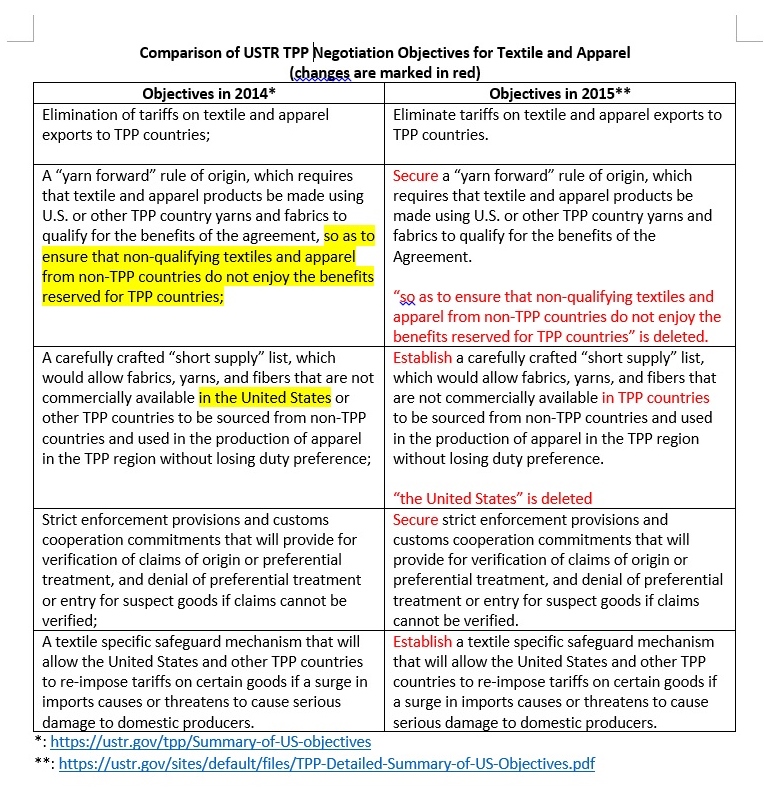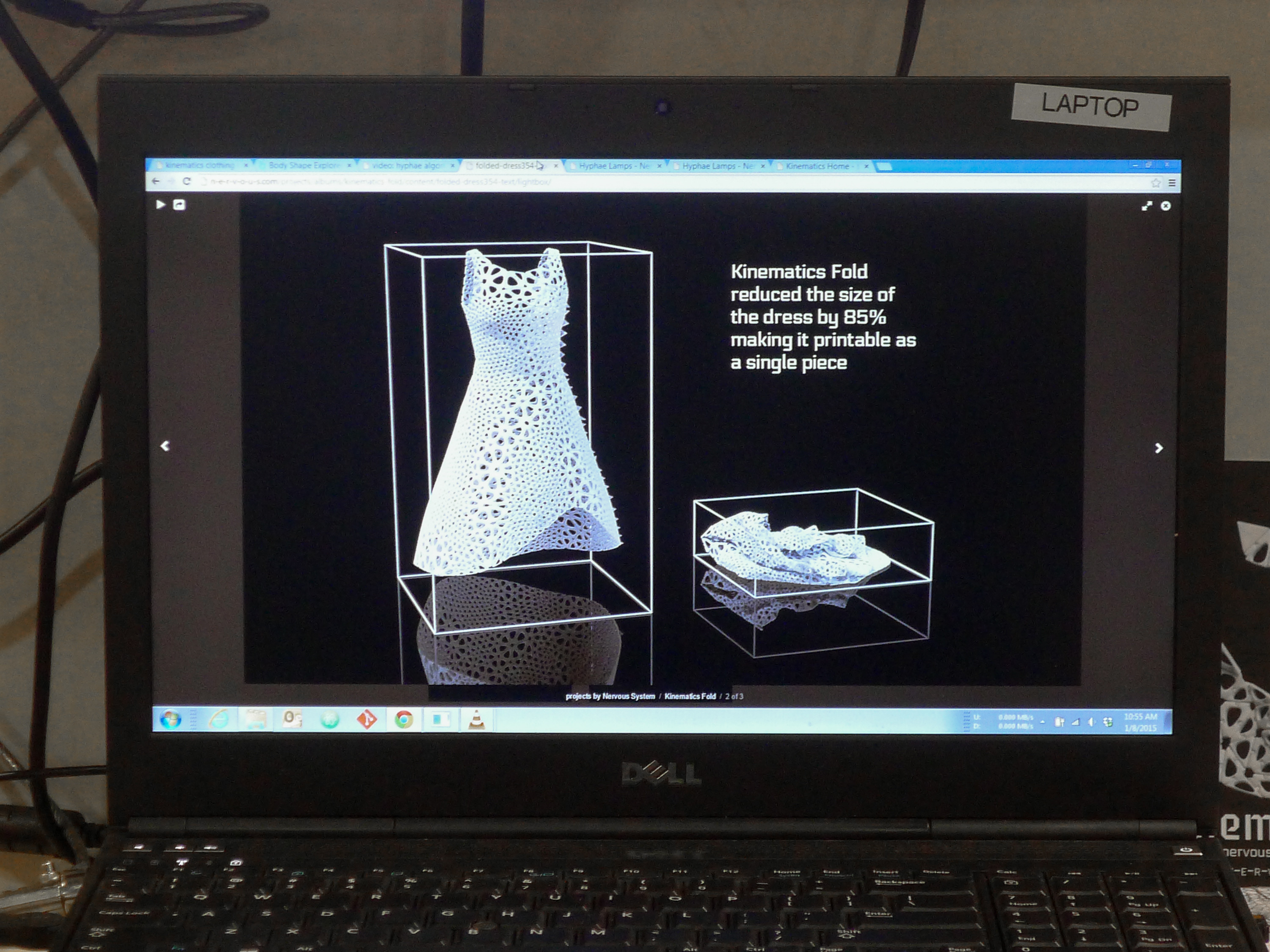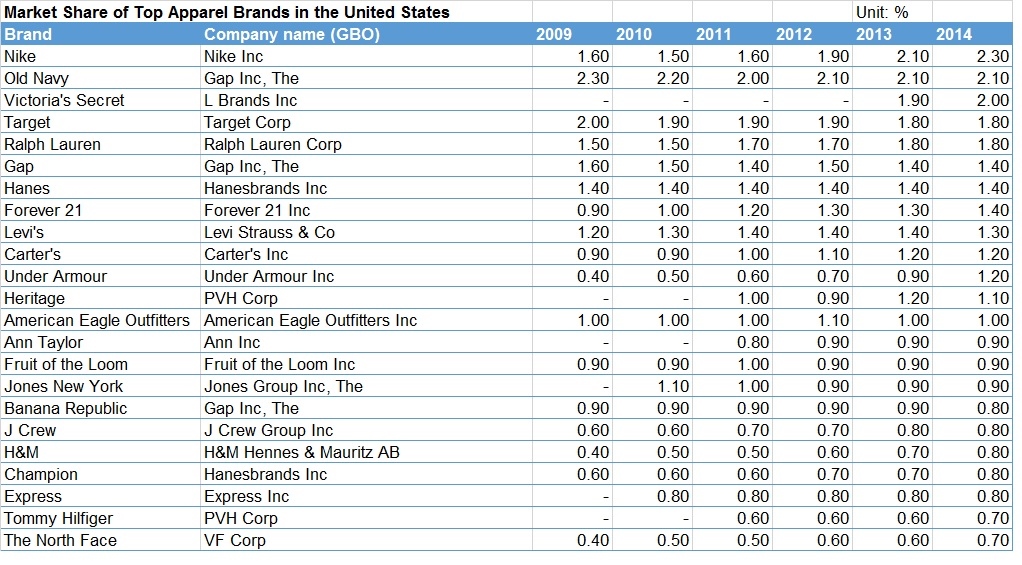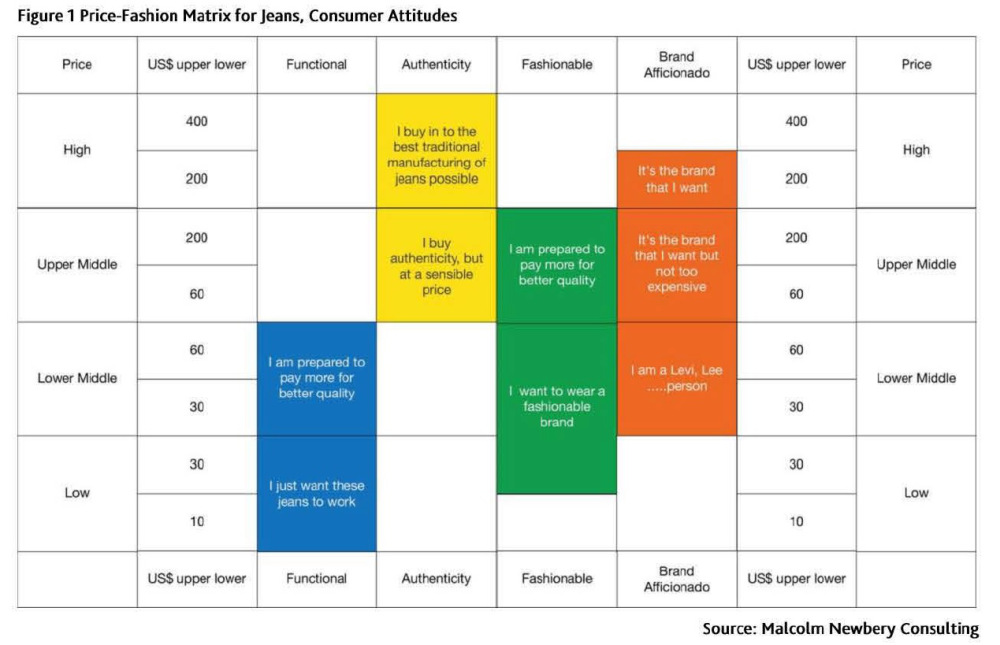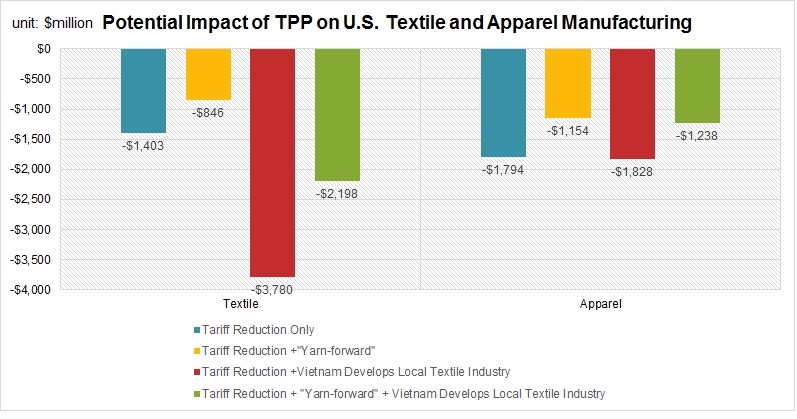