s president, Oscar Gonzalez, says the company now boasts an advantage over China—a large pool of apparel workers who were laid off in past downsizings. Excess labor has helped him keep wage increases to 2% or 3% a year he says. “Every Monday when we recruit,” he adds, “there are long lines of applicants.”
Welcome for any comments and discussion questions.
US Tariff Phaseout Schedule for Textile and Apparel in TPP by OTEXA Code
[This post is updated on July 1, 2016]
Please also read:TPP tariff phase-out can steer Vietnam sourcing plans
The United States includes as many as 38 different types of phaseout schedule in TPP and 8 of them apply to the textile and apparel (T&A) sector.
In general, T&A products with lower base tariff rate seem to be given more generous phaseout treatment than T&A that are subject to higher base tariff rate. For example, although T&A products under category EIF can immediately enjoy duty-free treatment once TPP takes into force, their base tariff rate is also the lowest (7.9% on average). In comparison, whereas T&A products under category US6, US7, US8 and US9 are subject to the highest base tariff rate, they are given the least generous tariff cut (i.e. 35%) once TPP takes into effect. This will makes average tariff rate applied to these products remain the highest almost throughout the whole phaseout period. It should be noted that even though US11 apparently seems to be the most restrictive phaseout category (i.e. 50% cut on day 1 and the resulting rate will remain unchanged until the end of year 12), its average tariff rate actually will be lower than phaseout category US6, US7, US8 and US9.
In the following table, the U.S. phaseout schedule for T&A in the released TPP text based on the 8-digit Harmonized System (HS) code is matched with the Office of Textiles and Apparel (OTEXA) product category. Results show that products equivalent to around 37.5% of the value of U.S. textile and apparel imports from Vietnam in 2015 will enjoy immediate duty-free treatment once TPP takes into force (i.e. EIF), approximately 4% will be subject to medium-level protection (i.e. EIF+B5) and 58.6% are under high (i.e. EIF+ any of the followings: US6, US7, US8, US9, US10, US11) or very high level of protection (i.e. any of the followings: US6, US7, US8, US9, US10, US11).
Note: “Level of protection” in the above table is defined as the following: 1) Low level of protection: EIF only; 2) Medium level of protection: EIF+B5; 3) High level of protection: EIF+any of the followings: US6, US7, US8, US9, US10, US11; 4) Very high level of protection: any of the followings: US6, US7, US8, US9, US10, US11 only.
Sheng Lu
Potential Impact of the Trans-Atlantic Trade and Investment Partnership (T-TIP) on Related Textile and Apparel Trade Flows
The presentation was delivered at the 2015 International Textile and Apparel Association (ITAA) Conference in Santa Fe, New Mexico on November 13, 2015. Welcome for any suggestions and feedback.
Tariff Remains a Critical Trade Barrier Worldwide for the Textile and Apparel Sector
According to data from the World Trade Organization:
- In 2013, average applied tariff rate remained at 10.73% for textiles and 18.25% for apparel worldwide. Compared with the average tariff rate for all sectors, the rate for textiles on average is 1.4 percentage points higher and the rate for apparel is 8.9 percentage points higher. This implies that although tariff may not be a critical trade barrier for some sectors anymore, it still significantly matters for the textile and apparel sector.
- Least developed countries (LDC) overall set a higher tariff rate for textiles and apparel than the world average level. Ironically, many LDCs heavily rely on imports for textile supply. Should these LDCs lower their tariff rate for textiles, it may help apparel manufacturers there save sourcing cost for yarns and fabrics and improve the price competitiveness of finished apparel products.
- At the country level, countries with the highest tariff rate for textiles include Ethiopia (27.8%), Sudan (27.4%), Argentina (23.3%, Brazil (23.3%), Gabon (19.8%), Cameroon (19.6%), Chad (19.6%) and Congo (19.6%). And countries with the highest tariff rate for apparel include Zimbabwe (72.26%), South Africa (41.02%), Namibia (41.02%), Swaziland (41.02%), Botswana (41.02%), Lesotho (41.02%), Bolivia (40.0%), Sudan (40.0%), Argentina (35.0%), Ethiopia (35.0%) and Brazil (35.0%). Interesting enough, many of these countries are members of the African Growth and Opportunity Act (AGOA) which are eligible for the third country fabric provision.
Sheng Lu
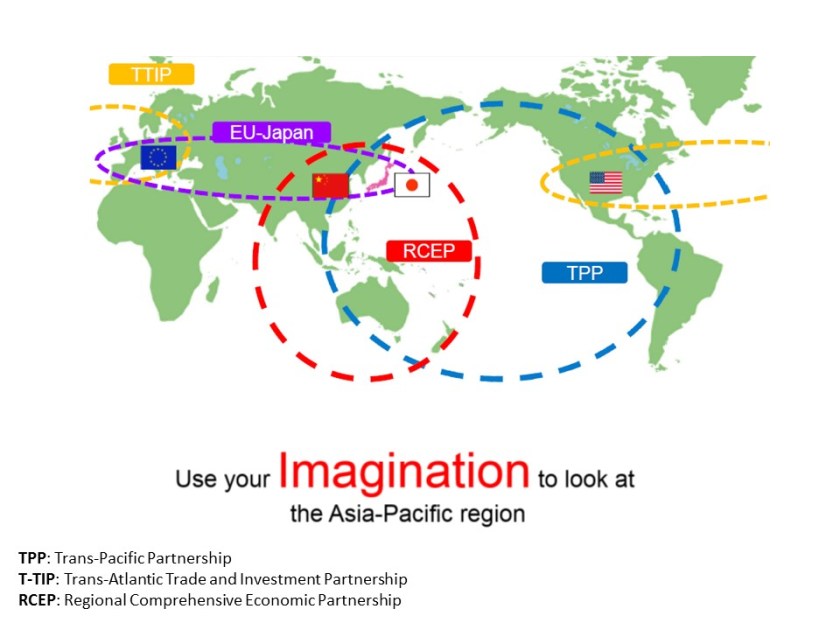
The Future of Asia-Pacific and Implications for the U.S. Textile and Apparel Industry
The following discussion questions are proposed by students enrolled in FASH455 (Global Apparel & Textile Trade and Sourcing) Fall 2015 after learning the unit on textile and apparel industry & market in the Asia-Pacific region. Please feel free to leave your comment and engage in our online discussion.
