About Karin De León
Karin De León has been working in the textile and apparel sector in Guatemala for more than 25 years, promoting the development of the industrial cluster, participating in the creation of strategies, supporting the strengthening of the supply chain, and attracting investment.
As part of her role at the Apparel and Textile Association of Guatemala (VESTEX), for 10 years she held the position of Executive Director of CECATEC-RD (Central American and Dominican Council of Clothing and Textiles), the entity that integrates textile & apparel industry associations of Central America and the Dominican Republic and which is responsible for coordinating the inter-institutional relationship with public and private entities of the United States of America, Mexico and Colombia mainly.
From 2020 to the beginning of 2022, she served as Chief of Staff of the Ministry of Economy of Guatemala and later became General Coordinator of the National Competitiveness Program (PRONACOM), a government entity responsible for promoting the country and attracting investment.
Karin is currently VESTEX’s investment and promotion director, and representative of Guatemala in CECATEC-RD. She coordinates the inter-institutional relationship with government entities of the United States (such as the United States Trade Representative and the Department of Commerce) as well as private institutions mainly related to the United States, Mexico, and Colombia.
Sheng: Can you provide a brief introduction to VESTEX and a general overview of your member companies?
Karin: VESTEX is the Apparel and Textile Association of Guatemala, a private association representing the Guatemalan textile and apparel export sector. It focuses on promoting the industry’s exports through strategic alliances with public and private institutions at the national and international levels. Its strategic axes are Sectoral Resilience, which seeks to position the industry as a generator of investment and formal employment in the country; Sectoral Sustainability, through the promotion of sustainability as a long-term strategy for industry continuity and compliance, providing companies in the sector with tools that facilitate compliance with the obligations established in the laws and regulations.