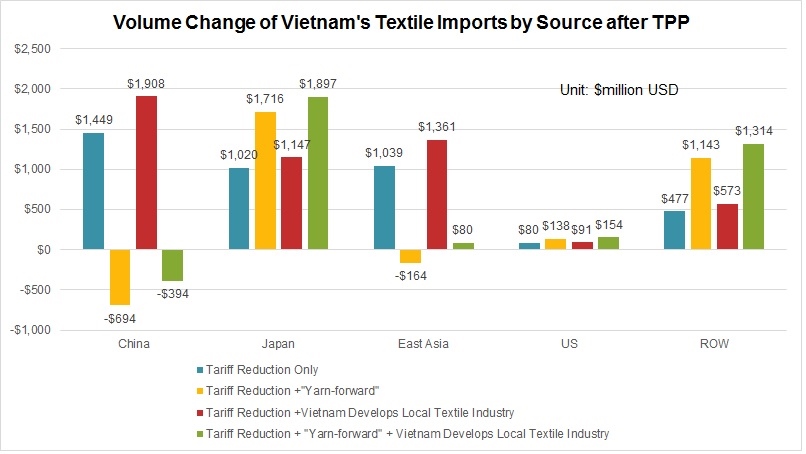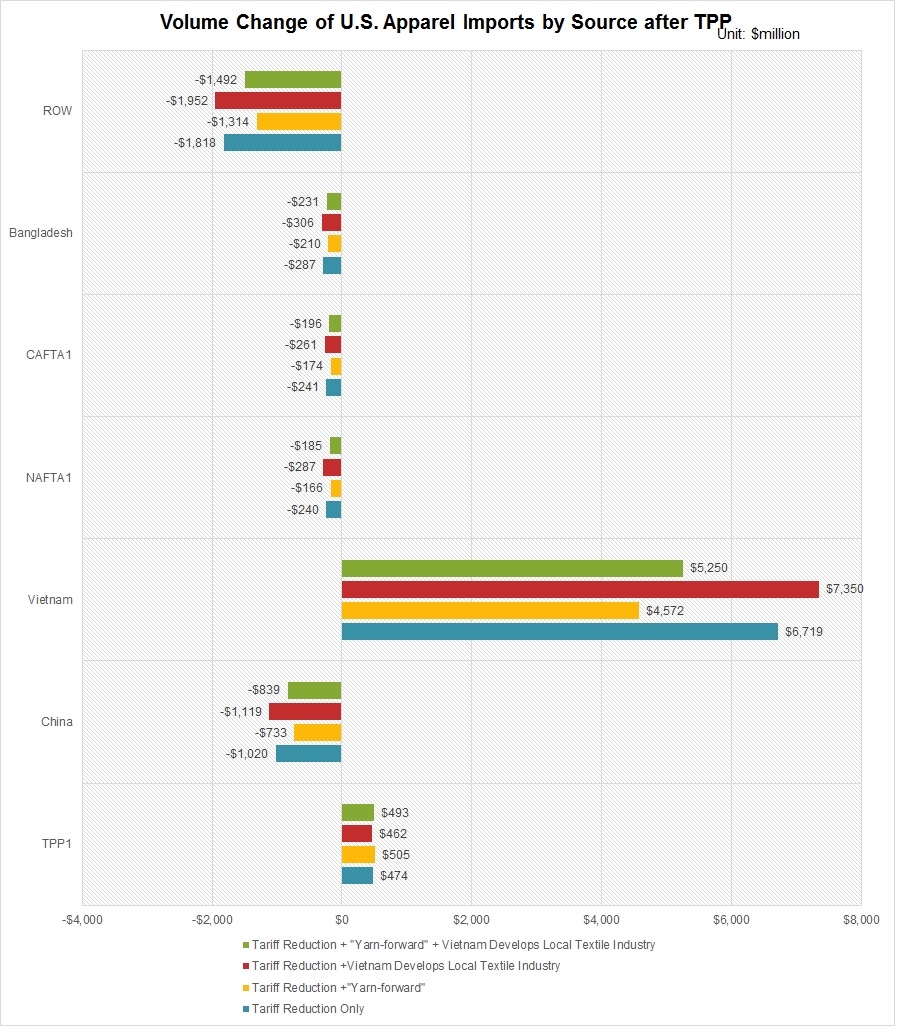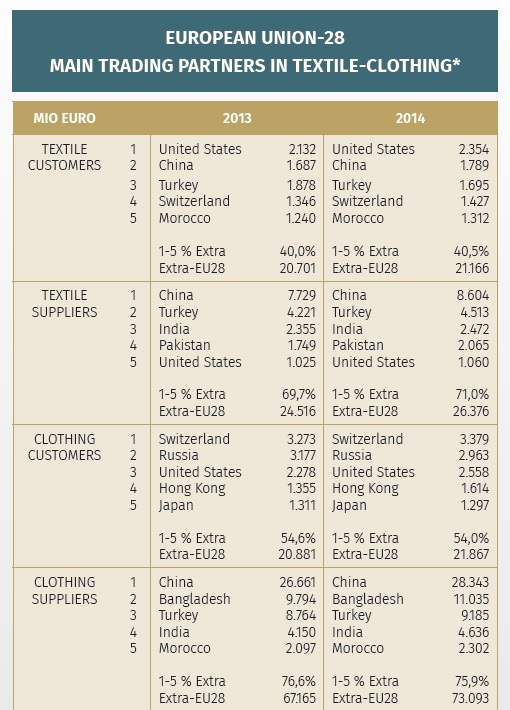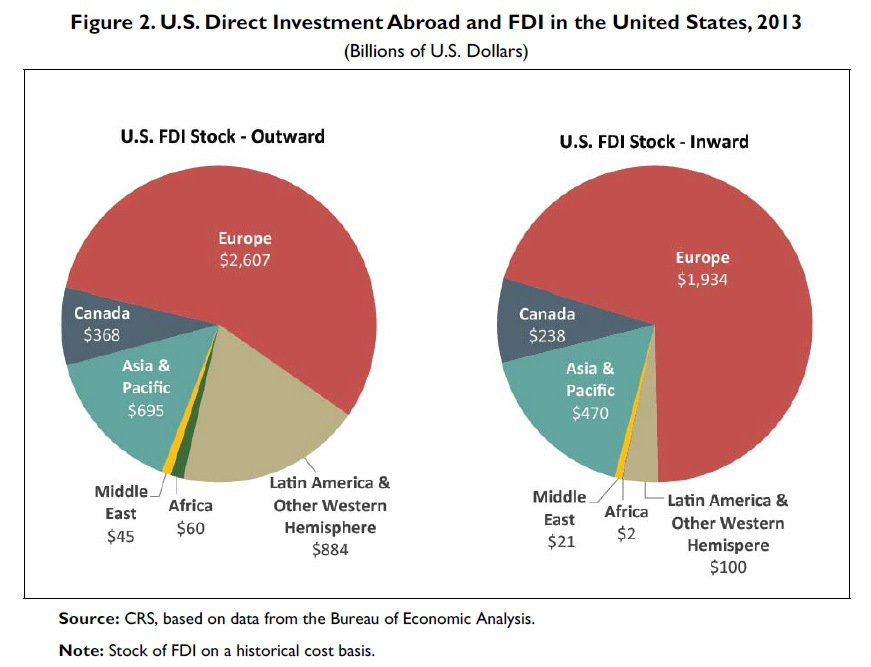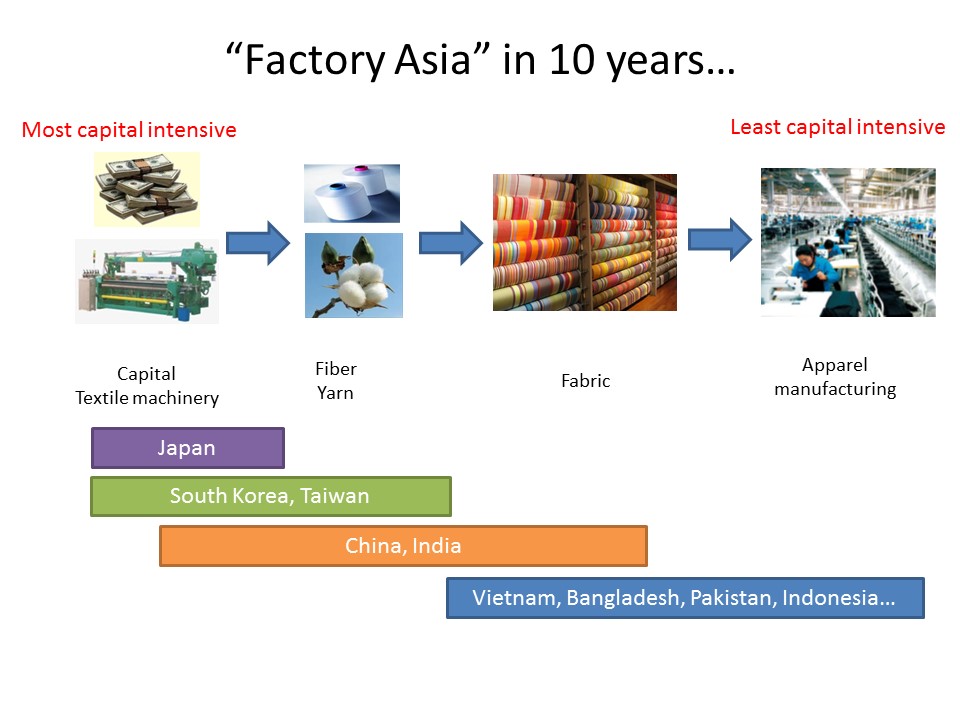