- We’ve heard so much about China’s superior involvement in the textile & apparel sectors globally, but how are these industries contributing to the local economy?
- As rules on working conditions and minimum wage have been enforced in Mainland China many business people have moved their operations to Southeast Asia, do you think the Southeast Asia will eventually become like mainland China forcing businessmen to seek low wages elsewhere?
- Will Vietnam shift its sourcing of yarns and fabrics from China to US after TPP? What are some setbacks associated with this? What are some potential opportunities?
- While Vietnam is currently one of the primary exporters of apparel to the United States, what should be the actions taken by the United States if they continue to “refuse” to cut out Chinese Textiles? Or, should the United States continue their trading patterns with Vietnam despite their reliance on Chinese Textiles?
- The Asia pacific region is made up of a variety of countries with different strengths and political infrastructure. How does the variety of policies and governments affect how we do business abroad, and is there a way to set standards that are not individualized to each country?
- China and the US can be seen as a threat to one another. However the president of China said the “Pacific Ocean has enough space for the two large countries”. Do you think they are threats to each other, or are they ultimately helping each other’s economies grow?
- What will happen as more and more countries that used to produce apparel move into producing more capital intensive production?
- What are the advantages or disadvantages of excluding China from international trade agreements such as TPP?
- If the T&A industry in China is envisioned by policymakers as beginning to focus more on technical textiles, how will the textile industry in China compete with the industry in the United States?
- Why has East Asia become one of the most economically interconnected regions in the world?
- What are some of the reasons that China still remains one of most price competitive export markets in the World? Also, does China face challenges in losing their top spot as leader in price competitiveness? If so, what are some of the reasons they are in danger of competition?
- How is the discussion about yarn forward rules of origin different in regards to TPP countries than the same discussion between the NAFTA/CAFTA-DR countries?
[Discussion for this post is closed].
FIBERcast8: Two Years After the Rana Plaza, What Has Changed?
Panelists:
- Zara Hayes, Director of Clothes to Die For
- Sarah Hamilton, Producer of Clothes to Die For
- Mara Burr, Senior vice president from the Albright Stonebridge Group
- Avedis Seferian, President and CEO of Worldwide Responsible Accredited Production(WRAP)
- Marsha A. Dickson, Professor of Department of Fashion and Apparel Studies, Irma Ayers Professor of Human Services, Co-Director of Sustainable Apparel Initiative, University of Delaware
Panel discussion questions:
- What does the Rana Plaza tragedy bring out those aspects of the garment industry that many people don’t know?
- What was it like going to Bangladesh and talking to survivors of the Rana Plaza? What are the behind the scene stories of filming the documentary Clothes To Die For?
- What changes are happening in the Bangladesh garment industry after the Rana Plaza? Particularly, what people in Bangladesh are doing to prevent tragedies like the Rana Plaza from happening again?
- The Alliance for Bangladesh Worker Safety (the Alliance) is a major effort from the U.S. business community in response to the Rana Plaza tragedy. What the Alliance has being doing, what major accomplishments have been achieved and what is the future work plan of the organization?
- Has corporate social responsibility (CSR) practices in the Bangladesh garment industry critically improved after the Rana Plaza? Compared with other leading apparel manufacturers in the world such as China, Vietnam, India, Cambodia and Indonesia, is Bangladesh still significantly lagging behind in terms of corporate social responsibility practices?
- How does the academia look at the Rana Plaza? Does the tragedy lead to some new research questions? What is the “academic” recipe for improving the CSR practices in the Bangladesh garment industry?
- Will enhanced factory inspection increase production cost and make apparel “Made in Bangladesh” lose price competitiveness?
- To prevent tragedies like the Rana Plaza from happening again, what each individual consumer can do or should do?
- Sub-contracting is regarded as an indispensable part of today’s global apparel supply chain. But factories undertaking sub-contracting work operate in a “black box”—many of them are off the chart for inspection and audit. Any progress or new thinking on how to solve the sub-contracting issue in the garment industry?
The People’s Republic of Capitalism Part IV
Discussion questions
- Is China still a “communist country”? Why or why not?
- What is your view on China’s overall strategy to develop its economy first and leave problems such as income gap, corruption, human right and pollution to be solved at a later time?
- How different is the business environment in China versus in the United States?
- Given the problem such as human rights, pollution and corruption in China, should the U.S. government support and encourage U.S. business connections with China? Why or why not?
- Anything in the documentary that is particuarlly interesting to you?
Please feel free to share your thoughts & comments.
USTR Michael Froman Comments on the Textile and Apparel Chapter under TPP
In an event hosted by the Council on Foreign Relations on October 15, 2015, U.S. Trade Reprehensive Michael Froman left a comment on the textile and apparel chapter (T&A) under TPP. He said that:”
“You know, we worked very hard to find solutions that could address the broad range of stakeholder interests here, even when we had conflicting interests here in the U.S. I’ll take textile as an example. You know, we have a domestic textiles industry that’s been investing in more production in the U.S., growing their employment in the U.S. And obviously we have a strong sector of our economy that brings in apparel from other countries, apparel importers and retailers. We worked very closely with both groups of stakeholders to come up with a solution, to come up with an outcome that we think both will be comfortable with and both will be supportive of. And that’s been very important to us to try and address the broad range of U.S. stakeholder interests, whether it’s labor, environment, importers, exporters, to make sure we’re covering everybody’s interests well.”
In the remarks, Forman also ruled out the possibility that TPP would be renegotiated. He said that:
“So this isn’t one of those agreements where, you know, you can, you know, reopen an issue or renegotiate a provision. This is one where, you know, every issue is tied to every other issue and every country’s outcome is balanced against every other country’s outcome. And so that’s the agreement that we’ll be putting forward under TPA for a vote by Congress.”
According to Inside U.S. Trade (October 9, 2015), the final TPP reflects some of the key priorities of the U.S. textile industry by allowing limited exceptions from the prevailing yarn-forward rules of origin and by including tariff phaseouts for “sensitive apparel items” of 10 to 12 years.
