(Photo above: Julia Hughes presented at the 25th Annual Textile and Apparel Importer Conference. Courtesy of the United States Fashion Industry Association)
Julia K. Hughes is the President of the United States Fashion Industry Association (USFIA). USFIA represents all segments of the fashion industry, from apparel brands to retailers to service companies. Ms. Hughes represents the interests of textile and apparel importers on trade policy issues to government officials, both in the United States and overseas. She has testified before Congress and the Executive Branch on textile trade issues. Ms. Hughes is also recognized as an expert in textile and apparel issues and is a frequent speaker at international conferences including the Apparel Sourcing Show, MAGIC, Foreign Service Institute, National Association of Manufacturers, Cotton Sourcing Summit, USIA’s Worldnet, the International Textiles and Clothing Bureau, Young Presidents’ Organization, World Trade Organization Beijing International Forum and others.
Julia Hughes is also well known to students enrolled in TMD433. She is featured in the book Travels of a T-shirt in the Global Economy, which highlights the global nature of the textile and apparel industry in the 21st century and those complicated economic, social and political factors associated with this important sector.
Interview Part
Sheng Lu: Would you please briefly introduce the current status of the U.S. fashion industry which your organization represents? For example, how large is the industry, how important is it to the US and the global economy, and what types of companies are involved as well as their business functions?