VESTEX partners comprise companies that integrate the entire supply chain of the apparel and textile sector, encompassing yarn and fabric manufacturers, apparel producers, as well as firms providing specialized services and accessories to the industry.
Sheng: Studies show that there is consistent interest among U.S. fashion companies in expanding nearshoring from the Western Hemisphere, including Guatemala. What is your observation? What makes Guatemala an attractive destination for apparel sourcing today? What are the unique advantages of sourcing from the country?
Karin:Guatemala has become an increasingly attractive destination for apparel sourcing due to its unique combination of industrial integration, geographic advantages, and strong compliance standards. The country offers a highly integrated apparel cluster that encompasses every stage of the supply chain—from spinning yarn and weaving fabrics to apparel manufacturing, printing, finishing, and packaging. This full-package model not only streamlines operations and enhances traceability but also allows for greater flexibility and product diversity, raising the added value of garments and positioning Guatemala as a competitive supplier for niche and complex products requiring skilled labor and high-quality materials.
Another key differentiator is Guatemala’s strategic location. With access to ports on both the Atlantic and Pacific coasts—separated by only 249 miles—the country can efficiently serve both the East and West coasts of the United States. Guatemala manages the second-largest maritime cargo operation in Central America (after Panama), which is critical for companies seeking to balance and mitigate geopolitical and logistical risks. In addition, proximity to the U.S. substantially reduces environmental impact: sourcing from Guatemala lowers CO₂ emissions from maritime transport by approximately 84% compared to sourcing from Asia. Transit times are also highly competitive, with shipments reaching Miami in as little as three days, enabling U.S. buyers to manage inventories more effectively and respond to market demands with agility.