Besides the basket of goods that will become duty-free upon entry into force (which include cotton shirts and cotton sweaters), TPP sets up three other categories for tariff reductions on apparel:
Major exceptions other than the “short supply list” mechanism under TPP include:
- An “earned import allowance“ program for cotton pants made in Vietnam from third-country fabric by importing a specified amount of U.S. cotton pants fabric. This would allow cotton pants from Vietnam would enter the U.S. duty-free as soon as the agreement is implemented. It is said the ratio for the program is “close” to 1:1. However, for men’s cotton pants, there could be a 15 million square meter equivalents (SMEs) annual cap until year 10, after which it will increase to 20 million. There is no quantitative limit for the other types of cotton pants that can be shipped under the program, such as women’s, girls’ and boys’ pants.
- A limited list of cut-and-sew items that Vietnam and other TPP countries can ship to the U.S. under the preferential TPP duty rate. These include synthetic baby clothes, travel goods including handbags, and bras.
JCPenney’s Global Sourcing Practices
In the class, we discussed how global U.S.-based apparel companies have become. The typical business model in the U.S. apparel industry today is “producing anywhere in the world and selling anywhere in the world”. Here is one more example: JCPenney.
JCPenney has been importing products from across the world since 1959. The company’s sourcing organization has eight offices globally aside from its office in Dallas. The offices are in Shanghai, Hong Kong, Korea, Bangladesh, Guatemala, Pakistan, India, and Taiwan.
In terms of its future growth opportunities, JCPenney identifies the following three:
- Omnichannel: Implementing the necessary tools, processes and technologies that enable us to serve the customer no matter how they’re shopping with us. By creating a seamless shopping experience in stores and online, customers are likely to shop and spend more at JCPenney.
- Center Core: Strengthening and revitalizing the highest traffic area in the store to become a leading destination for women’s shoes, handbags, fashion jewelry, intimate apparel and accessories, which are anchored by two very strong businesses: Sephora inside JCPenney and the Fine Jewelry store.
- Home: Restoring our Home store to its previous sales productivity with a compelling assortment of value-driven products backed by a promotional strategy that builds customer loyalty and increases traffic.
(Source: JCPenney’s 2014 Annual Report)
What role do you see global sourcing could play in helping JCPenney achieve these strategic development goals? How do you understand the statement that sourcing is part of a company’s overall business strategy? Do you think JCPenney will likely to source more “Made in USA” products in the future? Please feel free to share your views.
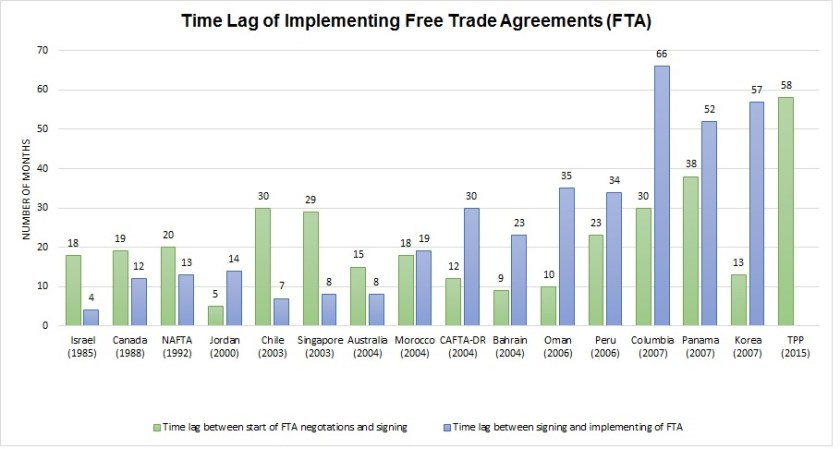
When Will TPP Take Effect? Let’s look at the History
With the conclusion of the Trans-Pacific Partnership (TPP) negation on Oct 5, people now wonder: when will the agreement eventually take effect?
As shown in the chart above, since the 1985 US-Israel Free Trade Agreement, the average time lag between signing and implementing a free trade agreement (FTA) in the United States is 25.5 months (over 2 years). However, since 2006 the average time lag increased to 48.8 months (around 4 years).
So looks like it will take a while…
Potential Impact of TPP on the Textile and Apparel Sector: A Summary of Recent Studies
With the conclusion of the Trans-Pacific Partnership (TPP) negotiation on Oct 5, 2015, it is time to think about its potential impact. Specifically for the textile and apparel (T&A) industry, the followings studies may offer some hints (to read more, you can click each title):
Trade Statistics
Statistics show the 12 TPP partners altogether imported $65 billion worth of textiles and $154 billion worth of apparel in 2013, which accounted for a world import share of 20 percent and 32 percent, respectively (WTO, 2015). In 2014, around 55 percent of U.S. textile and apparel exports (or $13.3 billion) went to the other 11 TPP partners, and 17 percent of U.S. textile and apparel imports (or $17.8 billion) came from the TPP region (OTEXA, 2015).
Impact of TPP on U.S. Textile and Apparel Manufacturing: A Preliminary Estimation
TPP overall will have a negative impact on U.S. domestic textile and apparel manufacturing. In all simulated scenarios, the annual manufacturing output in the United States will decline by $846 million–$3,780 million for textile and $1,154 million–$1,828 million for apparel than otherwise.
2.The “yarn-forward” rule may not substantially benefit U.S. domestic textile and apparel manufacturing as some people had suggested, for two reasons: 1) results show that Vietnam is more likely to use Japanese textiles than U.S. textiles when yarn-forward rule is in place. 2) U.S. apparel imports from Vietnam directly compete with those imported from NAFTA and CAFTA regions, the largest export market for U.S.-made yarns and fabrics. When NAFTA and CAFTA’s market share in the U.S. apparel import market is taken away by Vietnam, U.S. textile exports to NAFTA and CAFTA will decline anyway, regardless of whether Vietnam uses U.S.-made textiles.
3.Results suggest that compared with the “yarn-forward” rule, development of Vietnam’s local textile industry will have an even larger impact on the future of U.S. domestic textile and apparel manufacturing. Particularly, when Vietnam becomes more capable of making textile inputs by its own, not only Vietnam’s overall demand for imported textiles will decline, but also Vietnam’s apparel exports will become even more price-competitive in the U.S. as well as the world marketplace.