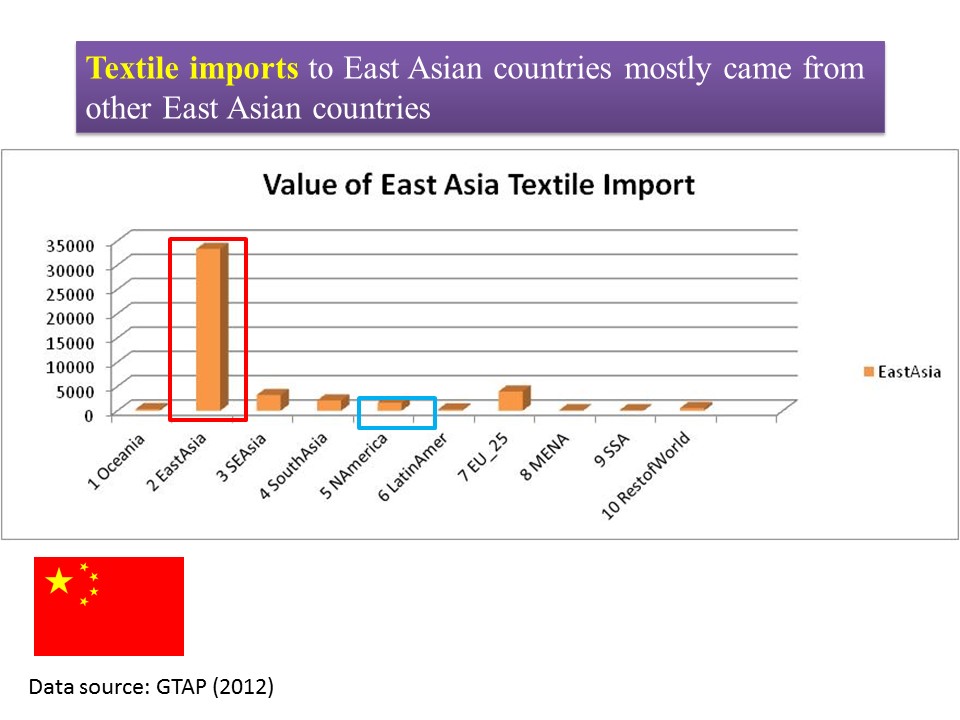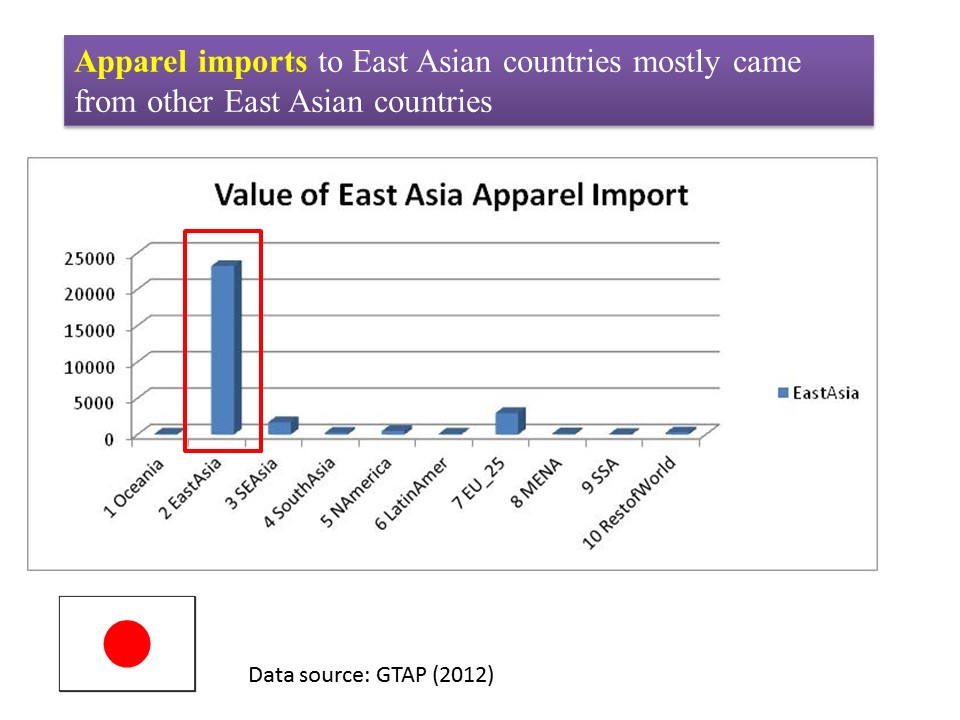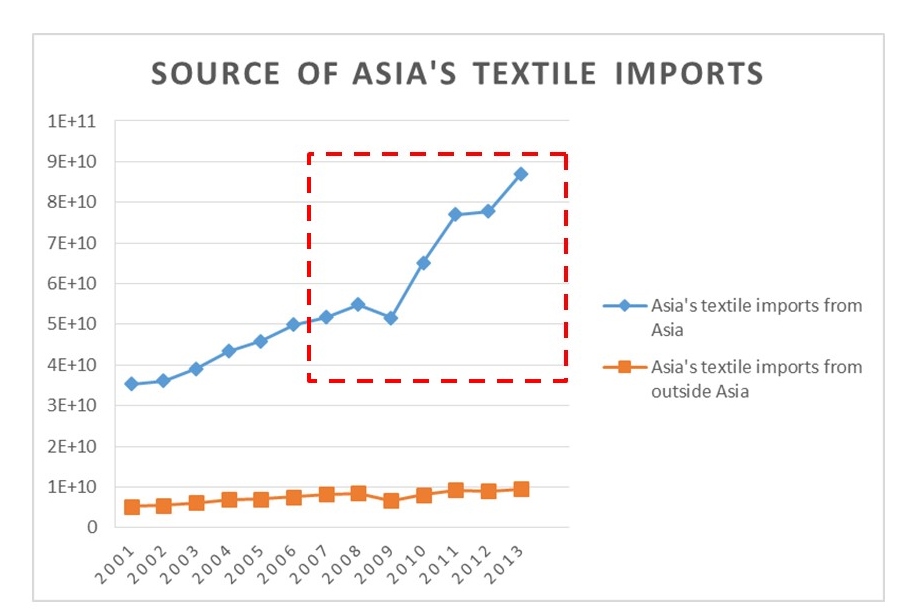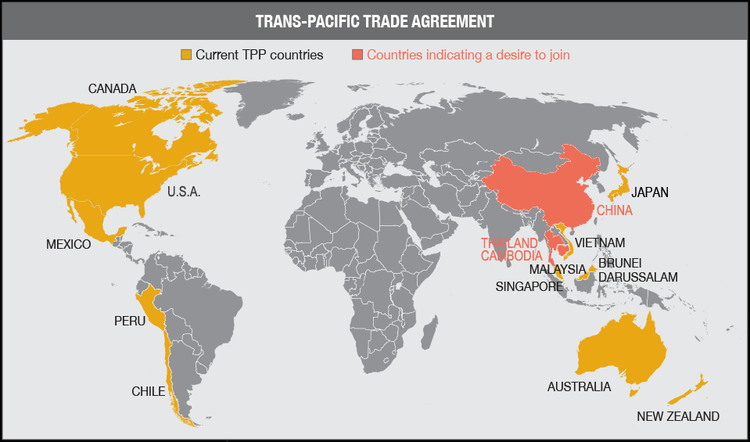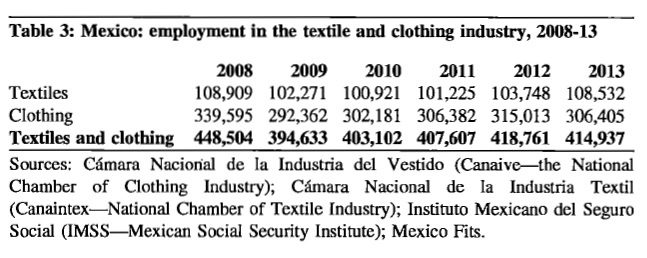