Equally important, Guatemalan apparel companies operate under a strong framework of labor and environmental compliance. Companies demonstrate a full-spectrum commitment to input traceability, adherence to strict rules of origin, and continuous process improvement to reduce resource consumption. Investments in monitoring and ESG systems underscore their transparency and alignment with global sustainability standards.
Taken together, this integration of cluster capabilities, geographic proximity, and compliance with international norms positions Guatemala as a reliable, sustainable, and strategically advantageous sourcing partner for U.S. fashion companies.
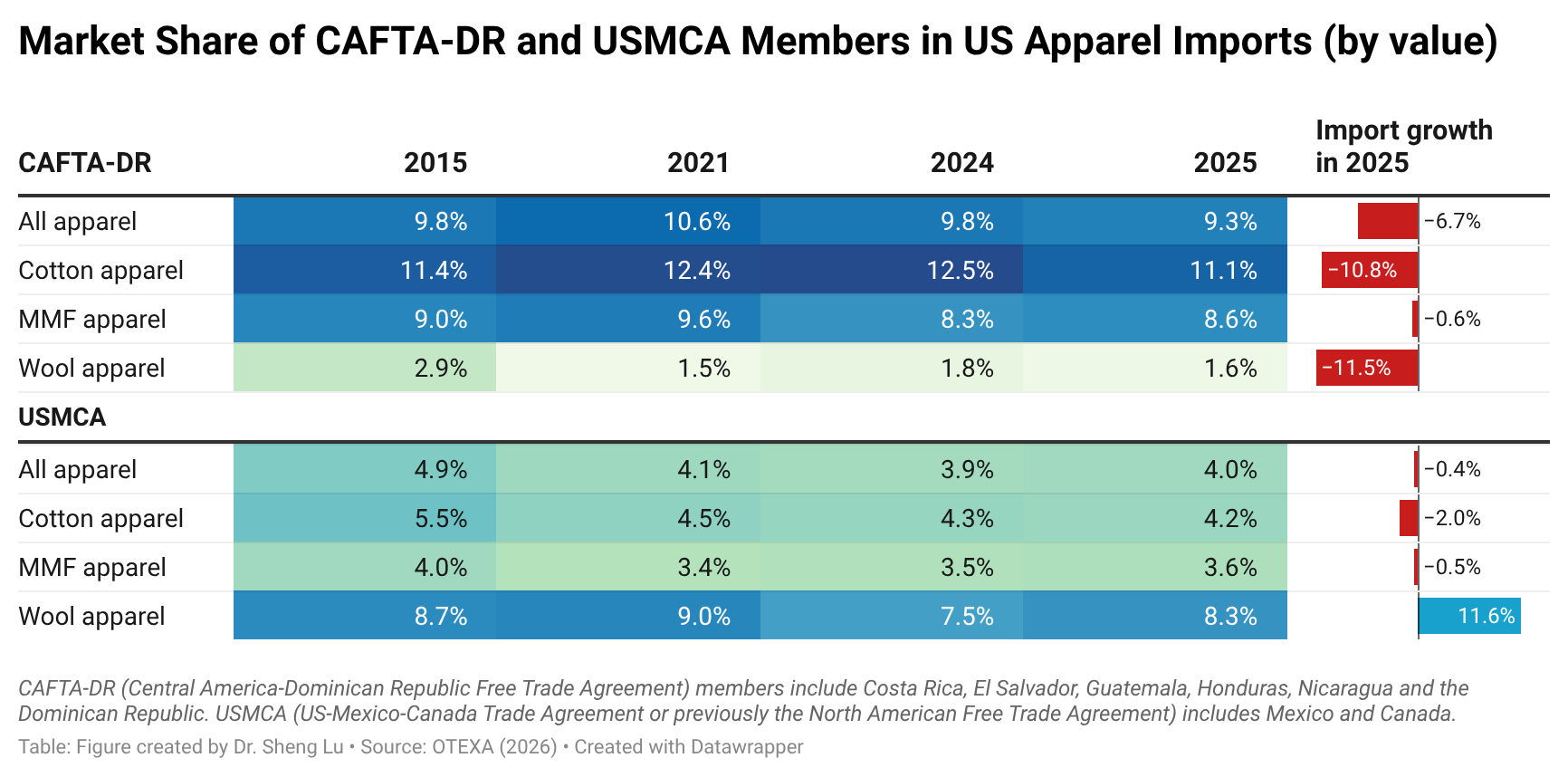
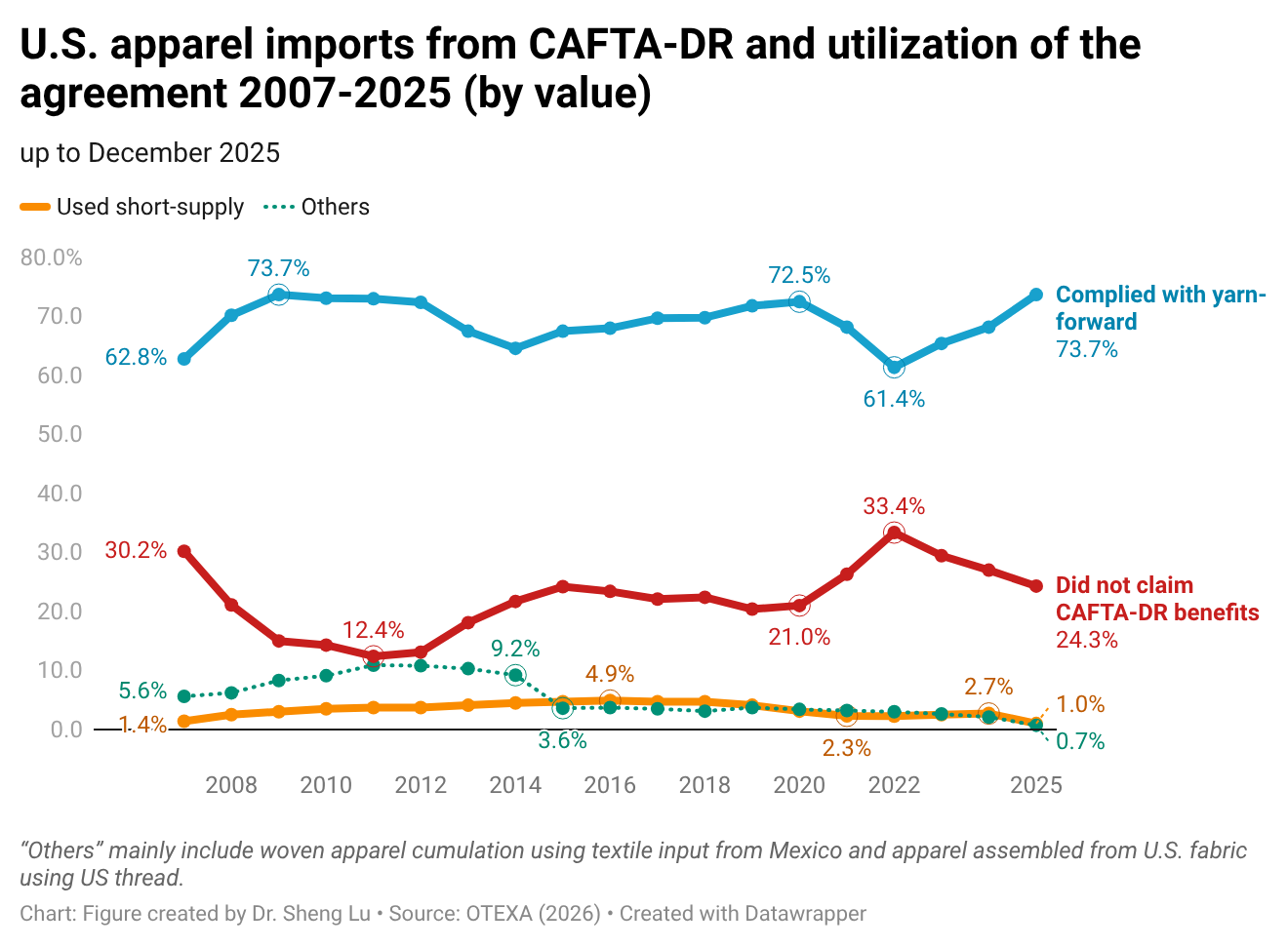
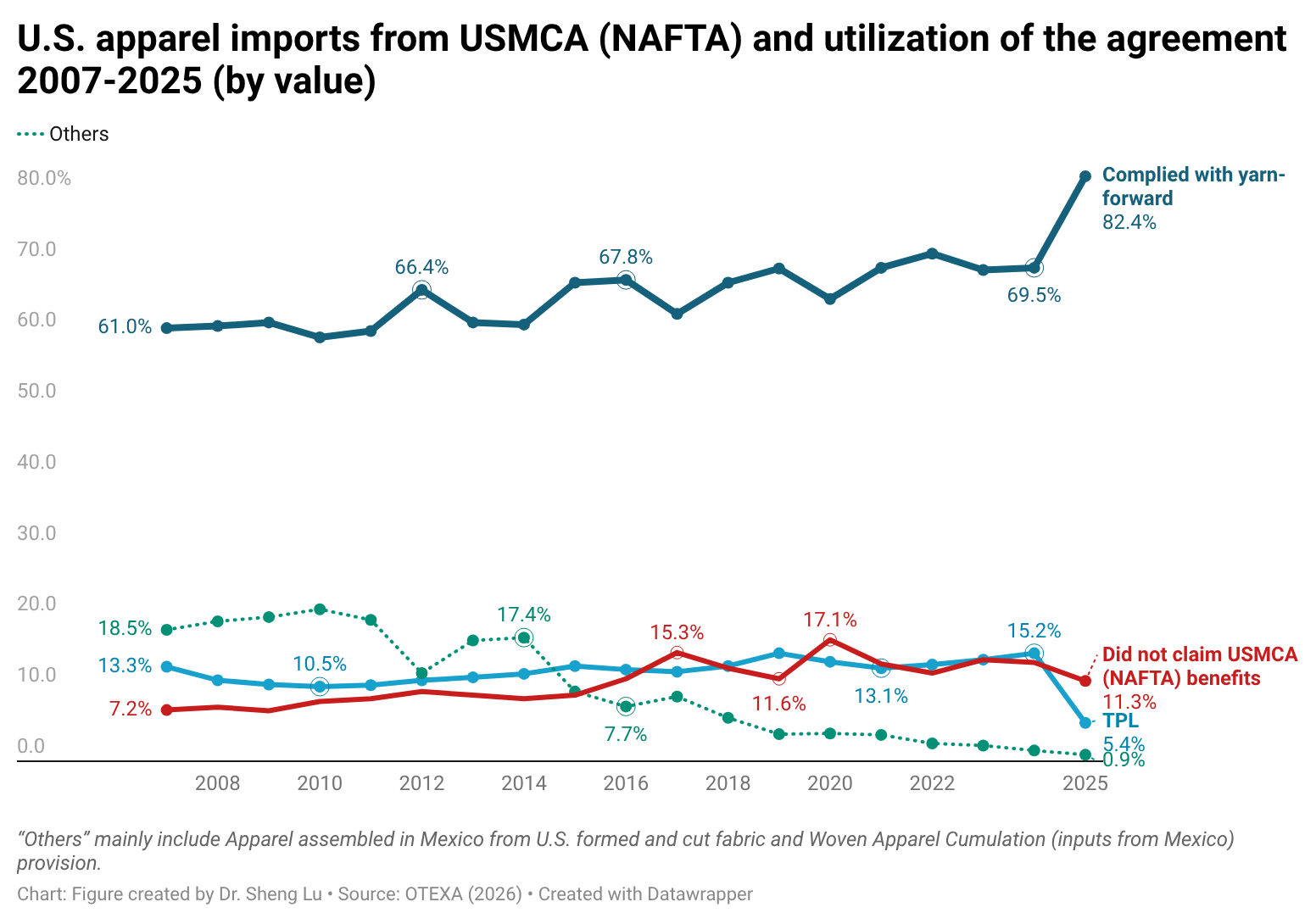
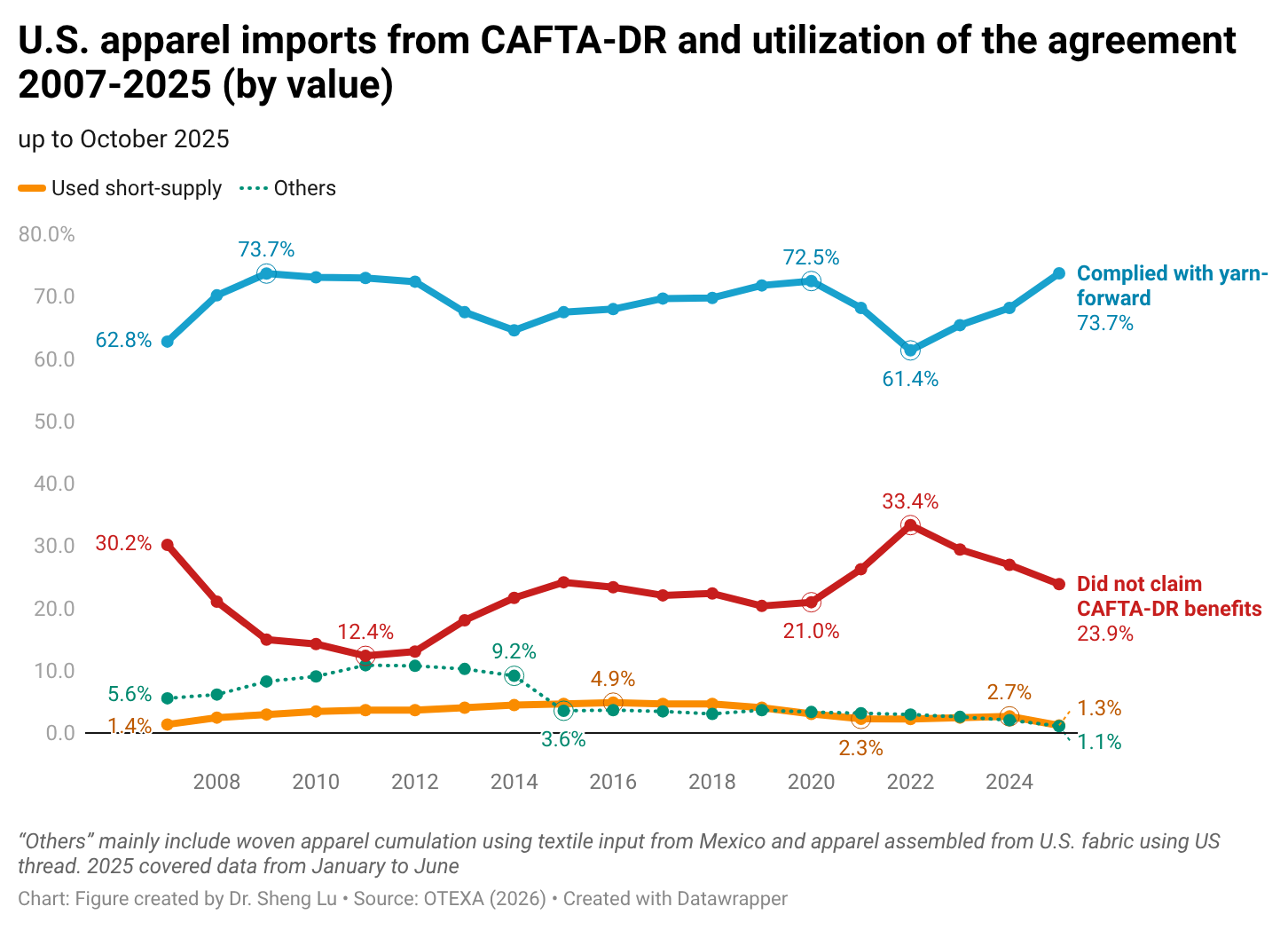
Sheng: How important is the Dominican Republic-Central America Free Trade Agreement (CAFTA-DR) in supporting Guatemala’s apparel exports to the U.S. market? What impact do CAFTA-DR’s apparel-specific rules of origin have on garment exporters’ supply chains and export strategies in Guatemala?
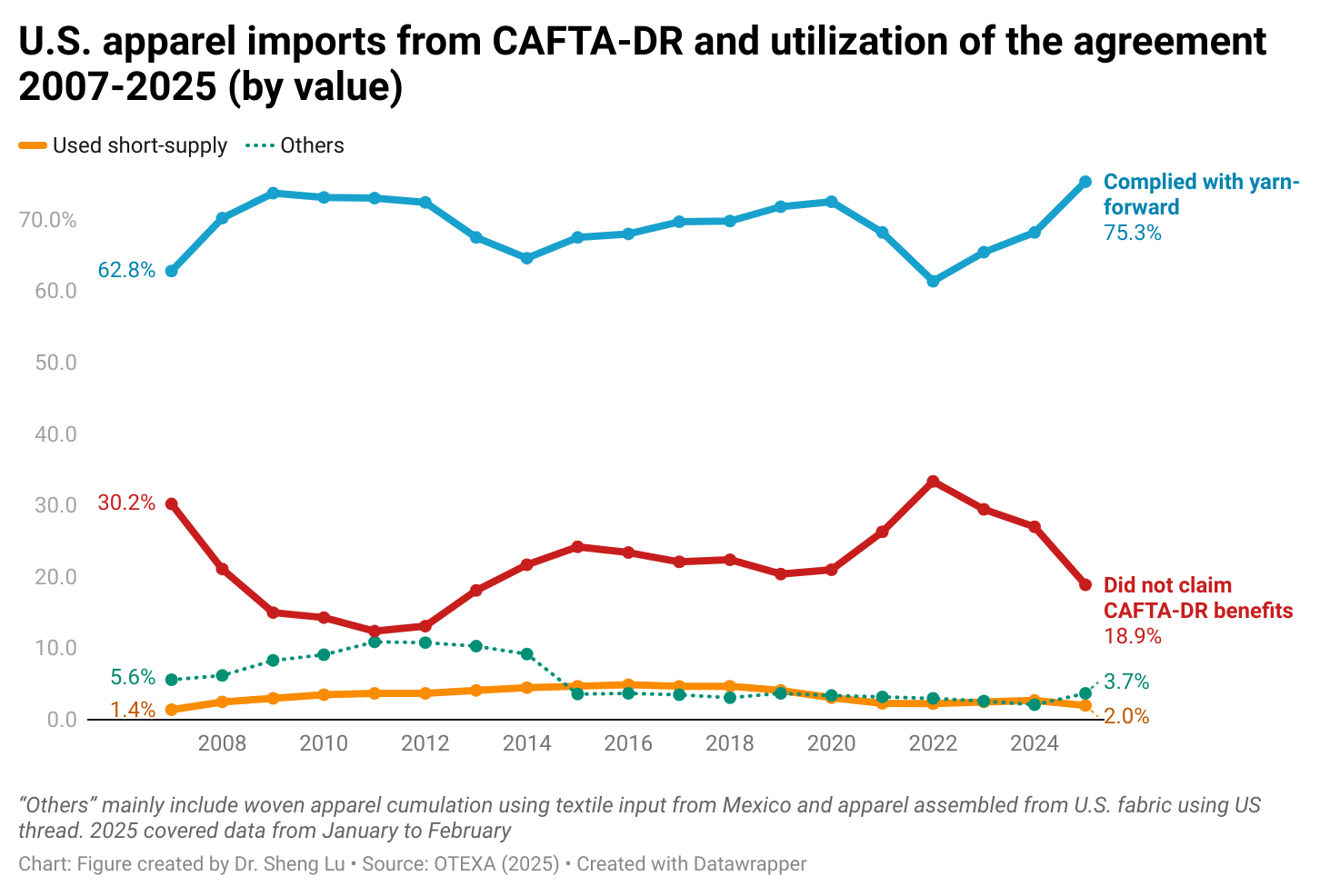
Karin:CAFTA-DR has provided certainty by encouraging long-term investments in textile infrastructure and capabilities. CAFTA-DR has been the basis for the development of Guatemala’s apparel industry. The yarn-forward rule established under the agreement has not only fostered integration with the U.S. supply chain but also promoted stronger collaboration among Central American countries. By allowing the accumulation of inputs and processes within the region, CAFTA-DR has significantly strengthened intraregional trade.
This integration has facilitated the specialization of each Central American country. In Guatemala’s case, it has enabled the use of specific yarns and fabrics produced in other countries and manufactured locally, fostering a greater diversification of production.