“Import Sensitive” Clothing and the TPP X-basket : What might include
Based on examining three recent trade programs, including: U.S. International Trade Commission (USITC) monitoring program on T&A imports from China based on the U.S.-China Textile Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) (2008—present), Office of Textiles and Apparel (OTEXA) monitoring program on U.S. T&A imports from Vietnam (2007-2008) and U.S. textile safeguard measures against China (2003-2005), it seems “import sensitive” T&A in the United States mostly refer to cotton and man-made fiber apparel and fabrics. OTEXA product Code 338, 339, 340, 345, 347, 348, 352, 447, 638, 639, 640, 645, 646, 647, 648 and 652 are most likely to be included in the TPP X-basket.
Because Vietnam’s T&A exports to the United States heavily concentrate on these “import sensitive” T&A categories, the X-basket has the potential to substantially affect the actual trade liberalization that can be enjoyed by the T&A sector under TPP:
- By the most conservative estimation, i.e. the X-basket only covers Category A “import sensitive” apparel products, it will affect about 41.6 percent of U.S. apparel imports from Vietnam (or 38.7 percent of total U.S. T&A imports from Vietnam) if trade pattern remains the same as in 2014.
- In the worst case, i.e. the X-basket covers all “import sensitive” T&A products identified by this study, it will affect about 70.0 percent of total U.S. T&A imports from Vietnam, if trade patterns remains the same as in 2014.
2015 US Fashion Industry Benchmarking Study
The survey results show that TPP matters for the U.S. fashion industry, with as many as 79 percent of respondents saying implementation of the agreement will impact their business practices. Specifically:
- 72 percent expect to source more textiles and apparel from TPP partners, suggesting the imminent impact of TPP for the U.S. fashion industry could be trade creation.
- Fewer than 10 percent expect to source less from non-TPP members after the implementation of the agreement, suggesting the trade diversion effect of TPP could be limited.
- 48 percent expect to strategically adjust or redesign their supply chain based on TPP, implying TPP could be a game changer and has the potential to shape new patterns of textile and apparel trade in the Asia-Pacific region in the long term.
- However, as few as 7 percent expect to export more products to TPP partners, while only 10 percent expect to invest more in TPP partners (building factories, operating retail stores and e-commerce operations) after implementation of the agreement. It seems the U.S. fashion industry hasn’t focused much on TPP’s potential to promote exports and achieve greater market access.
- Additionally, 45 percent say the TPP Short-Supply List should be expanded, and comments indicate the proposed “yarn-forward” Rule of Origin is a major hurdle to the industry realizing real benefits from the agreement. In fact, as many as 83 percent support or strongly support abandoning the strict “yarn-forward” Rule of Origin and adopting a more flexible one in future FTAs (Figure 21). This suggests that the benefit of TPP for the U.S. fashion industry and the utilization of the agreement will largely depend on the Rule of Origin. In particular, there is a strong call among U.S. fashion companies to make the textile and apparel Rule of Origin less restrictive and more flexible in TPP.
Why does the US Textile Industry Want Yan-forward Rule of Origin (RoO) in TPP?
The US textile industry insists yarn-forward RoO in TPP is not because they expect a substantial increase of textile exports to Vietnam as the case of NAFTA and CAFTA which help capture the export markets in Mexico and Central America. But rather it is because:
1) Without yarn-forward, situation will get even worse. Particularly, a less restrictive RoO will make Vietnam’s apparel exports which contain textiles made in China, Taiwan or South Korea qualified for duty free access to the US market. Definitely this will be a more imminent and bigger threat to the US textile industry than simply facing competition from Vietnam’s apparel which contains Japanese made textiles. And still many US textile companies don’t treat the Japanese textile industry very seriously, although I think they should. Remember, Japan currently is the fourth largest textile supplier to Vietnam and the NO.1 textile supplier to China.
2) With yarn-forward RoO in place, at least US textile companies can invest in Vietnam (remember, globalization is about movement of capital as well. Many apparel companies in Mexico and Central America actually are invested by US companies). Without yarn-forward RoO however, Vietnam can simply rely on imported textiles as the case mentioned in (1) and there will be no incentive for US textile companies to move factories to Vietnam (meaning, capital holders will lose).
So overall yarn-forward RoO may win a few more years for the US textile industry. But in the long run, it is my view that the US textile production and its exports to the Western Hemisphere countries may still inevitably decline (especially those output to be used for apparel assembly purposes) after the implementation of TPP. In the 21st century, the nature of competition is supply chain v.s. supply chain.
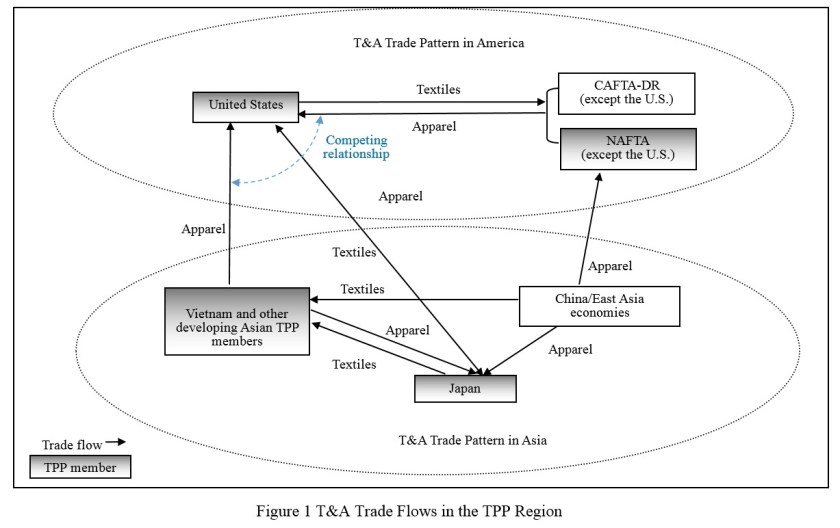
Regional Production-Trade Network Remains an Important Feature of Global Textile and Apparel Trade
Regional production-trade network (RPTN) refers to a vertical industry collaboration system between countries that are geographically close to each other. Within a RPTN, each country specialized in certain portions of supply chain activities based on its respective comparative advantages so as to maximize the efficiency of the whole supply chain.
There are three major textile and apparel (T&A) RPTNs in the world today:
- Asia: more economically advanced countries/regions such as Japan, South Korea, Taiwan, Hong Kong and China supply textiles to the less economically developed countries such as Vietnam, Bangladesh and Sri Lanka for apparel manufacturing, where the wage level was much lower. On the other hand, Japan is a leading apparel importer and consumption market in Asia.