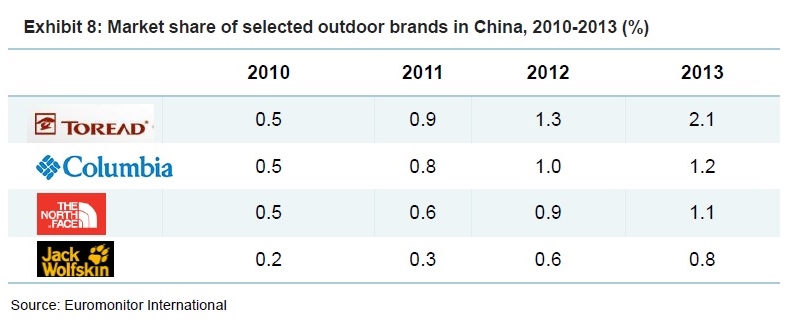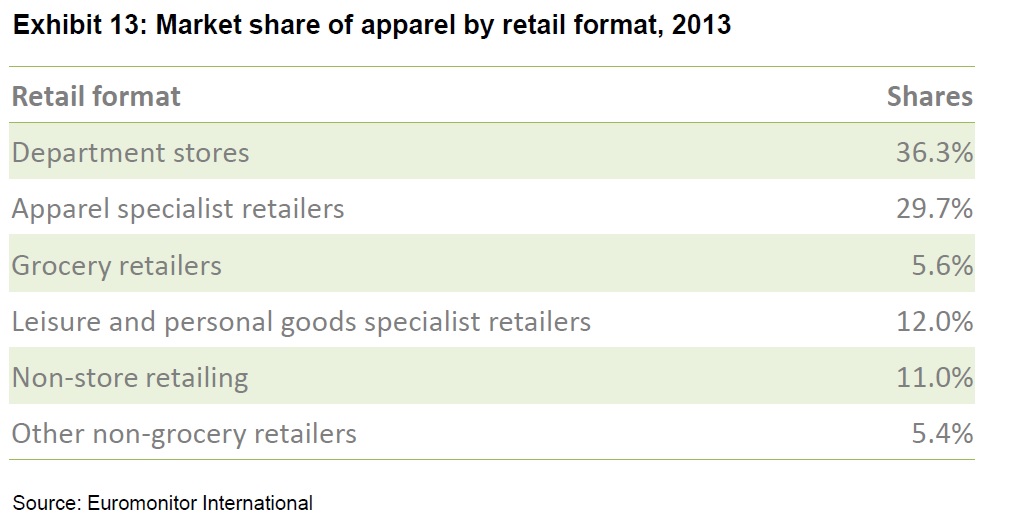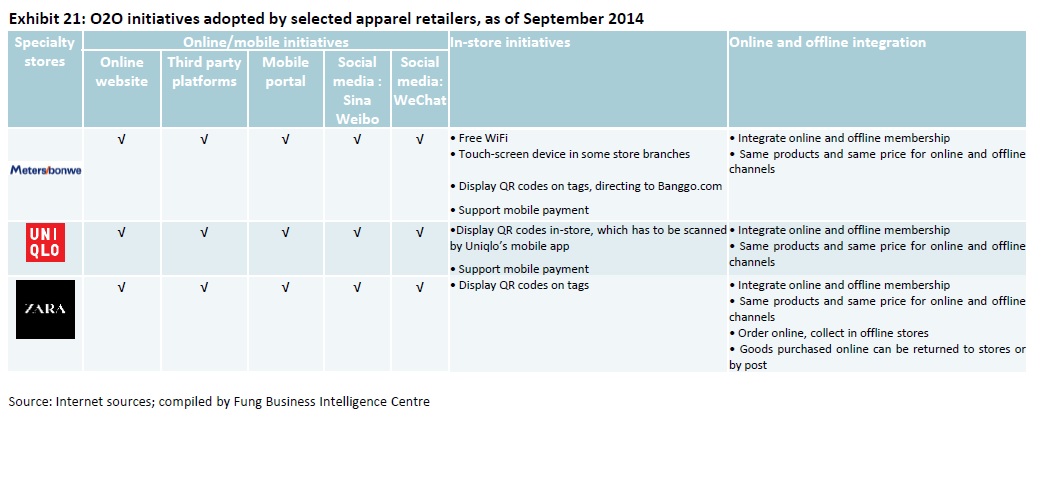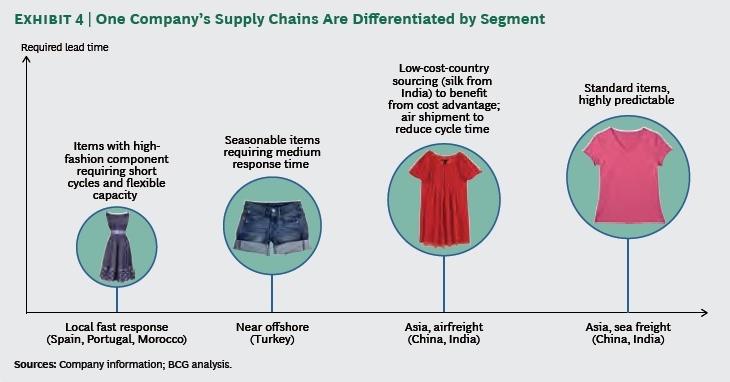
As the saying goes, change is the only constant in the fashion apparel industry. According to a newly released market report by Lectra*, “the pace of fashion has never been faster and neither has the pace of change”.