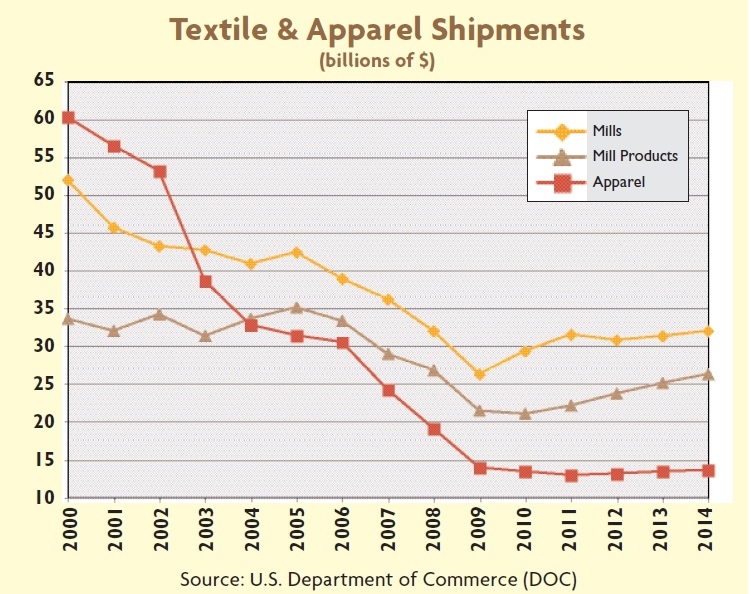
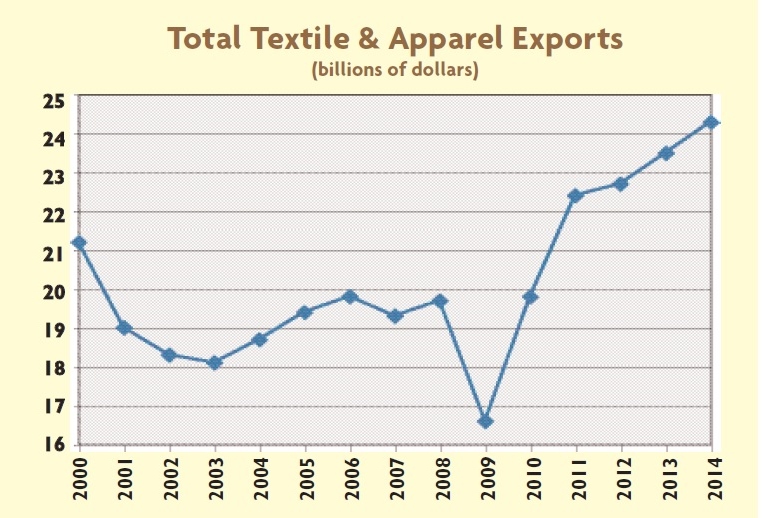
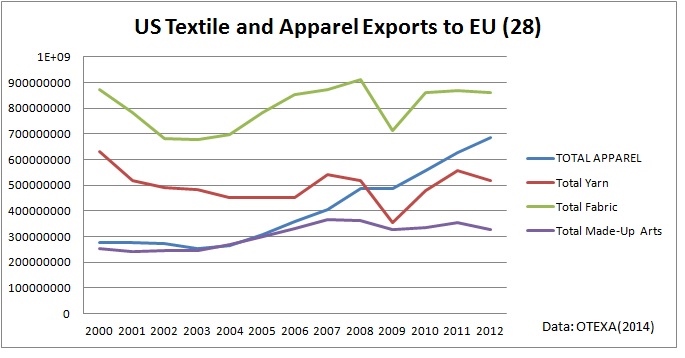
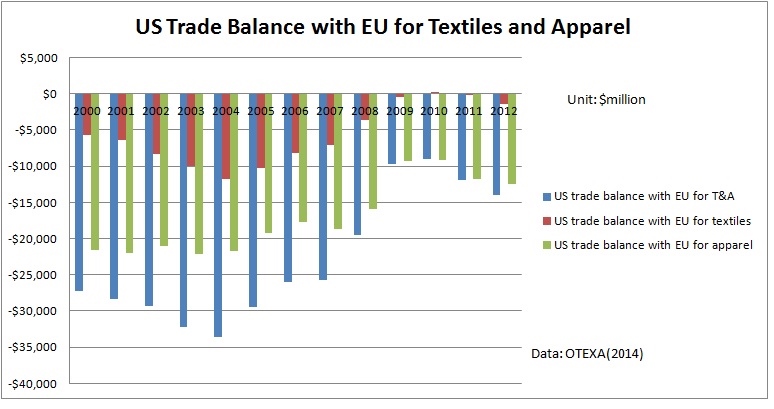
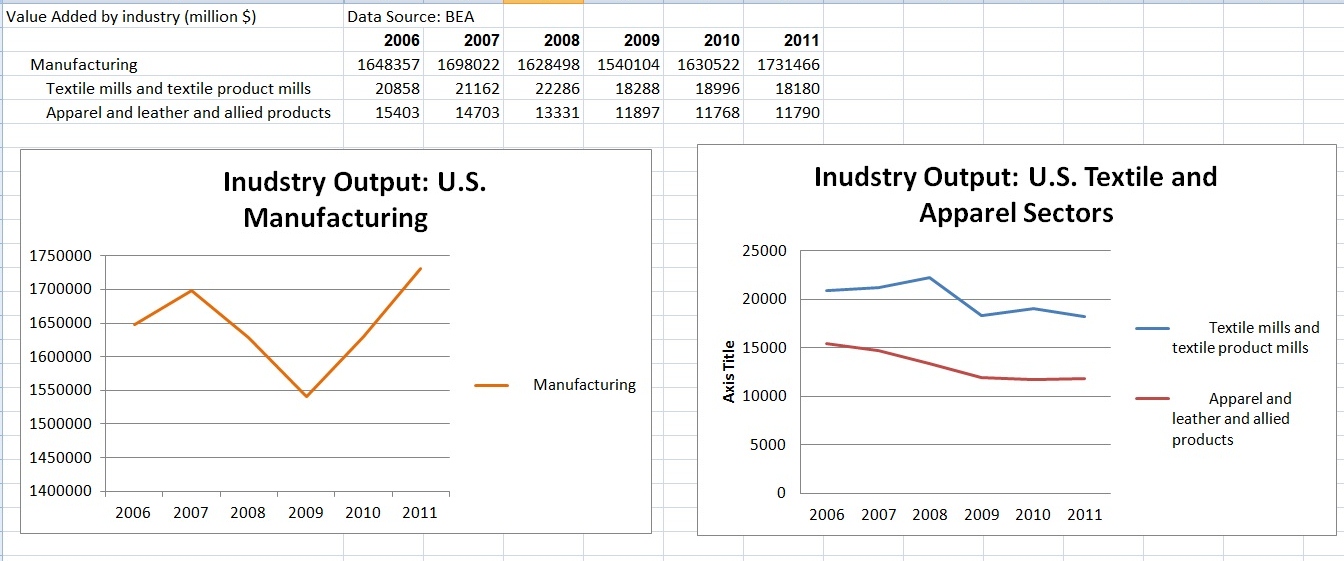
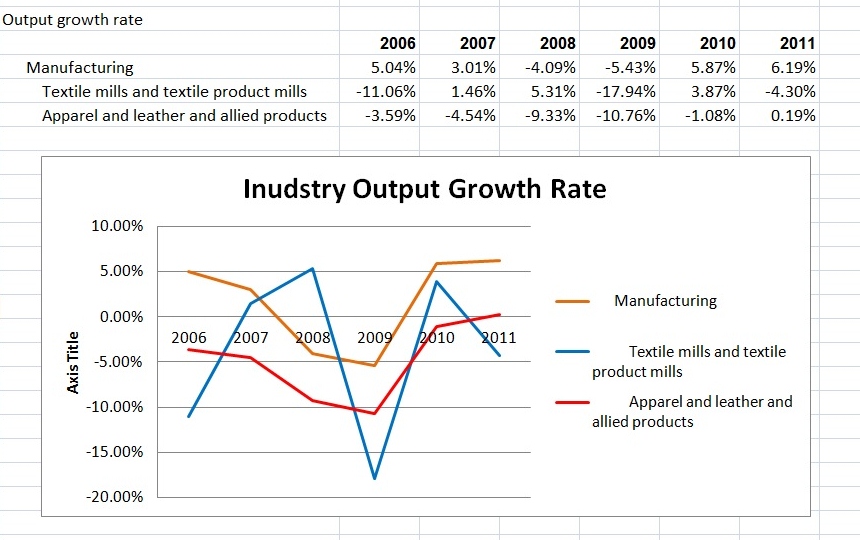
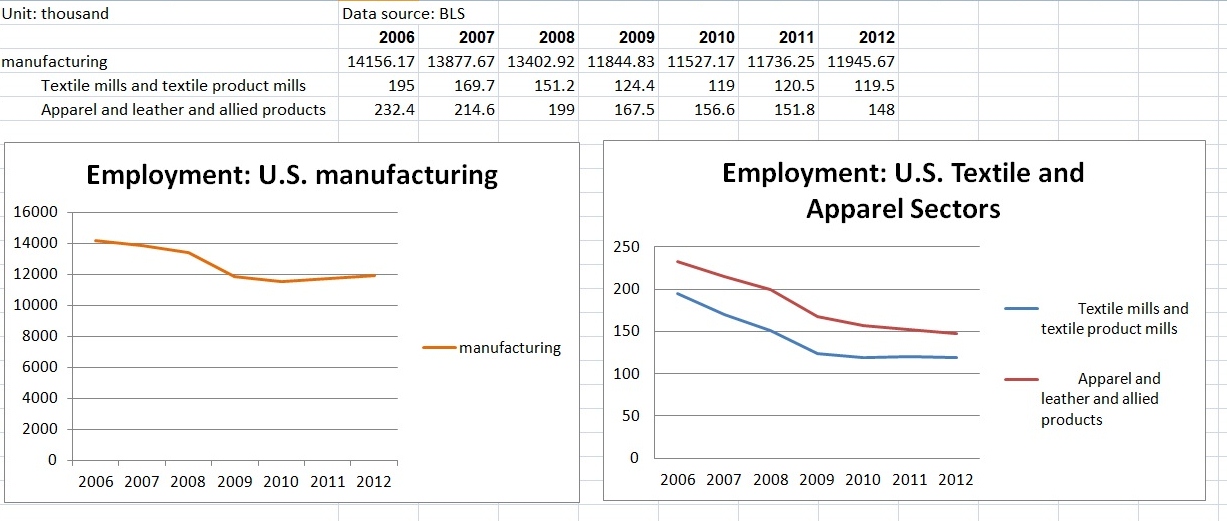
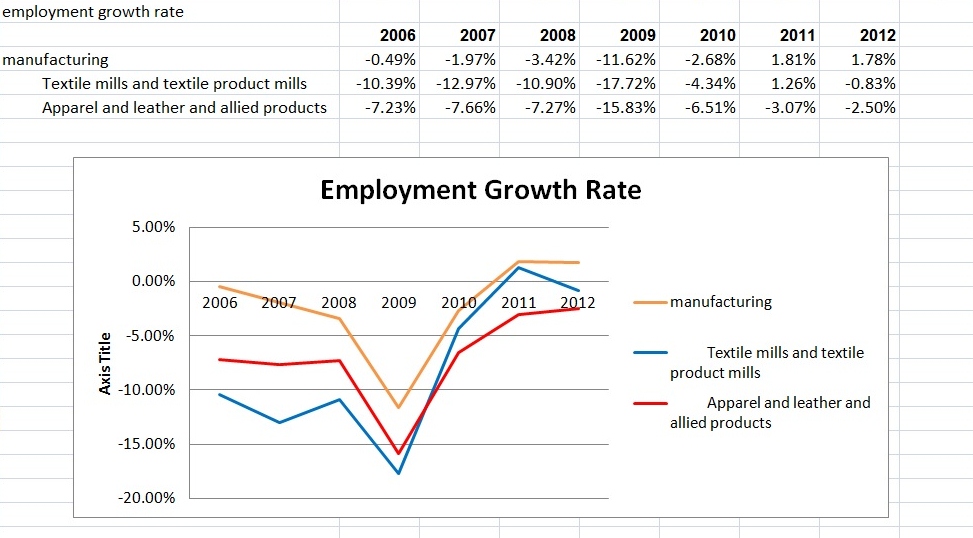
Julia Hughes: The phrase “the fashion industry” may call to mind images of Fashion Week and photo shoots. In this era of global trade, however, the high-fashion runways are just one part of the broader textile and apparel industry that ranges from high-end luxury brands to fast-fashion retailers—and the thousands of companies in between that produce and sell clothing, shoes, and other textile products.