- Europe: among EU members, textile inputs can be supplied by developed countries in Southern and Western Europe such as Italy and Germany. In terms of apparel manufacturing in the European Union, low and medium-priced products can be undertaken by developing countries in Southern and Eastern Europe such as Poland and Romania, whereas high-end luxury products can be produced by Southern and Western European countries such as Italy and France. Furthermore, finished apparel can be shipped to developed EU members such as UK, Germany, France and Italy.
- America: within the region, the United States as a developed country supplies textile materials to developing countries in North, Central and South America (such as Mexico and countries in the Caribbean region), which assemble imported textiles into apparel by taking advantage of the local low labor cost. The finished apparel articles are eventually exported to the United States for consumption.
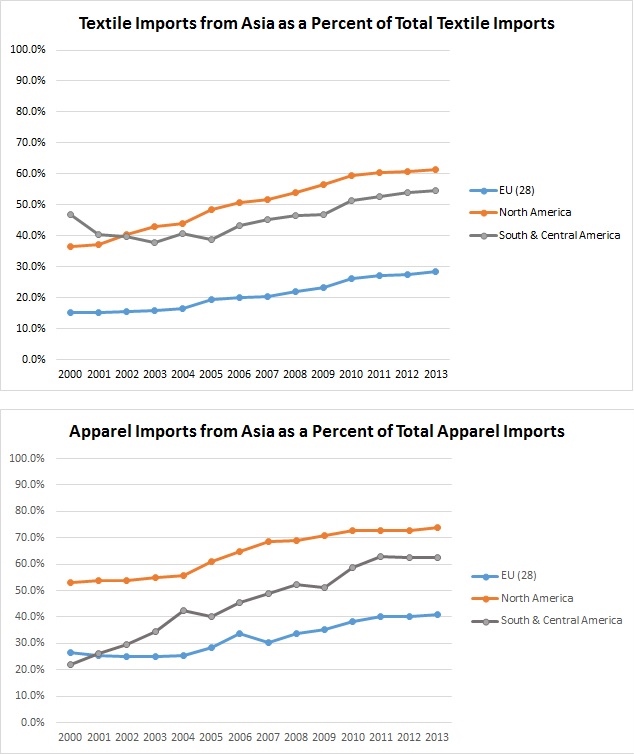
Latest data from the World Trade Organization (WTO) shows that RPTN in the above three regions remain an important feature of today’s global T&A trade as the graphs shown below:
(Note: Data comes from the World Trade Organization)
Particularly, three specific trade flows are worth watching:
One is Asian countries’ growing dependence on textile supply from within the region, which rose to 90.2% in 2014 from 87.7% in 2000. This is a reflection of a growing integrated T&A supply-chain in Asia. As a result, apparel “Made in Asia” is becoming even more price-competitive in the world marketplace today and this has posted pressures on the operation of the T&A RPTNs in EU and America.
Second one is the stable intra-region trade pattern both for textile and apparel in EU. In 2014, 58.8% of EU’s (28 members) textile imports and 46.2% of apparel imports came from other EU members; at the same time, 68.8% of EU’s (28 members) textile exports and 74.7% of apparel exports also went to other EU members.
Additionally, developing countries in North, Central and South America still heavily rely on regional supply of textile inputs; at the same time, their finished apparel are also mostly consumed within the region. Data show that 80.3% of American countries’ textile imports still came from within the region in 2014; at the same time, 88.9% of American countries’ apparel exports were also shipped to the region, mostly the United States and Canada as the final consumption market.
Sheng Lu
Global Trade of Used Clothing (Updated: October 2015)
Please also check the updated study: Why is the used clothing trade such a hot-button issue?
United States
- Generates 1.4 million tons of used clothing annually
- Exports 800,000 tons of used clothing annually
- 20% of used clothing sold domestically in thrift stores
- Non-wearable material of used clothing is reprocessed into fibers for upholstery, insulation, soundproofing, carpet padding, building and other materials.
Central and South America
- Very large used clothing market in most countries
- Imports of used clothing mostly come from the United States
- Cotton wipers made from used clothing are exported back to the United States
Europe
- Generates 1.5-2 million tons of used clothing annually
- Large used clothing sorting centers located in Western and Eastern Europe
- 10-12% used clothing (only those top quality) sold in local secondhand shops
Africa
- One of the largest used clothing markets in the world
- 80% of population wear secondhand clothes
- Most used clothing imported from the United States, Europe, India and Pakistan
East Asia
- Most used clothing is collected in Japan, South Korea and Taiwan
- Countries in the region also import used clothing from the United States, Europe, India and Pakistan
- Some large used clothing sorting centers are located in Malaysia and Philippines.
India and Pakistan
- Residual used clothing are imported and sorted by grading companies
- Wearable used clothing is extracted from “mixed rags” and sold locally or shipped to Africa
- Recycled yarns are used to make new sweaters
- Cotton wipers made from used clothing are exported to the United States
Australia
- Used clothing is collected and sold through local shops and exported
Source: Planet Aid (http://www.planetaid.org); UNComtrade (2015)
USTR Adjusts Language of TPP Negotiation Objectives for Textile and Apparel
On September 22, the U.S. Trade Representative Office (USTR) releases a detailed summary of its latest TPP negotiation objectives. Specifically for the textile and apparel chapter, compared with the negotiation objectives released in 2014, some wording changes are made this time:
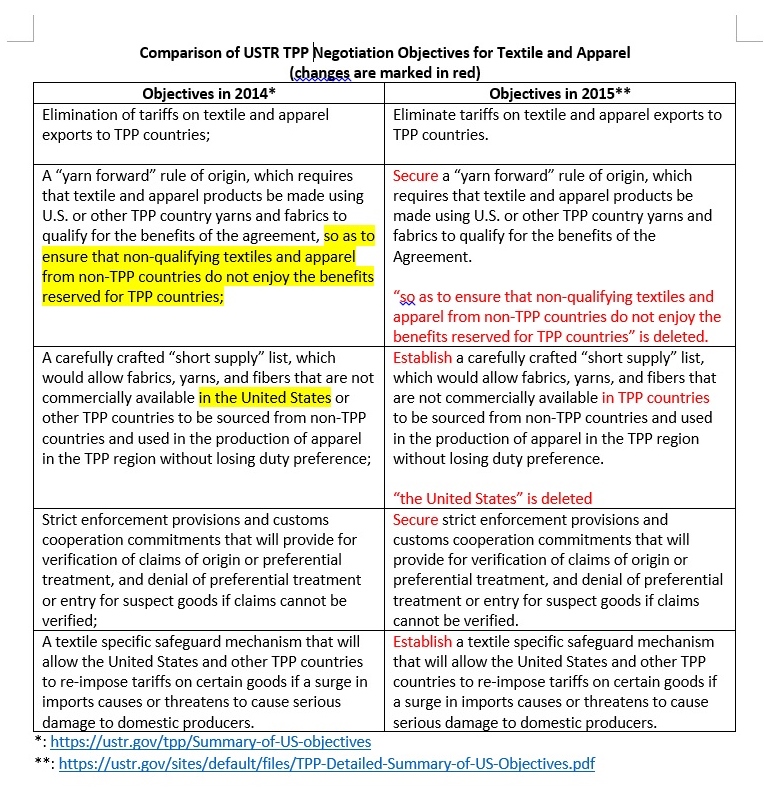 Does the change imply that the U.S. side has agreed to allow more exceptions to the “yarn-forward” rules of origin in TPP, but in the format other than “short supply list”? For example, will it be “earned import allowance” or tariff preference level (TPL)?