Lectra’s report highlights a few factors driving the changes in the fashion apparel industry:
1. Consumers
Consumers has much more control than in the past, implying the fashion industry can no longer define what to make and sell without taking consumers’ inputs into consideration. Some companies have alter their business models to be completely demand-driven, i.e. allowing integrating all their resources to meet the customized needs of all consumers.
Social and economic changes like internet access and growing prosperity, have also spurred the growth of new fashion markets in emerging countries that had typically been only supplier region, creating new opportunities for western fashion brands and retailers to expand business.
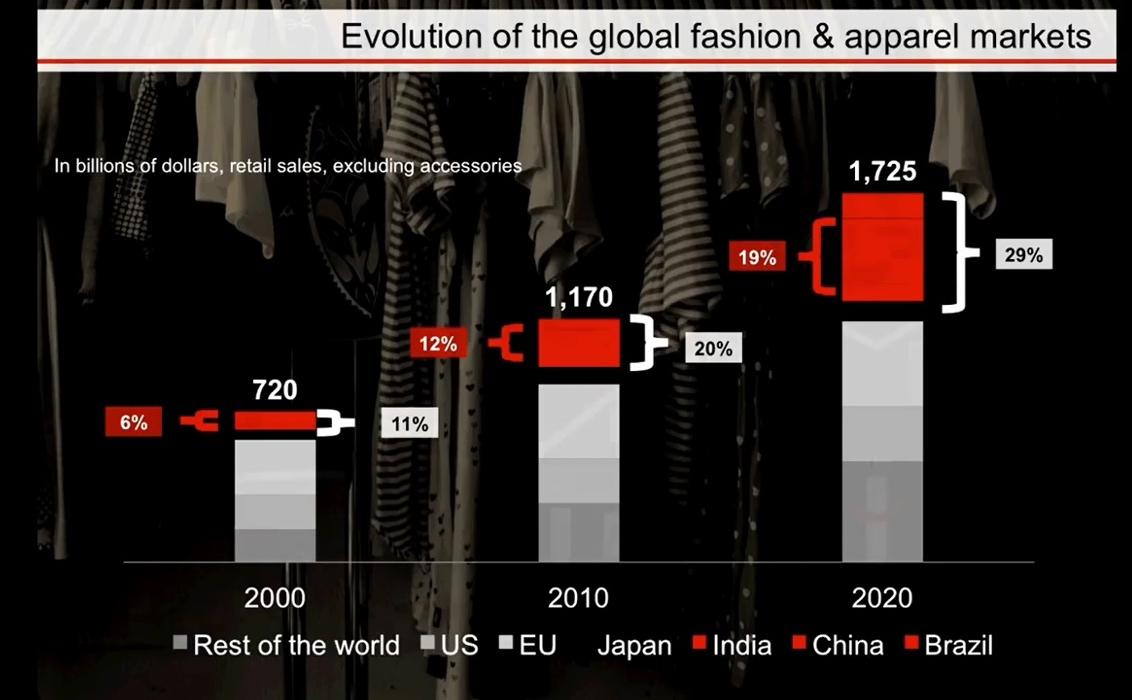
2. Globalization
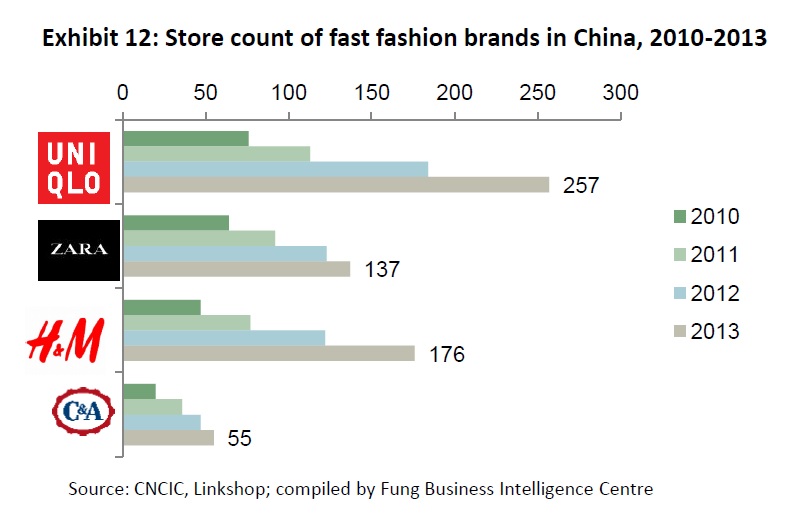
Historically, local brands dominate local market. However, because of the strategies of geographic expansion and international growth of many fashion brands, in more and more markets, local brands have to face competition from foreign brands. (for example: the Australian fashion industry is worried about the competition from H&M).
But globalization does not reduce diversity and localized consumer preferences. On the contrary, increased internationalization means that populations are more heterogeneous than in the past and retailers have to bring a localized response to individual markets.
