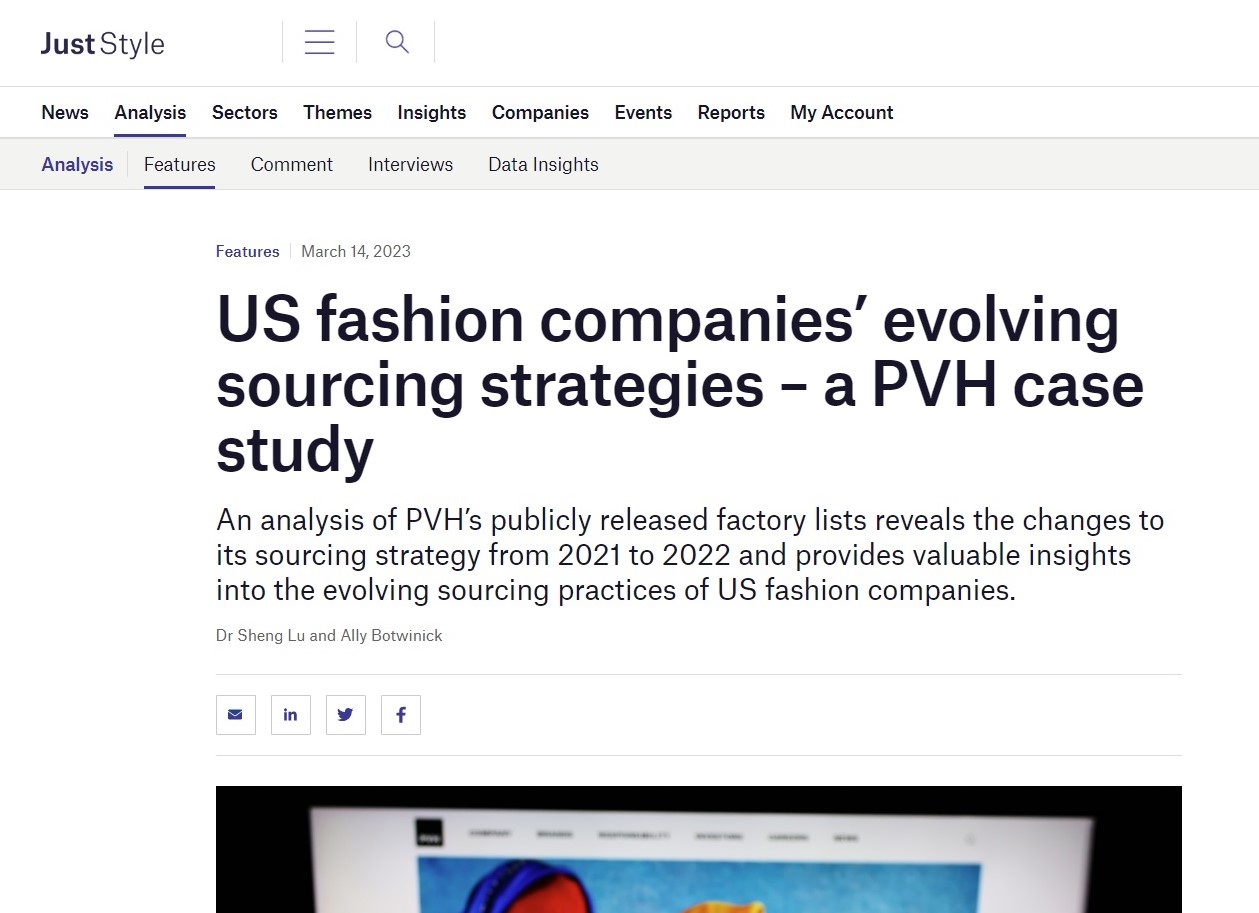
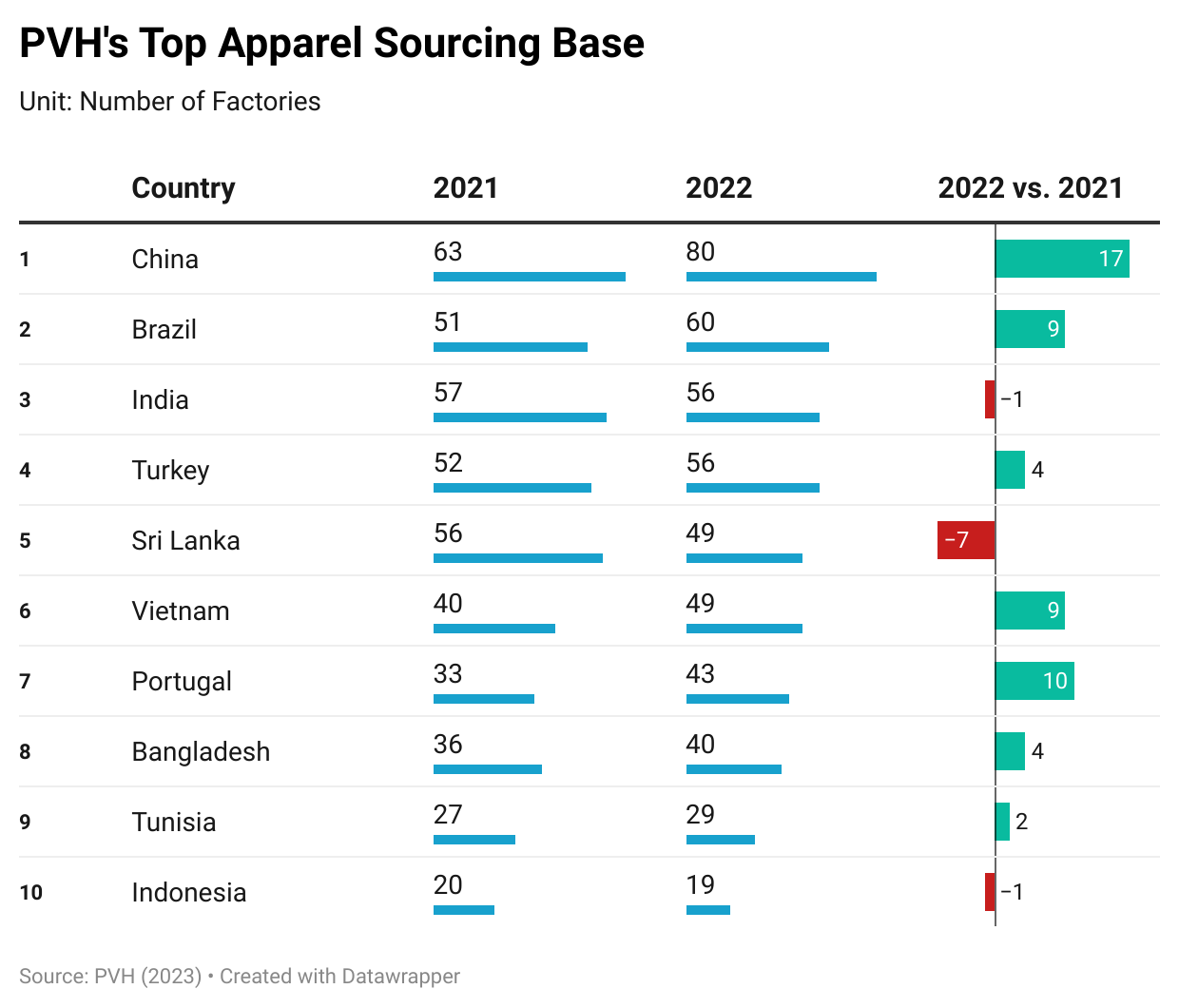
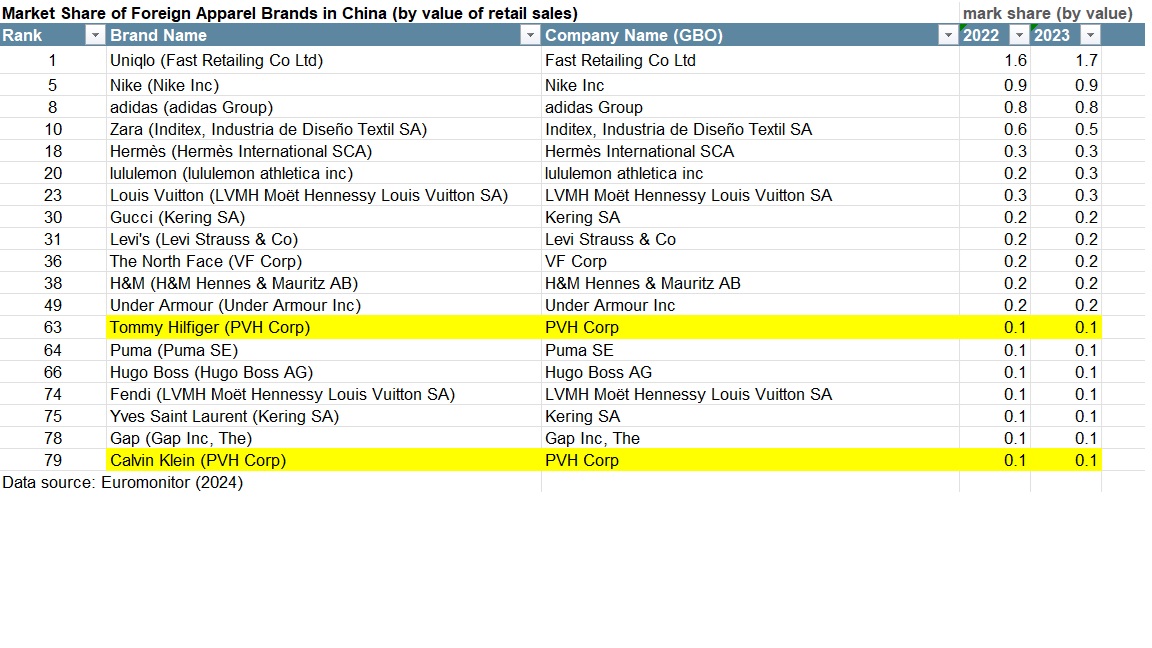
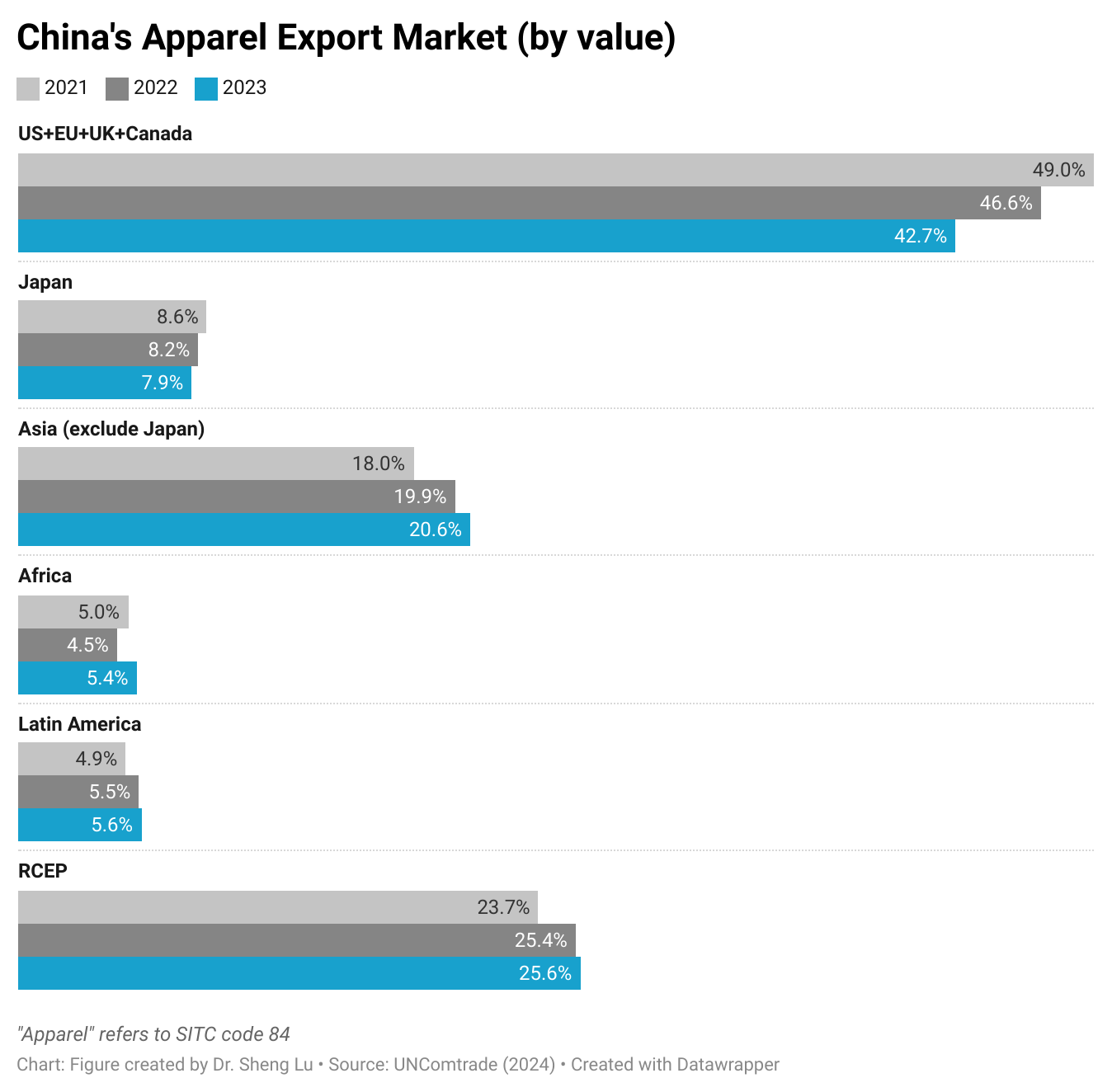
About Julianna Alfieri
Julianna Alfieri is the Senior Global Sourcing Specialist for Amscan, which serves over 40,000 retail outlets across the globe and owns Party City Holdings Inc. Born and raised in Long Island, Julianna has always had a passion for all things fashion. This passion led her to pursue a Bachelor’s degree in Fashion Merchandising and Management, with a minor in Sustainable Apparel & Textile Innovation, from the University of Delaware. Julianna furthered her expertise with a