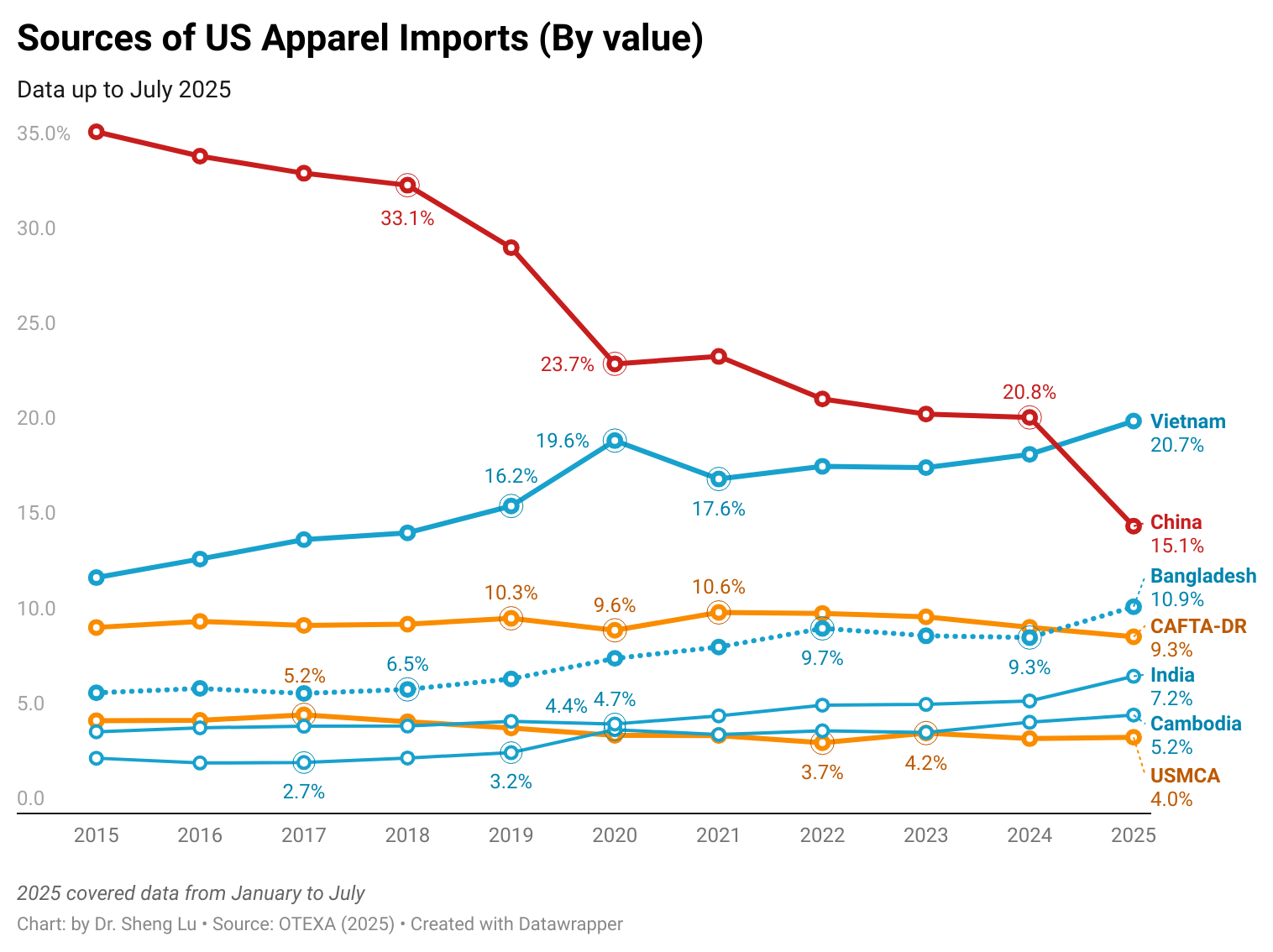
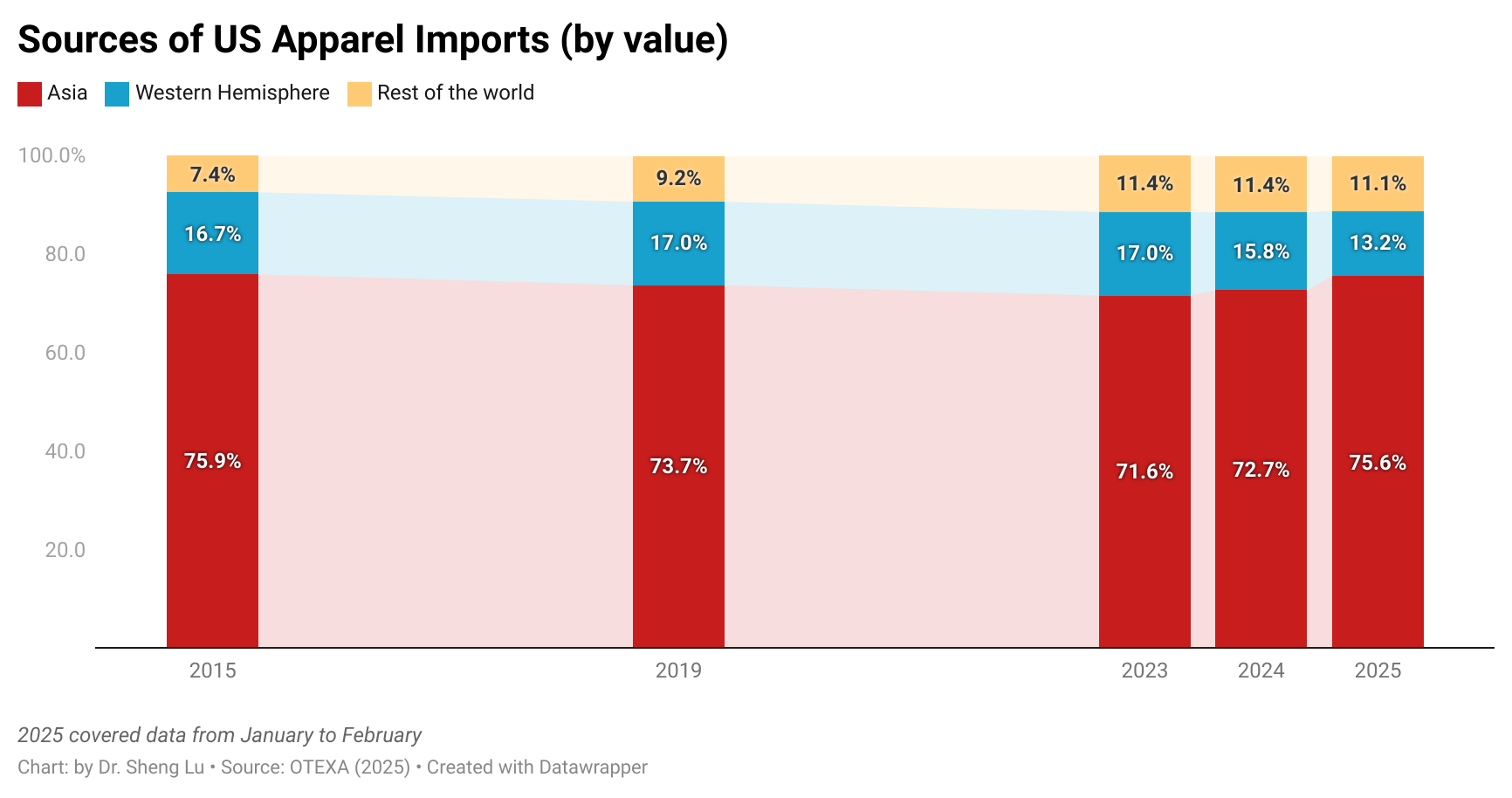
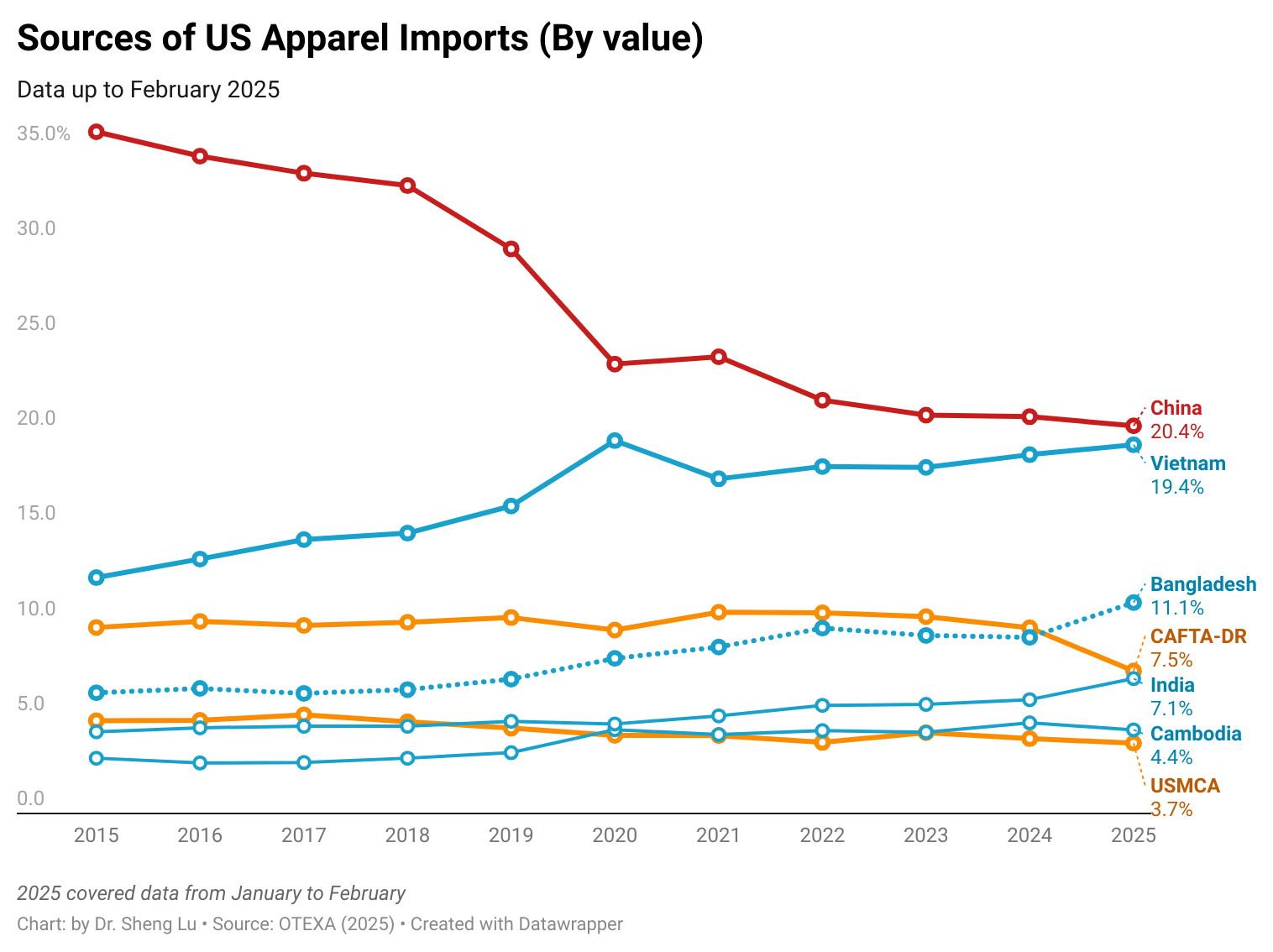
According to OTEXA figures, in the year ending June 2025, 89.17% of Guatemala’s total apparel exports to the U.S. entered under the Free Trade Agreement preferences. Of this total, 79.69% qualified under the yarn-forward rule—that is, garments made with yarn from the U.S. or yarn produced within one of the Central American countries. CAFTA-DR, and particularly its rules of origin, have been the basis of Guatemala’s strategy in recent years, not only to attract foreign direct investment but also to encourage significant reinvestments.
Sheng: Data shows that an increasing share of yarns and fabrics used by Guatemala garment factories are now locally made in Guatemala and other Central American countries. Could you discuss the recent trends in textile manufacturing capacity building in Guatemala, as well as the industry’s current priorities in building a more vertically integrated regional supply chain?
Karin:Guatemala offers a series of competitive advantages that are reinforcing its role as a regional hub for textile and apparel manufacturing. At the country level, it benefits from a stable macroeconomy, a solid exchange rate, competitive electricity prices within the region, and a reliable energy supply. At the industry level, Guatemala stands out for its robust apparel and textile cluster and highly skilled workforce.
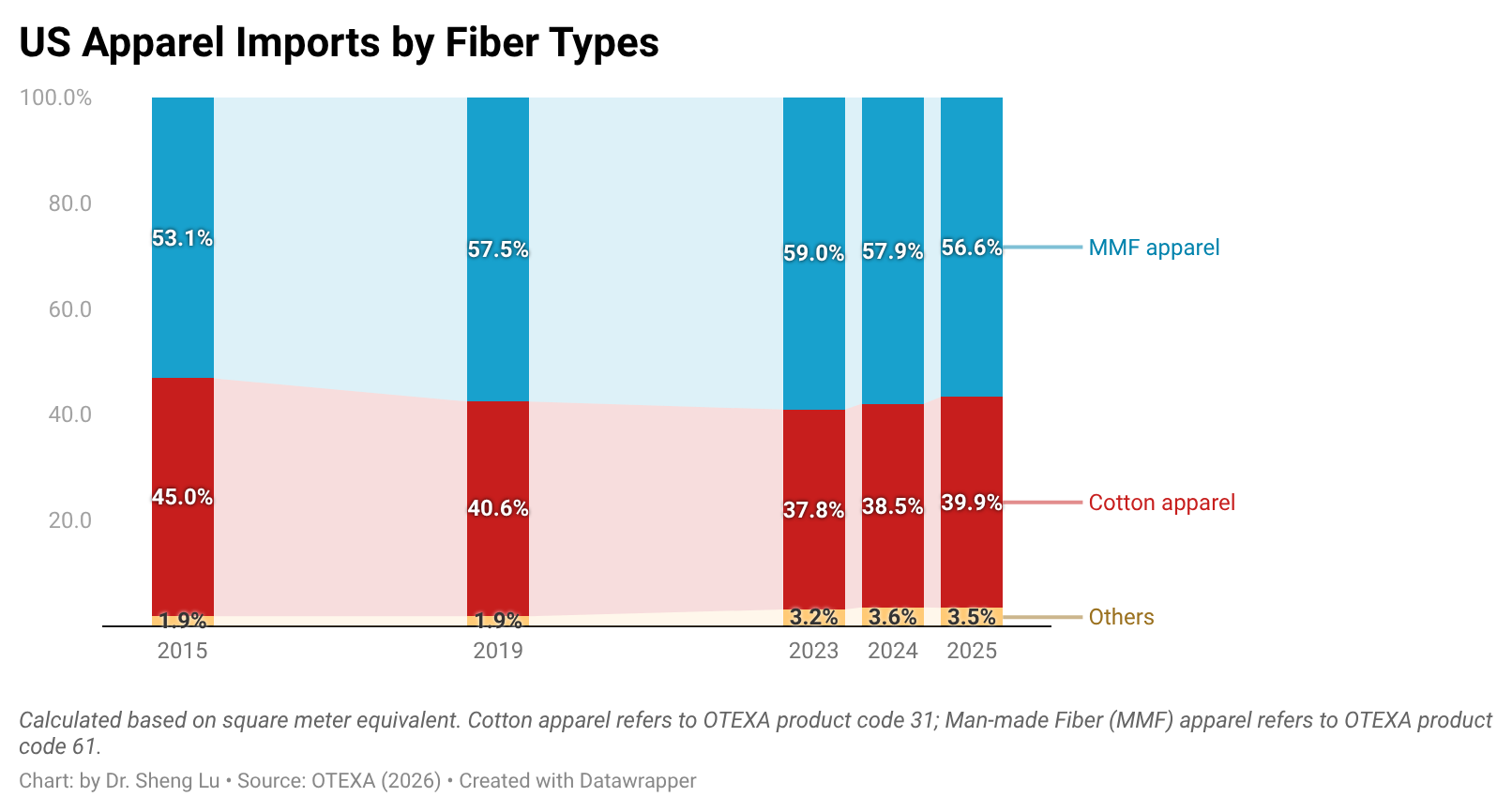
Since the pandemic in 2020, when many global companies accelerated nearshoring strategies, Guatemala has successfully attracted new foreign investment and supported the expansion of companies already established in the country, particularly in the spinning industry. Installed capacity is primarily focused on cotton, although blends are also produced. By the end of 2024, apparel exported to the U.S. consisted of 62.8% cotton, 36.4% synthetics, and 0.8% wool, reflecting the central role of cotton in the country’s production while also showing diversification into other fibers.
Driven by shifting market demand, textile production in Guatemala has been expanding beyond knits, with a modest increase in woven fabrics as well. Investments in innovation and technology have enabled the industry to offer specialized processes, including antimicrobial treatments, absorption, UPF protection, enzymatic washing, softening, and plush finishing, among others. A particularly important advancement has been the investment in elastic knit fabrics, which has opened the door to the production of categories such as sportswear, intimate apparel (seamless), shapewear (technical lingerie and compression fabrics), and medical textiles.
We recognize, however, that there remain challenges and opportunities to broaden the regional textile offering—particularly in the production of yarns and fabrics made from fibers not yet manufactured locally. Expanding capacity in these areas would further strengthen vertical integration and supply chain resilience.