Does the change imply that the U.S. side has agreed to allow more exceptions to the “yarn-forward” rules of origin in TPP, but in the format other than “short supply list”? For example, will it be “earned import allowance” or tariff preference level (TPL)?
On the other hand, does the change imply that the “short supply list” under TPP will be stricter than previously expected? (in the 2014 version of the negotiation objectives, it read like the “short supply list” may include those products that are not commercially available in the US but are commercially available in other TPP members. However, in the 2015 version, only those products that are absolutely not commercially available in the whole TPP region are eligible for the “short supply list”.)
Sheng Lu
Trade and Development
This video provides a great summary of what we discussed in class on trade and development. Please keep in mind that:
- Textile and apparel industry (T&A) plays a critical role in generating economic growth, reducing poverty and promoting human development both in history and today. This is why T&A remains a critical sector in the 21st global economy, even though people may think clothing is such a “simple” product.
- Apparel sourcing is far more than just about how to get the product at the lowest price. Throughout the supply chain, sourcing decisions and practices are closely connected with many people’s destiny in the world, especially those living in the developing countries. As future professionals working in the fashion apparel industry, please think about your impact and responsibilities.
Please feel free to share any comments and thoughts on the video
What Might Apparel Sourcing in the 3D-Printing Era Look Like?
(photo credit: WGSN)
Wearing 3D-printed apparel is no longer a dream (see the pictures above)! But what is the implication of 3D-printing technology on apparel sourcing? Here is my personal vision:
First, 3D printing may create brand new T&A supply chains and business models. 1) Because 3D printing is highly technology and capital intensive with little input from low-skilled labor, it implies that developed countries rather than developing countries may enjoy the comparative advantage in manufacturing 3D-printed apparel. 2) Because apparel will be directly printed by machines, cross-the-border transportation can be largely reduced in the 3D printing era, generating potential cost-saving opportunities both for manufacturers and consumers. 3) 3D printing will empower consumers to more directly involve in the product development process. Yet given consumers’ limited technical knowledge and equipment, many new types of customer services ranging from design assistance to on-site apparel printing may emerge in the 3D printing era.
Second, 3D printing may result in a more sustainable T&A supply chain. 1) Because 3D printing is digital-based, it may help reduce waste during the product development process. 2) Because 3D printing is highly customized and can produce on-demand, it may result in less overproduction in the textile and apparel (T&A) industry. 3) 3D printing has the potential to be made by recycled material. 3D printed apparel itself may be recycled as well, resulting in almost zero carbon emission in the whole product life-cycle.
However, 3D printing my create new challenges for apparel sourcing. 1) When 3D printed apparel substitute traditionally-made apparel among ordinary consumers, demand for apparel sewing workers will be substantially reduced. Millions of unskilled or low-skilled workers currently employed in the T&A sector may have to find new jobs. 2) Workforce in the T&A industry may have to substantially update their knowledge structure in the 3D printing era. The T&A industry may even be short of talents for certain positions such as 3D printing designers and engineers. 3) The application of 3D printing will require an update of the current legal system to better address issues such as intellectual property right protection, consumer privacy protection and data security in a digital-based context.
What is your vision for the future of apparel sourcing in the 3D-printing era?
Sheng Lu
Apparel Sourcing Opportunities in Madagascar and Mauritius
Please feel free to share your thoughts on the following discussion questions:
- Why does the United States Agency for International Development (USAID) promote apparel sourcing from Africa?
- From the video, how do you see the social and economic impact of the textile and apparel industry on Madagascar and Mauritius?
- Do we need African Growth and Opportunity Act (AGOA)? Why or why not?
- With regard to the status of the textile and apparel industry in Madagascar and Mauritius, anything shown in the video interests or surprises you?
China to Become the World’s Largest Apparel Market in 2019
According to forecast made by the Euromonitor, China will exceed the United States and become the world’s largest apparel market by 2019. Specifically, annual apparel sales in China will reach $333,312 million in 2019, an increase of 25% from $267,246 million in 2014. In comparison, apparel sales in the United States is estimated to reach $267,360 million in 2019, which is only 3% higher than $260,050 million in 2014.