Graduate Degree from Parsons School of Design in Fashion Sustainability. Her diverse background includes experience in fashion styling, retail, marketing, and indexing, all of which have shaped her approach to global sourcing. With these educational and professional experiences, Julianna has built a solid foundation and acquired the necessary tools to excel in the industry.
Disclaimer: The views expressed in this interview are those of Julianna Alfieri and do not reflect the views or positions of her employer or any affiliated organizations.
Sheng: What does a Senior Global Sourcing Specialist do? What does your typical day look like? Also, what makes you love your job, or what is the most exciting part of it?
Julianna: As a Senior Global Sourcing Specialist, my role revolves around fostering cross-functional collaboration and maintaining strong relationships with vendors and suppliers. I oversee specific categories of the company’s business, ensuring effective communication and negotiation to maximize the quality of goods while meeting financial objectives. This involves working closely with my sourcing team, global offices, and utilizing various systems to streamline sourcing processes.
On a typical day, I work closely with my sourcing team and global partners to analyze costs, manage vendor relationships, and collaborate on major projects within my designated categories. Additionally, I assist in updating data in relevant systems and ensuring smooth transitions for new suppliers while also contributing to major projects aimed at enhancing redundancy categories and diversifying our supplier base.
The dynamic nature of the role keeps me engaged and continuously learning, allowing me to apply my education to real-world scenarios and witness the tangible outcomes of our efforts, such as seeing products I’ve contributed to in stores. What I find most exciting is the opportunity for constant growth and the collaborative aspect of working with our global partners!