In this context, VESTEX has taken a leading role in supporting and guiding companies interested in exploring these opportunities. In coordination with Guatemala’s foreign direct investment promotion agency, efforts are underway to identify high-demand inputs that are currently unavailable in the region but represent strategic opportunities for local production.
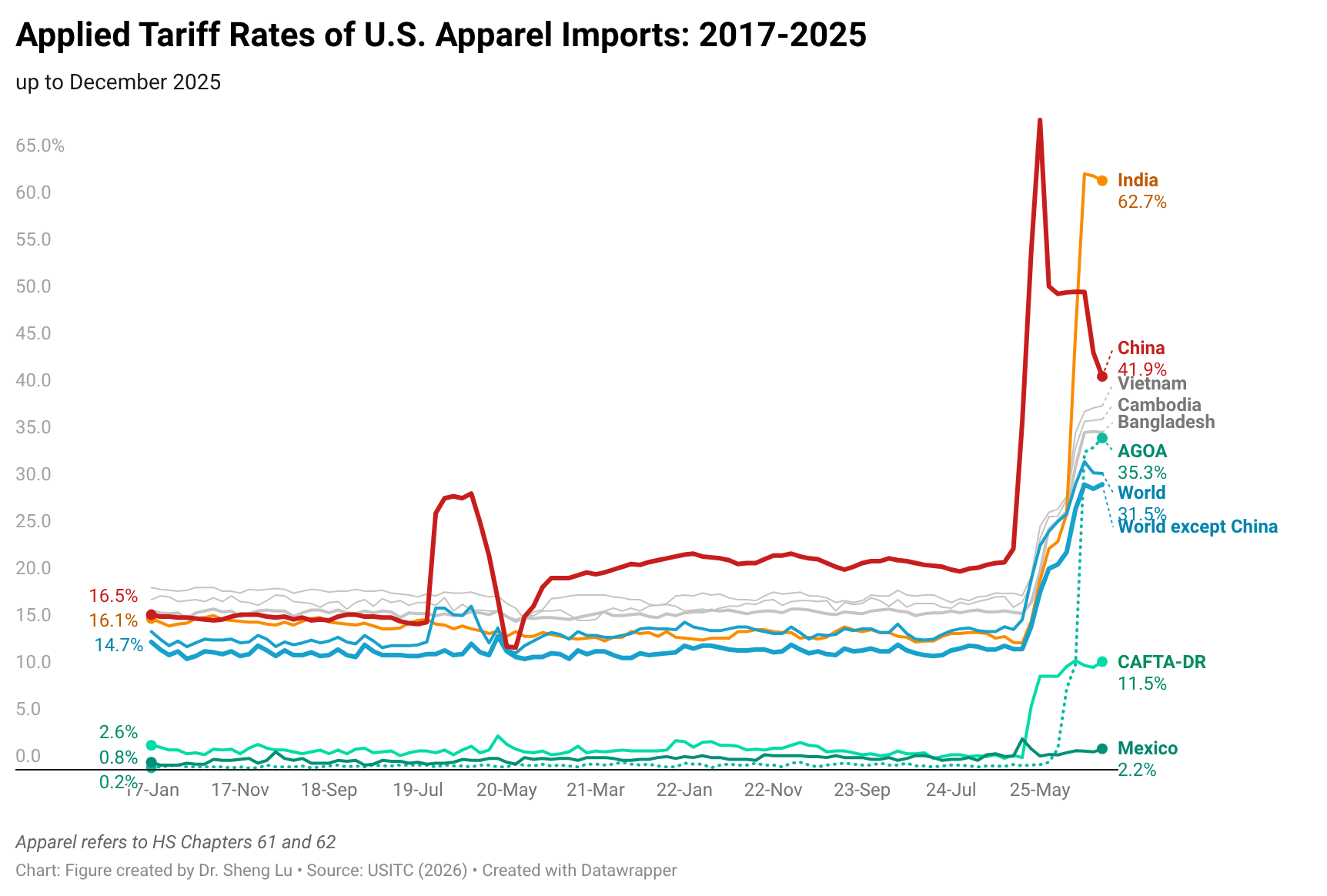
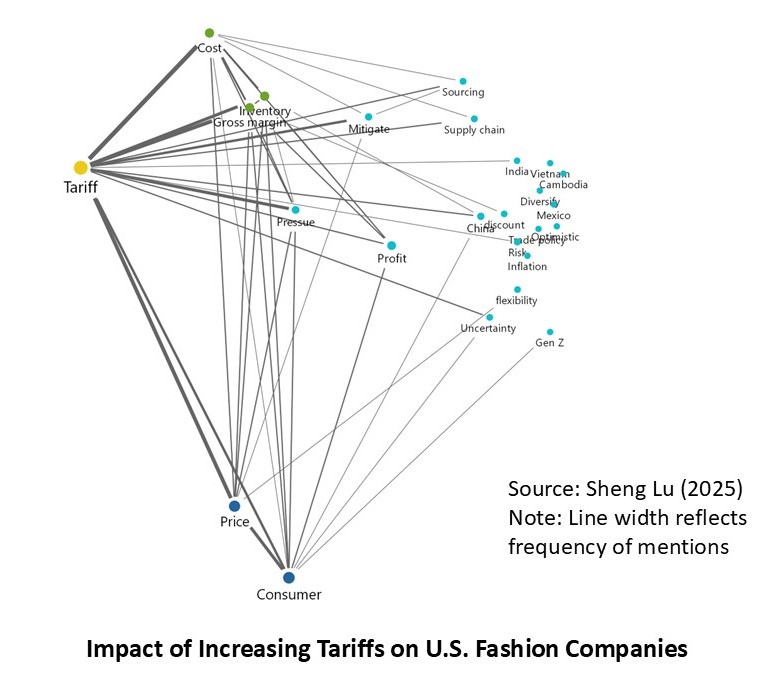
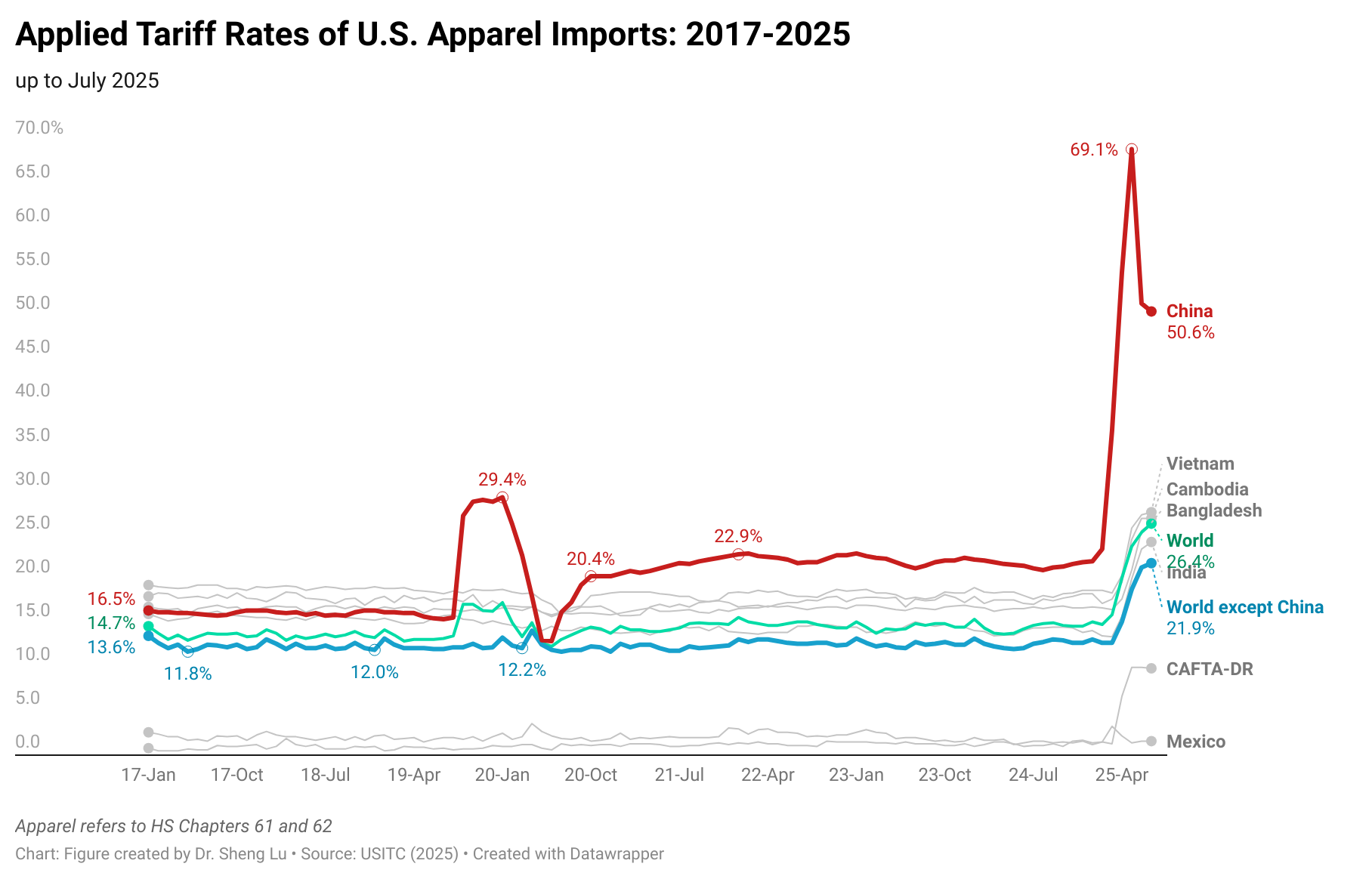
Sheng: Since April 2025, U.S. apparel imports from CAFTA-DR countries, including Guatemala, are subject to a new 10% “reciprocal tariff.” How has this tariff increase and the Trump administration’s trade policy so far impacted Guatemala’s garment industry and exports?