United States Fashion Industry Association members and affiliates include companies across the value chain, which support our mission to remove barriers to textile and apparel trade. These companies include:
- Brands, retailers, importers, and wholesalers of textiles and apparel.
- Service providers, including consultants, customs brokers, freight forwarders, law firms, logistics providers, steamship lines, and testing and certification companies that help those brands, retailers, importers, and wholesalers.
- Manufacturers and suppliers of finished products and inputs for finished products, as well as supplier associations, business councils, and promotional groups.
- Agencies that promote the industry from a specific region, country, city, or other geographic entity.
- Academic institutions.
This industry includes companies and professionals across the value chain, working in roles ranging from design and development, to sourcing and logistics, to trade policy and compliance, to retail and marketing. USFIA members include all of these types of companies and individuals…
Sheng Lu: The United States Association of Importers of Textiles & Apparel (USA-ITA) has been a big name in the industry for 25 years. What leads your organization to change the name and rebrand yourself? Particularly, how will the USFIA distinguish itself with the American Apparel and Footwear Association (AAFA), whose members also include many US-based apparel companies and retailers?
Julia Hughes: The United States Association of Importers of Textiles & Apparel (USA-ITA), founded in January 1989 by nine U.S. importers, was instrumental in eliminating the global apparel quota system. At that time, it seemed like an almost insurmountable task to change the political dynamic enough so that the special protection for textiles and apparel would finally end.
On January 1, 2005, the quotas were officially eliminated, and since then, the industry has increasingly globalized. As a result, new challenges arise every day for apparel brands, retailers, and importers, ranging from challenges with compliance at the factories to challenges with transportation at the ports of entry. Over the years, the association has evolved with our members to address these new challenges—but our brand, including our name, logo, and official mission statement, had not changed in over two decades.
Accordingly, our major project in 2013 was rebranding the association to more clearly communicate our purpose and our direction for the future. It’s important to note that this project was not about changing our purpose or direction, but about ensuring that our brand accurately reflects the reality of the industry and the work we had already been doing for our members. The new brand—the United States Fashion Industry Association—was developed over 10 months with input from members and our trusted network across the value chain who participated in comprehensive overviews.
Why did we choose this name? First, our members are no longer just “importers.” While importing will be a critical aspect of our members’ sourcing plans for the foreseeable future, many of our members are truly global brands—for instance, designing product in the United States, producing that product in Asia, and then selling that product in Europe or Australia. Additionally, many of our members are also making product in the United States from U.S. and/or imported inputs. As we told WWD, “We are very supportive of Made in USA, and we sponsored some of the very first programs about Made in USA at MAGIC. It is a very important element, but it is one part of sourcing decision making.” Considering these realities, the phrase “Importers of Textiles and Apparel” no longer accurately described the industry or our members, so we needed to update it. (It was also a mouthful!) We settled on this exact name because “the fashion industry” is the phrase that companies, government, and the media uses most commonly to describe the wide variety of companies and professionals across the value chain—it best describes our association in 2013 and moving forward.
We spoke to our members and some trusted partners in our network about who we are and what sets us apart. From those conversations, we developed five values that we keep in mind with every decision we make. They are:
1. Integrity: Our members tell us that we listen to them, support them, and defend them—while our government partners tell us that we work with them to find creative solutions.
2. Substance: We maintain and articulate a deep understanding of the industry and challenges most important to our members—the sourcing and compliance executives who make tough decisions every day on how to address these challenges.
3. Focus: We keep a laser focus on our mission, which allows us to be agile and quickly seize upon opportunities to move the needle.