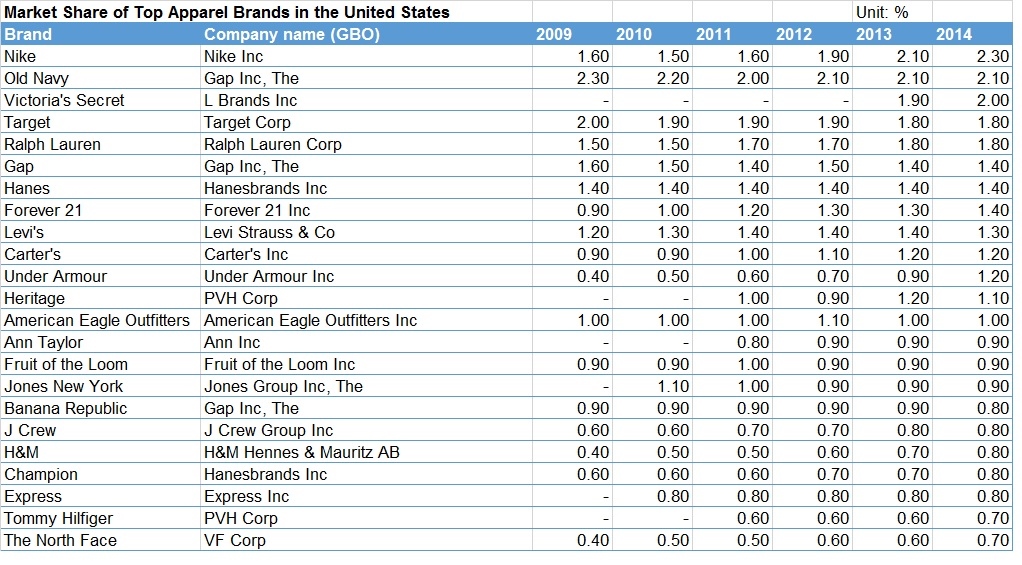
 However, it shall be noted that China seems to be an even more competitive apparel market than the United States. For example, no apparel brand was able to achieve a market share more than 1% in 2014 in China, whereas in the United States, market shares of several leading apparel brands exceeded 2%. Moreover, domestic brands overall outperform international brands in the Chinese apparel market.
However, it shall be noted that China seems to be an even more competitive apparel market than the United States. For example, no apparel brand was able to achieve a market share more than 1% in 2014 in China, whereas in the United States, market shares of several leading apparel brands exceeded 2%. Moreover, domestic brands overall outperform international brands in the Chinese apparel market.

 On the other hand, despite its overall market size, as a developing country, dollar spending on apparel per capita will remain much lower in China than many developed economies around the world. In 2014, each Chinese consumer on average spent $240 on apparel versus $815 in the United States, even though apparel spending accounted for a larger share in household income in China (around 10%) compared with the United States (less than 3%).
On the other hand, despite its overall market size, as a developing country, dollar spending on apparel per capita will remain much lower in China than many developed economies around the world. In 2014, each Chinese consumer on average spent $240 on apparel versus $815 in the United States, even though apparel spending accounted for a larger share in household income in China (around 10%) compared with the United States (less than 3%).
Several personal thoughts based on the data:
First, it is the time that U.S. apparel companies/fashion brands should start to seriously think about their sourcing strategy specifically for the Chinese market.
Second, for many Chinese apparel companies, serving the domestic market will help them more effectively achieve functional upgrading (i.e. shifting from low-value added manufacturing to higher-value added functions such as design, branding and distribution) than through exporting.
Third, controlling sourcing cost will be as important in China as in the United States. When China’s applied tariff rate is still as high as 9.63% for textiles and 16.05% for apparel (WTO, 2015), U.S. fashion companies/fashion brands may not have many options but to use “Made in China” to serve the Chinese consumers. In the long run, however, “Made in China” shall be gradually replaced by “Made in Asia”, especially when several free trade agreements (FTAs) involving China eventually take into effect (such as CEPA). However, China may strategically use rules of origin in these FTAs and encourage apparel manufacturers in the region to use Chinese made textile inputs (just like what U.S. did in NAFTA and CAFTA). Nevertheless, either for managing the apparel supply chain based on “Made in China” or “Made in Asia”, it doesn’t seem U.S. apparel companies/fashion brands will easily enjoy competitiveness over their Chinese competitors.
Data source: Euromonitor Passport(2015)
Does AGOA’s “third country fabric” provision discourage the development of Africa’s local textile industry?
 The following Q&A is adapted from the 2015 AGOA Forum Preview (15m:44s)
The following Q&A is adapted from the 2015 AGOA Forum Preview (15m:44s)
Question: What is the principal obstacle to the development of a local yarn industry in an apparel exporting country such as Kenya? Does AGOA’s “third country fabric” provision in place for 13 years act as a disincentive to such a development?
Florizelle Liser, Assistant US Trade Representative for Africa: That’s a really good question, but the answer is no. What we know is that African producers of apparel, like producers of apparel all around the world, need to have the flexibility to source their input from wherever of those can be produced most effectively, cost effectively for the products that they are sewing. So we want through the “third country fabric” provision to give the African producers of apparel that flexibility. We do know in terms of establishing textiles business on the ground producing those inputs right there in Africa and that more of that indeed is going to happen. The reason is that as U.S. buyers of apparel and this is an enormous market for apparel… as U.S. buyers of apparel source more of their apparel from Africa, then investors in textile mills, which are very expensive, will be incentivized and are being incentivized to actually establish those fabric mills right there in Africa, and then be able to save time, in terms of getting those inputs that are needed for the clothing that is being produced. So we see that happening already: it’s happening in Kenya, it’s happening in Ethiopia and around the continent. And that is what we need to have more of as we go forward in this ten-year extension of AGOA.
What do you think?
Is Wal-Mart’s $250 billion “Made in the USA” Program Another “Crafted with Pride Campaign”? (II)
In early 2014, Wal-Mart Store Inc. announced its commitment to buy $250 billion “Made in the USA” products (including textiles and apparel) over the next 10 years ($50 billion annually) with the hope to “help spark a revitalization of U.S.-based manufacturing” and “create jobs in America”.
So how is the program going so far, especially in the textile and apparel (T&A) area?