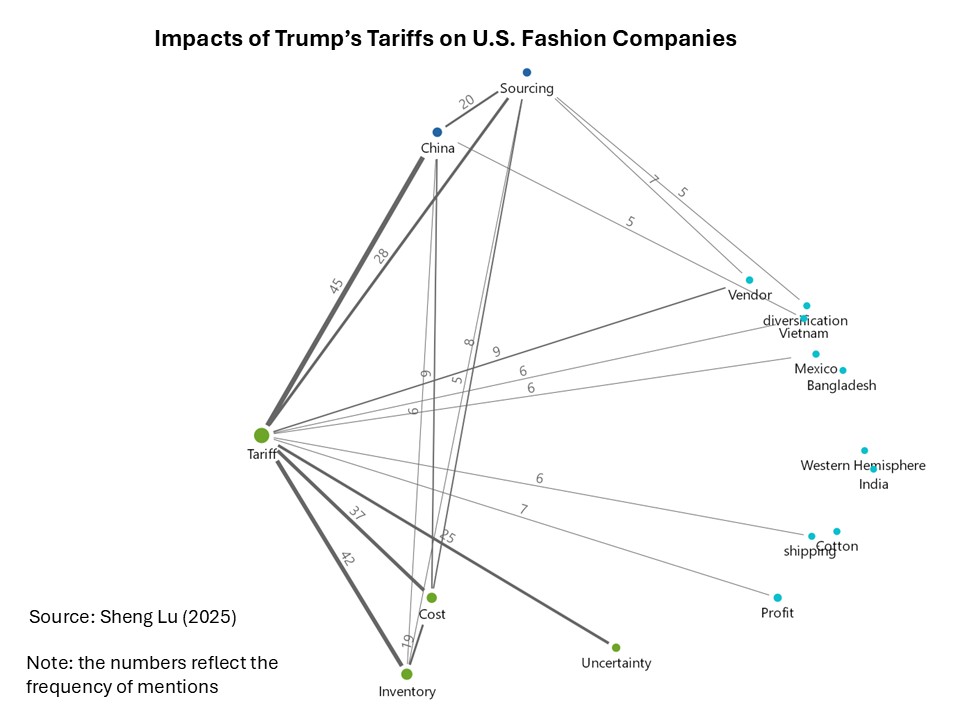
Karin:The main challenge for Guatemala’s apparel industry under the current U.S. trade policy has been the high degree of uncertainty. Markets and buyers demand stability, yet in recent months orders have slowed significantly as companies await clarity on the tariffs that will ultimately apply to each country. This hesitation has already resulted in lost opportunities: seasonal orders cannot be recovered once the selling window has passed.
Traditionally, Guatemala’s apparel sector grows between 3% and 5% annually; however, 2025 projections have been revised downward, and current expectations suggest growth closer to 1–2%. According to the Central Bank of Guatemala, as of June 2025, exports registered a modest 1.36% increase—well below what was anticipated under normal conditions.
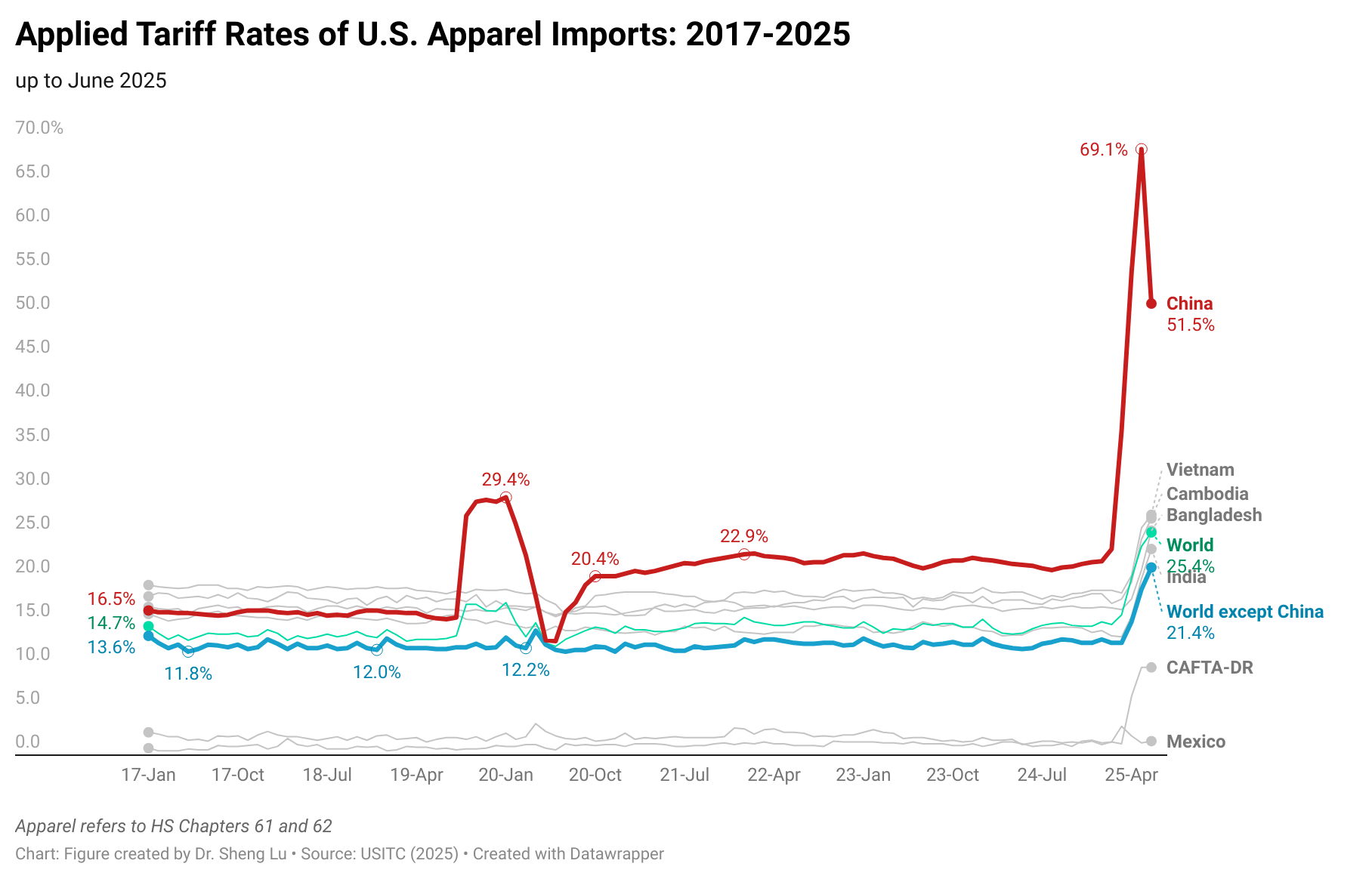
Another major impact has been the need for companies to absorb additional costs to maintain contracts with international brands. This has reduced profit margins, limited reinvestment capacity, and increased pressure on already tight production cycles. Buyers face uncertainty as well: they do not know how much a garment ordered today will cost by the time it is delivered six to nine months later, since tariff rates are subject to abrupt changes. The volatility recalls past episodes in China, where tariffs under former President Trump rose as high as 145% before being reduced to 30%, creating unpredictable supply conditions.