4. Collaboration: Our members collaborate to share best practices and amplify the industry’s voice on the critical issues, putting aside marketplace competition to work together toward common goals.
5. Foresight: We keep our members informed not only about the regulatory challenges today, but also the regulatory challenges of tomorrow—and as our industry globalizes, we likewise expand our reach.
Sheng Lu: As mentioned in your mission statement, the USFIA is dedicated to the removal of barriers that impede the free movement of textile and apparel products to the United States and international markets. What are the top trade policy and market access concerns for the USFIA right now?
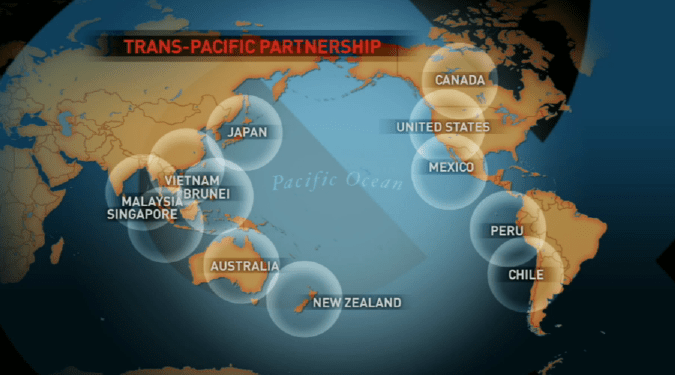
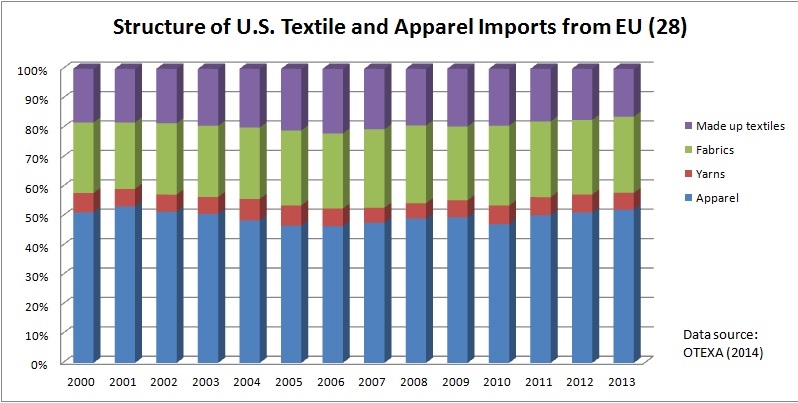
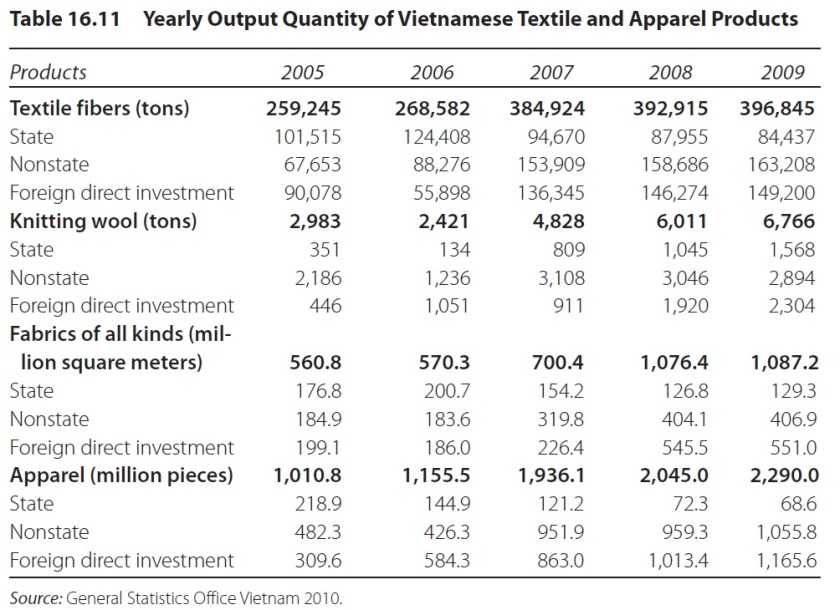
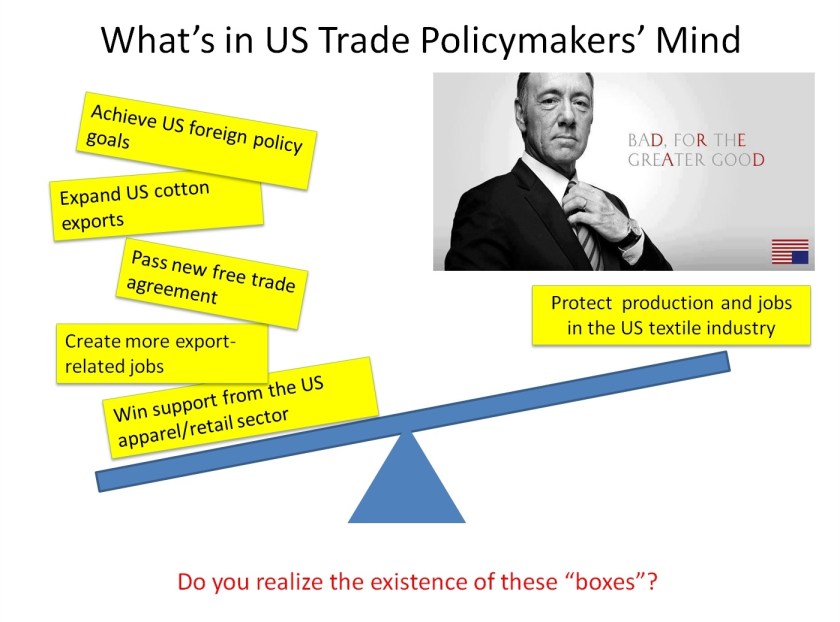
Julia Hughes: For 25 years, the United States Fashion Industry Association (USFIA)–formerly the United States Association of Importers of Textiles & Apparel (USA-ITA)–worked to eliminate barriers that impede the free movement of textile and apparel products to the United States and international markets. We participate in advocacy activities on a number of issues related to our mission in order to eliminate the tariff and non-tariff barriers that impede the industry’s ability to trade freely and create economic opportunities in the United States and abroad. Our top issues include:
Sheng Lu: You are featured in the well-known book Travels of T-shirt in the Global Economy. Interestingly enough, your counterpart in the book—Mr. Auggie Tantillo, now taps to lead the National Council of Textile Organizations (NCTO) which represents the US textile industry. In the T-shirt book, you two held very different views on whether the U.S. should restrict apparel imports from China. Now almost 8 years later, do you (and the USFIA) still debate often with Auggie (and the NCTO) on textile and apparel trade policy issues? If so, what are you mainly debating about?
Julia Hughes: Today, Auggie and I still disagree on some of the basic trade policy issues–especially the negotiations for new free trade agreements. NCTO is trying to hold onto the same textile rules of origin that were negotiated in the 1990s, the yarn-forward rule of origin. USFIA and our members continue to encourage the U.S. textile industry to take a fresh look at the global industry. But, so far, we remain far apart.