3. Technology
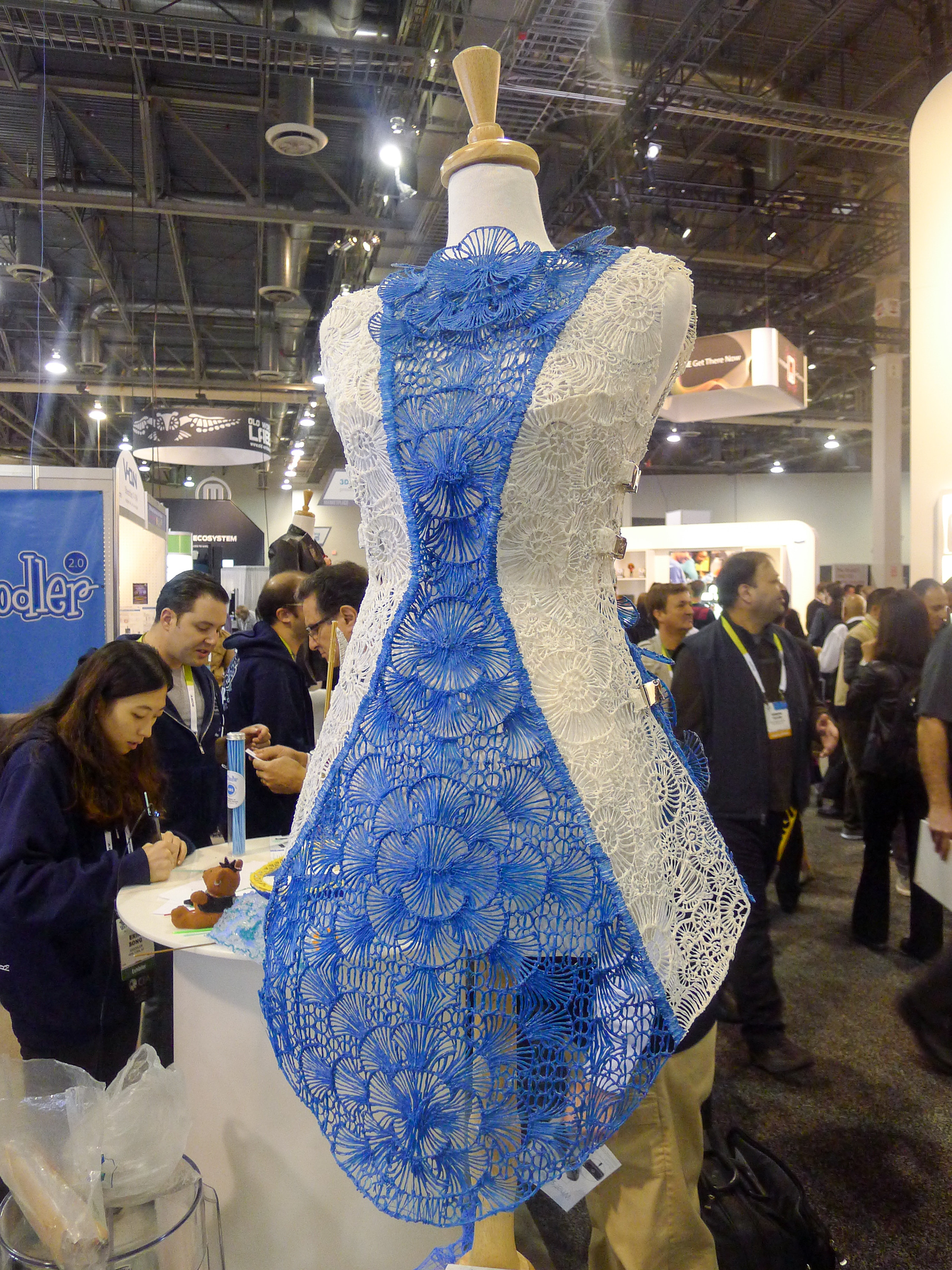
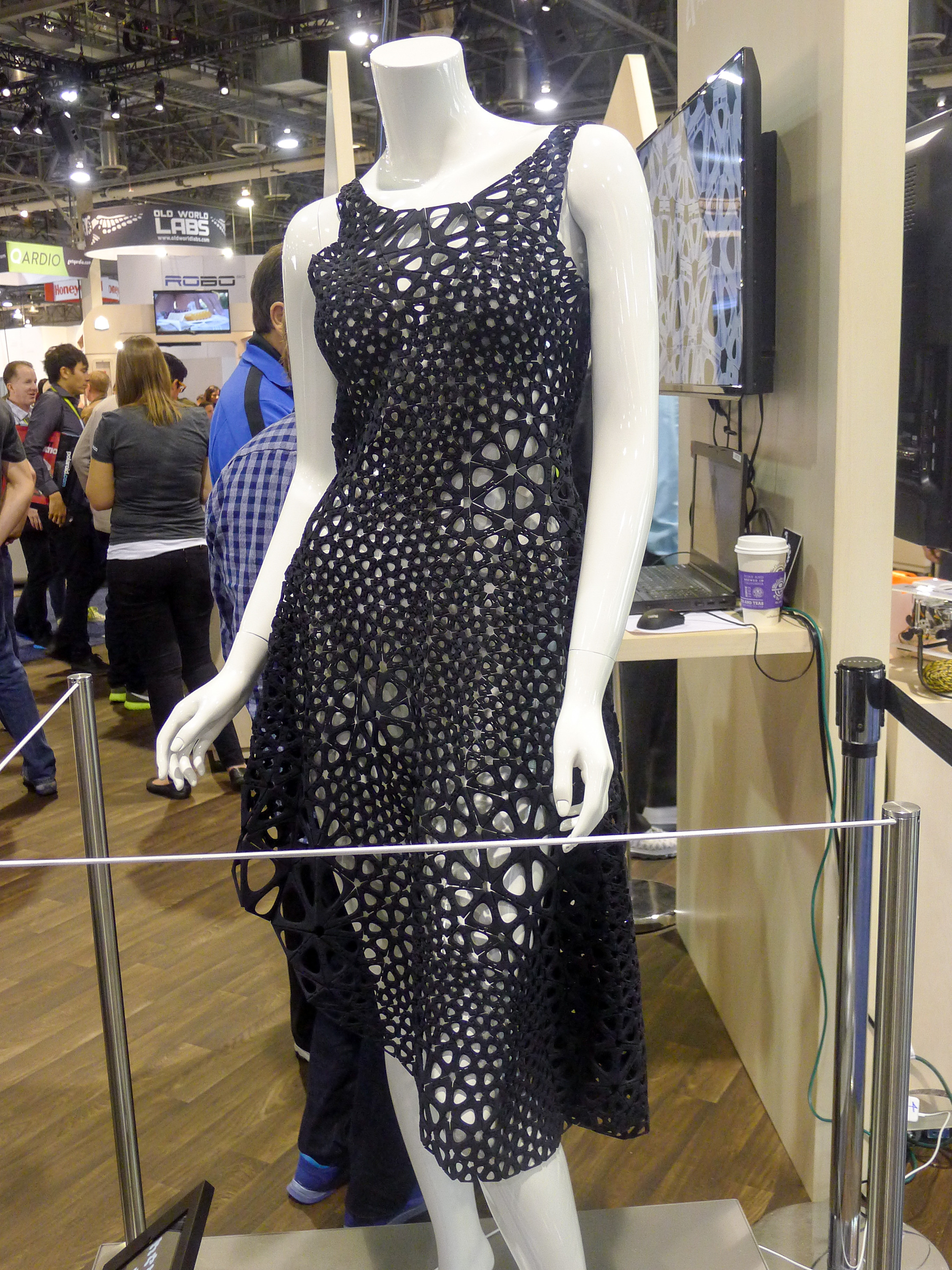
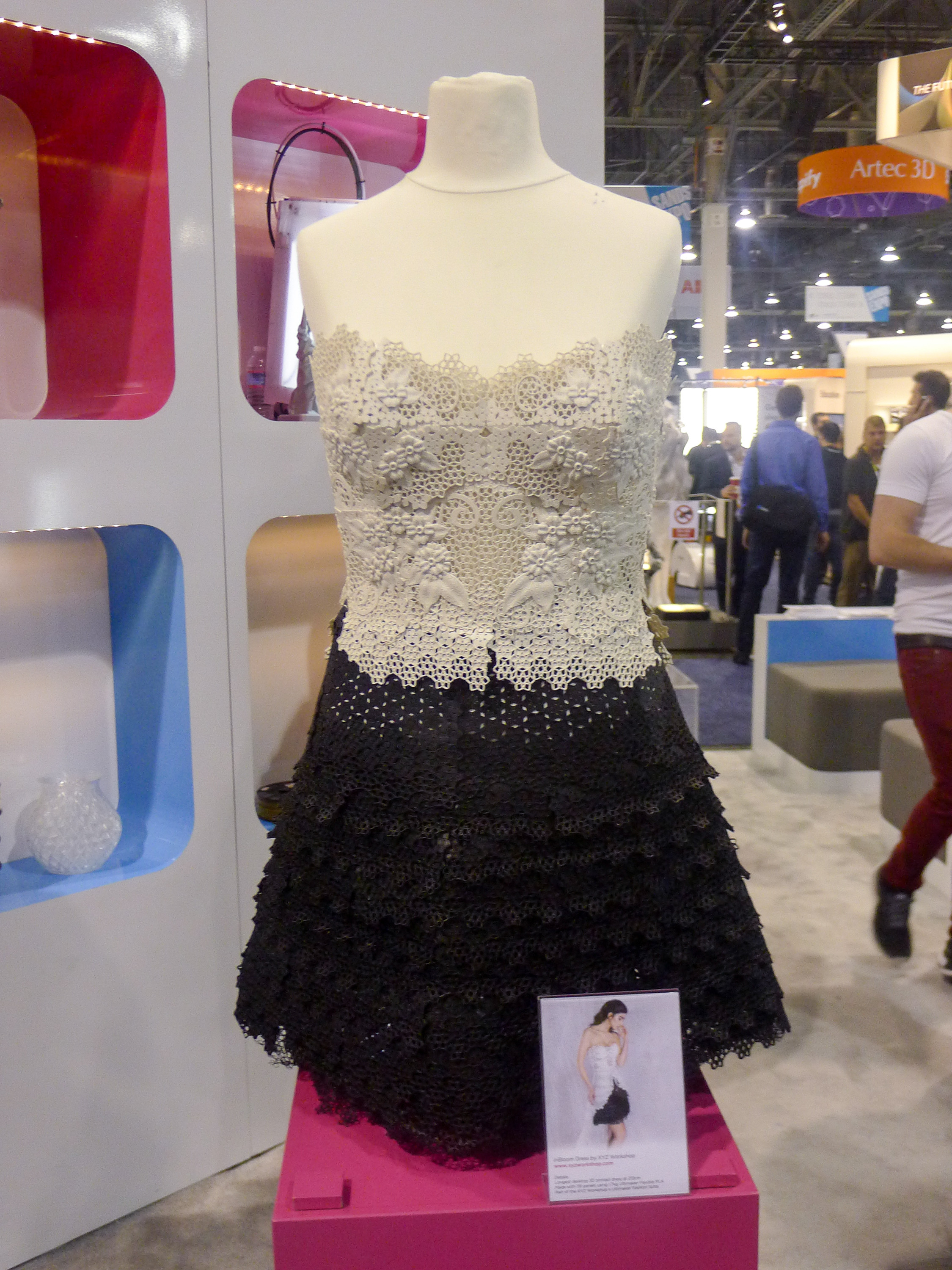
New social media and mobile technologies have given consumers the power of instantaneous sharing and buying without restriction of time, place and in many cases, price. The availability of new technologies such as RFID, product life cycle management (PLM) and many other supply chain management tools have also enabled brands, retailers and manufacturers to reduce product development cycle, improve efficiency and better collaborate across the global process.
For example, digital prototyping gives companies the agility they need to adapt to changes in the market and test new products before they start to incur real production costs. PLM facilities the collaboration between design and development departments and breaks the silo mentality that has reigned for so long in the fashion and apparel industry, eliminating bottle- necks that resulted from outdated linear processes and increasing decision making power earlier on in product development.
4. Change of Business models**