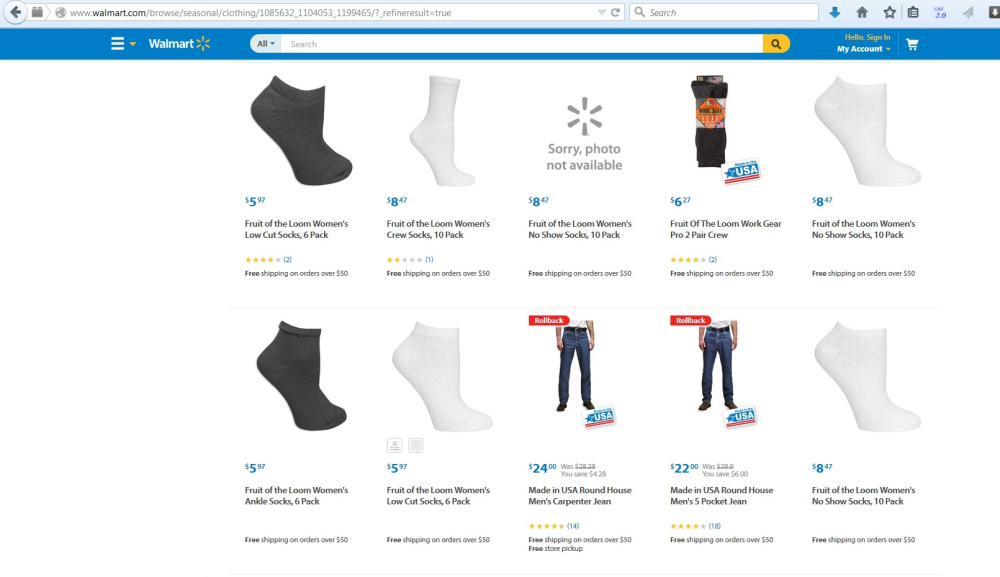
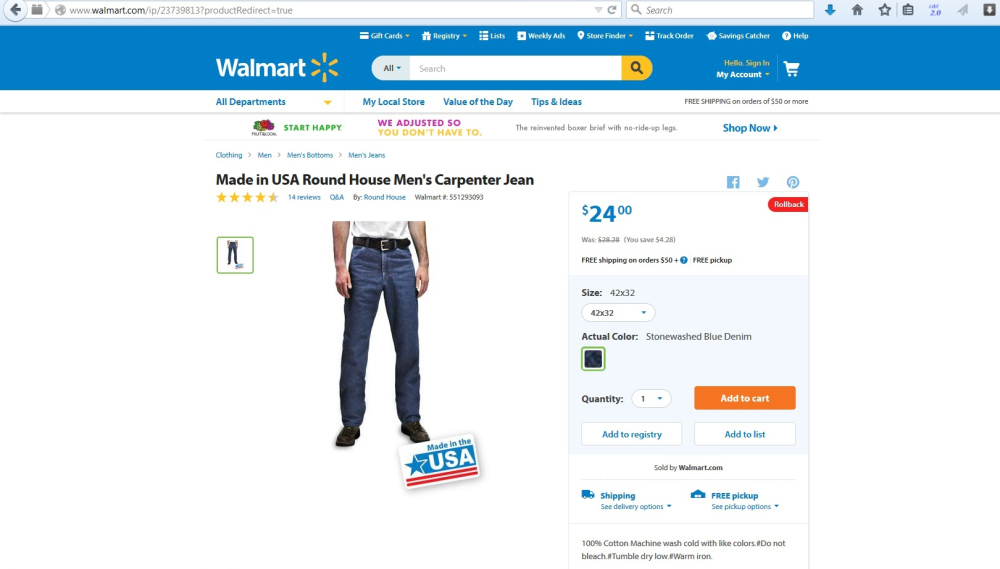
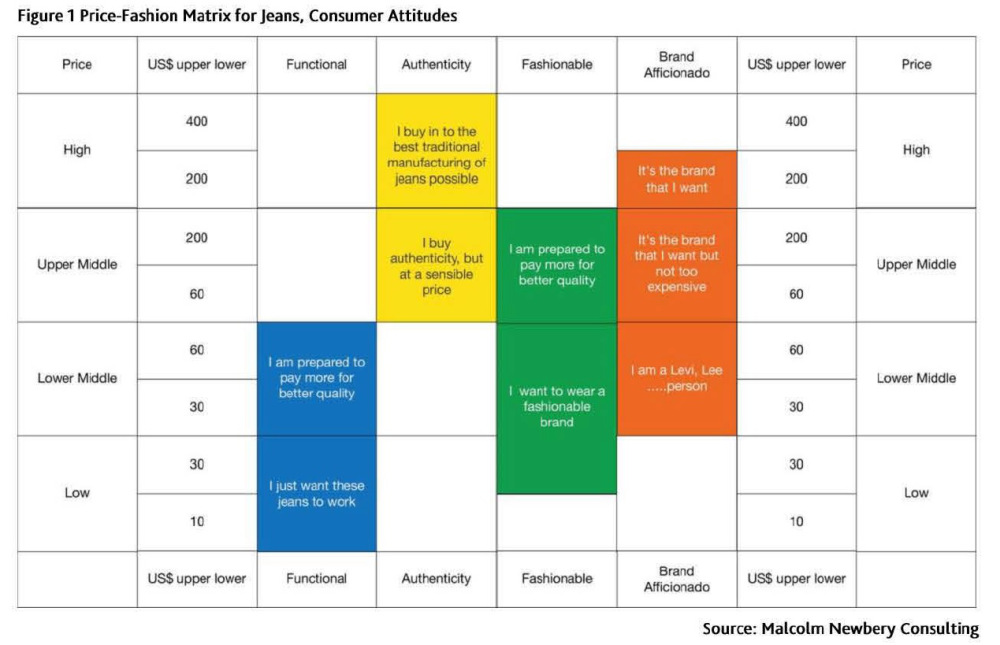
From exploring the company’s website, it is interesting to find that around 30 kinds of “Made in USA” T&A currently are being sold at Wal-Mart. However, majority of these T&A products are basic socks priced less than $10/unit. Wal-Mart also sells two types of men’s jeans, priced at $24/pair and $22/pair respectively. Although such a price level is higher than most jeans sold at Wal-Mart (which range from $8 to $20 per unit on average), it is still at the low-end of the market (see the chart below adopted from a Just Style report on the global jeans market).
On the other hand, as part of the “Made in USA” program, Wal-Mart sponsors a U.S. Manufacturing Innovation Fund with the purpose of “making it both easier and more competitive to make household goods in the U.S.”. T&A is one area this fund is willing to support as long as the research projects could “reduce the cost of producing textiles and apparel in the U.S., including weaving, fabric dyeing, cut & sew.
So what’s your view on Wal-Mart’s “Made in USA” initiative in the 21st century? How is it different from the “Crafted with Pride Campaign”? Will it bring back manufacturing jobs in the US as its objective stated? Will Wal-Mart repeat its record in history again? Please feel free to share your view.
[Please do not leave comment until after our case study 4]
Additional reading: Is Wal-Mart’s $250 billion “Made in the USA” Program Another “Crafted with Pride Campaign”? (I)