Nonetheless, we also have some areas where we can work together. Both our organizations support efforts to promote Made in the USA activities, as well as manufacturing in the Western Hemisphere. And, just this week I asked Auggie to help us with information about U.S.-based fabric mills. We also have collaborated on some proposals with Customs and Border Protection that build on the “trusted trader” concept and would focus enforcement measures on the companies who are not already proven to be compliant. And if I had to make a prediction, I would predict that in the next few years, we will find other areas where we can worth together productively.
Sheng Lu: Most of our students in the Textiles, Fashion Merchandising and Design (TMD) department will become professionals working for the US fashion industry after graduation. Does the USFIA have any resources available to our college students or have any future plans to expand the collaboration with the textile and apparel educational programs/academic institutions?
Julia Hughes: Yes! We welcome participation from universities, educators, and students in the fashion industry.
First, our website is a wonderful resource for information about the industry and our key issues. In addition to our issue pages, you’ll also find resources including recaps of past seminars, recordings of past webinars, our member publications, and more. (Some of this information is locked to USFIA members, but in the spirit of helping to grow our industry and future members, we’re always happy to help you access specific information you need! Just ask us!) We continue to build on the website, and in 2014, we will be launching a Value Chain Directory, which will provide comprehensive information on service providers and sourcing opportunities around the world.
Additionally, we host a number of events throughout the year, including our annual conference. We’re happy to work with educators and students to make attendance affordable, and we even have opportunities for universities to exhibit and students to volunteer.
We also encourage current and former students to visit our Career Center, which contains job opportunities at USFIA member companies. Even if you’re not looking for a job at the moment, it may be helpful to see what types of candidates these companies are seeking.
We’re always happy to work with universities, educators, and students to ensure that we educate the next generation of fashion industry leaders and professionals—future USFIA members!