In response to the application of new technologies and consumers’ updated demand, companies start to seriously reconsider their business models, especially the process of design, product development, production and distribution. As noted in the report, fashion brands, which have traditionally gone through retailers who sell on their behalf, have developed retail operations with the purpose of capturing a higher percentage of the final sale price and achieving complete control over the presentation, distribution and final price of their merchandise. Many retailers, however, also start to offer more and more private brands and exclusive products that can more effectively segment market and attract targeted consumers.
The traditional manufacturers are also looking for ways to cut costs and increase efficiency because of the pressure from retailers/brands. Manufacturers also have realized that selling directly to the end consumers is the most powerful way to protect revenue. As quoted by the report, roughly 60% of Chinese apparel manufacturers have launched their own brands. Armed with all that know-how, a growing number of Chinese manufacturers are now turning their efforts toward developing an offer for the domestic market and some are even setting their sights abroad. (recall the topic of “upgrading” in our lecture)
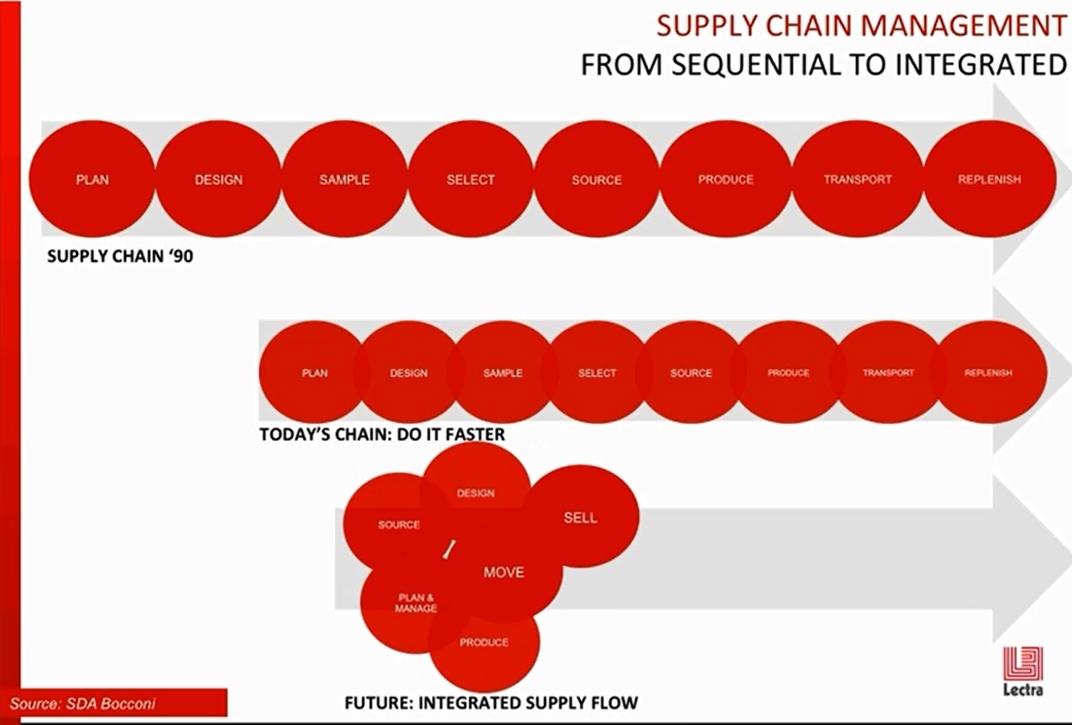
*: Lectra is a company which provides fashion-focused technology solutions such as the CAD system and the product life-cycle management (PLM) system.