Sheng: Can you walk us through the sourcing process—for example, the main procedures, who will be involved, and the general timeline?
Julianna: The overall sourcing process is an extremely collaborative effort involving multiple teams and stakeholders. It begins with identifying the need for specific products, which could stem from various reasons such as new product development, transitioning from existing suppliers, or finding vendors offering better cost or quality.
Once the product to be sourced is determined, we engage with suppliers from our matrix. Communication is managed internally for domestic vendors, while for international vendors, our global partners are involved. We evaluate potential suppliers based on their capability to produce the desired product and then proceed to cost negotiations.
Sample gathering is a crucial step where we collect samples from all potential vendors to assess quality and cost-effectiveness. This decision often involves input from both sourcing and product development teams. Using Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) systems, we then generate artwork for the product, collaborating closely with the art team.
Once artwork is finalized, it is shared with the chosen vendor to facilitate production specifications. Lead times for sample creation and production are negotiated with the vendor. Once we receive a pre-production sample, either our global partners or product development teams evaluate its quality and suitability.
Upon pre-production sample approval, the sourcing team updates our systems to indicate the selected vendor for the product. Throughout this process, sourcing manages communication between cross-functional teams and partners.
The timeline for this process typically spans 3 to 6 months, varying on factors such as the country of sourcing, vendor payment terms, lead times, and sample production quality.
Sheng: We know retailers today need to “balance” many sourcing factors today, from costs and speed to market to compliance risks. In practice, how do these factors actually affect companies’ sourcing decisions? For example, are there any specific factors that hold particular importance or are given significant weight in the decision-making process?
Julianna: Sourcing decisions within companies are deeply influenced by a number of factors. Among these factors, cost stands out as a primary consideration, directly impacting the financial health and competitiveness of the company. Balancing cost-effectiveness with other factors is essential to ensure optimal value for the organization.
Quality is another factor that holds significant weight in sourcing decisions. Maintaining specific standards of quality is essential to uphold the brand reputation, customer satisfaction, and overall product integrity. Innovation also drives sourcing decisions, as companies look for suppliers with advanced products, technologies, or processes to stay competitive and meet changing consumer needs.
Other critical factors include supplier reliability and supplier diversity. Dependable suppliers ensure consistent delivery schedules, minimize disruptions, and foster trust, while diversification enhances resilience and flexibility. Building strong relationships with suppliers encourages working together, coming up with new ideas, and achieving long-term success!
Finally, sustainability is now a crucial factor in sourcing decisions, driven by increasing consumer and regulatory demands for environmentally and socially responsible practices. Companies favor suppliers committed to sustainability, such as reducing waste and upholding fair labor standards. Embracing sustainability not only reflects a company’s corporate values, but also ensures long-term business success and resilience in a market that values conscious practices.
Sheng: From your observation, what are the critical sourcing trends and key issues to watch in 2024?
Julianna: In today’s climate, it is evident that there are several critical sourcing trends and key issues to keep a close eye on in 2024. Among these, prioritizing resilience, sustainability, and diversification stands out as essential for companies aiming to navigate the evolving sourcing landscape successfully!
The COVID-19 pandemic has led to a renewed emphasis on strengthening supply chain resilience. Companies are actively diversifying their suppliers and improving risk management to ensure operational continuity. Based on my personal experience in this industry, I’ve recognized the essential role adaptability plays in keeping operations running smoothly without interruption.
Additionally, there is growing attention on sustainability and ethical sourcing. Companies are under pressure to be transparent and accountable due to increased consumer awareness about environmental and social issues. In our organization, we maintain standards through the use of supplier audits to ensure sustainability compliance. Initiatives such as sustainable packaging and collaborations with suppliers certified by reputable organizations like the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) reflect our efforts to advance sustainability goals.