That said, Guatemala continues to hold a relative tariff advantage compared with Asian competitors, where rates now reach 15%, 18%, 25%, or even higher. This gap may ultimately favor Guatemala if U.S. buyers reconfigure sourcing strategies to prioritize suppliers who are both geographically closer and more reliable. Indeed, global sourcing is shifting away from a purely low-cost model toward one that values resilience, speed to market, and compliance.
Sheng: The 2025 US Fashion Industry Association Benchmarking Study indicates that U.S. fashion companies are increasingly seeking sourcing destinations that can provide sustainable apparel products, including those made with preferred fibers such as organic, recycled, regenerative, and biodegradable materials. What strategies or recent initiatives has the Guatemalan textile and apparel industry undertaken to meet this demand for sustainability?
Karin: Guatemalan mills already source recycled polyester yarns, organic or regenerative cotton, and biodegradable materials. Brands are actively demanding these products. In fact, mills have obtained various certifications and adhere to practices focused on circular economy, science-based target initiatives, and other sustainability standards.
Traceability is key for the textile and apparel industry, and Guatemala has managed to implement measures such as data management and continuous improvement as a way to demonstrate this.
- Adoption of Sustainable Certifications and Standards: Guatemalan manufacturers are obtaining certifications like GOTS (Global Organic Textile Standard), OEKO-TEX, Global Recycled Standard, Recycled Claim Standard, Blue Sign, Higg FEM, among others, ensuring their products meet international sustainability standards.
- Investment in Technologies: Many mills are upgrading to water and energy-efficient machinery, as well as more sustainable dyeing and finishing processes.
- Training and Capacity Building: Initiatives to train and certify workers and management on sustainable practices and standards are increasing, promoting a culture of sustainability throughout the industry.
- Integration of Circular Economy Principles: Some mills are exploring design for recyclability techniques to align with circular economy goals.
These initiatives collectively position the Guatemalan textile and apparel sector as a viable sourcing destination for sustainable fashion, aligning with global market trends and buyer preferences for more sustainable products.
Sheng: In addition to the questions discussed earlier, what are the top business and policy issues facing Guatemala’s textile and apparel industry over the next 1–2 years?
Karin:Over the next 1–2 years, Guatemala’s textile and apparel industry will face several pressing business and policy issues that will shape its competitiveness.
1. Infrastructure and logistics.
A key issue remains the need to strengthen national infrastructure, particularly ports, customs processes, and internal transport routes.
2. Limited availability of regional inputs.
The industry continues to face constraints in the local production of certain yarns, fabrics, and specialized fibers. Inputs such as viscose, spandex, and rayon are not yet manufactured in the region at scale, which limits vertical integration and forces reliance on imports from outside the hemisphere. Expanding textile capacity in these areas is a central issue to ensure resilience and broaden the exportable supply.
3. Market visibility and buyer perception.
Despite its high level of integration, many international buyers remain unaware of Guatemala’s strengths in complex products, compliance, and sustainability. A persistent challenge is to raise global awareness of the country’s capabilities in order to capture greater sourcing opportunities.
4. Policy uncertainty and trade volatility.
The recent 10% reciprocal tariff applied to CAFTA-DR countries has introduced significant uncertainty. Buyers hesitate to place long-term orders when tariff levels are unclear, and this volatility affects sourcing decisions. Stability and predictability in trade policy remain critical issues for the sector.
5. Differentiation and specialization under nearshoring.
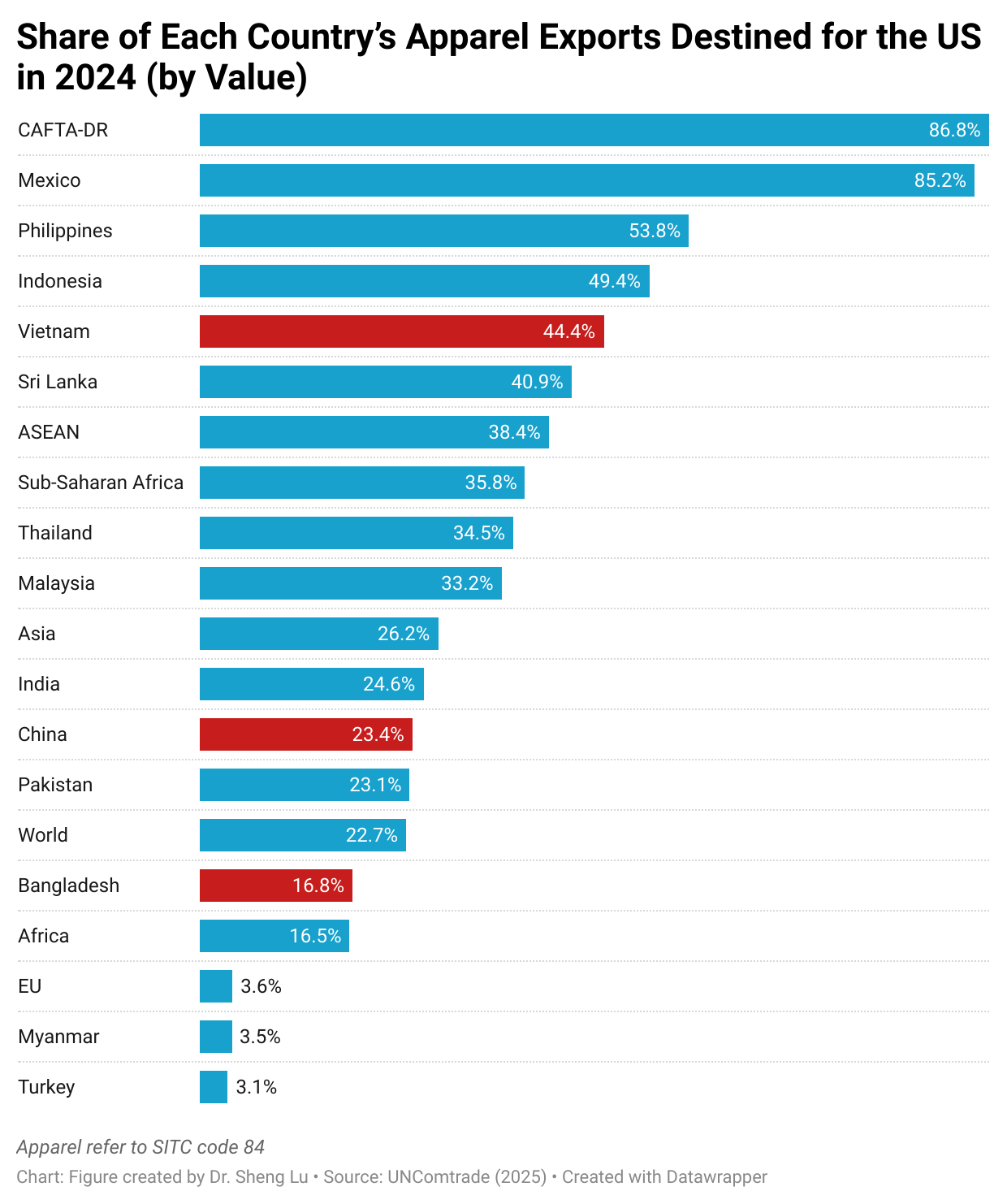
Another key challenge is sustaining competitiveness through higher-value products. Today, 54.11% of Guatemala’s apparel exports already include advanced finishing processes, and the industry is investing in spinning, woven fabrics, and technical textiles. However, scaling these capabilities requires reinvestment and foreign capital inflows—both of which are being constrained by global uncertainty. Given that Guatemala currently supplies only about 2% of U.S. apparel imports, a major issue ahead is how to convert this untapped potential into tangible growth.
In short, while the country is positioning itself strategically with competitive tariffs, geographic proximity, and an increasingly sophisticated textile base, the top issues over the next two years will be overcoming infrastructure and logistics bottlenecks, reducing dependence on imported inputs, strengthening promotion to buyers, and navigating trade policy volatility. Addressing these challenges will be crucial for Guatemala to capitalize on long-term opportunities in the ongoing global supply chain reconfiguration.
-The End-