One of the key challenges I’ve encountered in my sourcing career is the reliance on a limited supplier base. This became evident during our paper bag project when antidumping duties significantly impacted our sourcing strategy. The imposition of antidumping duties on paper bags from certain regions prompted us to explore alternative suppliers globally. This highlighted the importance of diversifying our supplier matrix to reduce dependence on specific regions and mitigate risks associated with geopolitical tensions or trade regulations.
Lastly, uncertain economic climates have significantly influenced what warrants close attention. Our company’s experience with Chapter 11 bankruptcy served as a pivotal moment, illuminating the crucial paths forward. As repeatedly emphasized, maintaining a diverse and resilient supplier base is essential for mitigating risks linked to potential disruptions in the supply chain. Additionally, closely monitoring costs and implementing cost-saving measures becomes imperative for navigating through uncertain economic times. Lastly, fostering robust supplier relationships and enhancing communication and collaboration with suppliers emerge as essential strategies for navigating challenges and ensuring continuity in the sourcing process, especially amidst economic uncertainty.
Sheng: Many retailers have adopted PLM (product life cycle management) and other digital tools to manage sourcing and the supply chain. From your observations, what changes have these tools brought to sourcing?
Julianna: Digital tools are vital for global sourcing as they streamline processes, enhance communication, and provide real-time insights, enabling companies to make informed decisions. Some important tools I work with closely include PLM (Product Lifecycle Management), BPCS (Business Planning and Control System), and Datamyne, as they help to optimize efficiency and mitigate risks in the complex global marketplace.
PLM helps to centralize information and documents, which ensures that all stakeholders have access to real-time data, updates, and feedback, leading to improved alignment. This helps for history purposes and checking previous decision making done by other team members. PLM also assists with processes such as supplier onboarding, product specifications management, and artwork/sample tracking.
BPCS provides a wide range of tools for managing inventory, procurement, and production planning. It helps ensure that inventory levels are optimized, procurement processes are efficient, and production activities are scheduled according to demand forecasts and inventory data. This visibility into inventory levels also allows sourcing partners to access crucial information, such as the amount of inventory on hand, helping us prioritize sourcing efforts based on urgency.
Lastly, Datamyne provides valuable insights into global trade data, including import and export information, tariffs, and compliance requirements. Datamyne also allows users to search for potential suppliers, thus mitigating risks associated with geopolitical factors and trade regulations. In response to the antidumping tariffs affecting our paper bags (previously mentioned), I utilized Datamyne to identify alternative vendors exempt from these tariffs. I thoroughly researched and explored these potential vendors to determine if they could serve as viable alternatives for sourcing paper bags, thereby circumventing the tariffs.
Sheng: Any reflections on your experiences at UD and FASH? What advice would you offer current students preparing for a career in sourcing after graduation?
Julianna: Reflecting on my experiences through the UD fashion program, I am grateful for the comprehensive education and real-world projects that have shaped my understanding of the fashion industry and the global sourcing world. UD provided me with valuable insights into various aspects of the industry and encouraged me to explore my interests deeply. Through specialized courses for my focus on sustainable apparel and textile innovation, I gained practical knowledge that is directly applicable to the sourcing realm. The exposure to relevant case studies and global issues was instrumental in honing my skills and preparing me for my career in global sourcing, and UD has paved the way for the inevitable challenges and opportunities ahead.
For current students preparing for a career in sourcing after graduation, my first piece of advice would be to prioritize networking and building relationships with peers and faculty members. Business is personal, and these connections can open doors to opportunities in the industry! Additionally, dedicating oneself to school projects and seeking any type of industry experience can provide clarity on career paths and offer invaluable insights into different work environments, and help in understanding one’s preferences within the industry.
Developing strong presentation skills and the confidence to speak up in team settings are essential for standing out as a leader and effectively communicating with vendors, global partners, and cross-functional teams.
Finally, staying informed about current events, especially in the sourcing landscape, is crucial for making informed decisions and staying ahead in the industry.
Feel free to reach out anytime if you’d like to connect, chat, or discuss industry insights – I am always here and eager to engage!
–The END–