New data available: WTO Reports World Textiles and Clothing Trade in 2021
According to the World Trade Statistical Review 2021 report released by the World Trade Organization (WTO), the textiles and apparel trade patterns in 2020 include both continuities and new trends affected by the pandemic and companies’ evolving production and sourcing strategies in response to the shifting business environment.
Pattern #1: COVID-19 significantly affected the world textile and apparel trade volumes, resulting in substantial growth of textile exports and a declined demand for apparel.
Driven by increased personal protective equipment (PPE) production, global textile exports grew by 16.1% in 2020, reaching $353bn. In comparison, affected by lockdown measures, worsened economy, and consumers’ tighter budget for discretionary spending, global apparel export decreased by nearly 9% in 2020, totaling $448bn, the worst performance in decades. The apparel sector is not alone. The world merchandise trade in 2020 also suffered an unprecedented 8% drop from a year ago, with COVID-19 to blame.
Notably, as economic activities returned in the second half of 2020, the world clothing export quickly rebounded to around 95% of the pre-covid level by the end of 2020. That being said, the unexpected resurgence of COVID cases in summer 2021, especially the delta variant, caused new market uncertainties. Overall, the world textile and apparel trade recovery process from COVID-19 will differ from our experiences during the 2008 global financial crisis.
Pattern #2: COVID-19 did NOT shift the competitive landscape of the world textile exports; Meanwhile, textile exports from China and Vietnam gained new momentum during the pandemic.
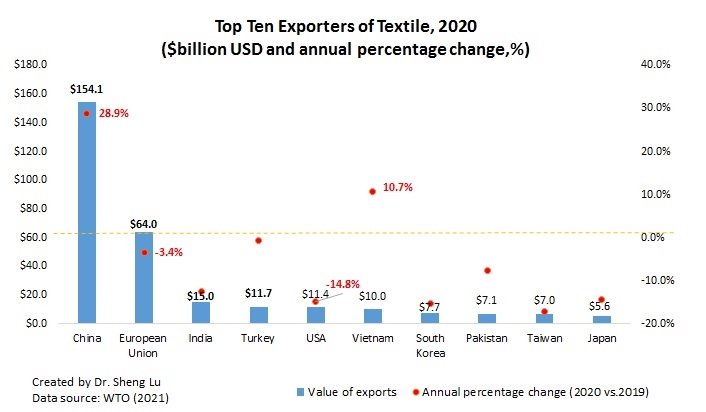
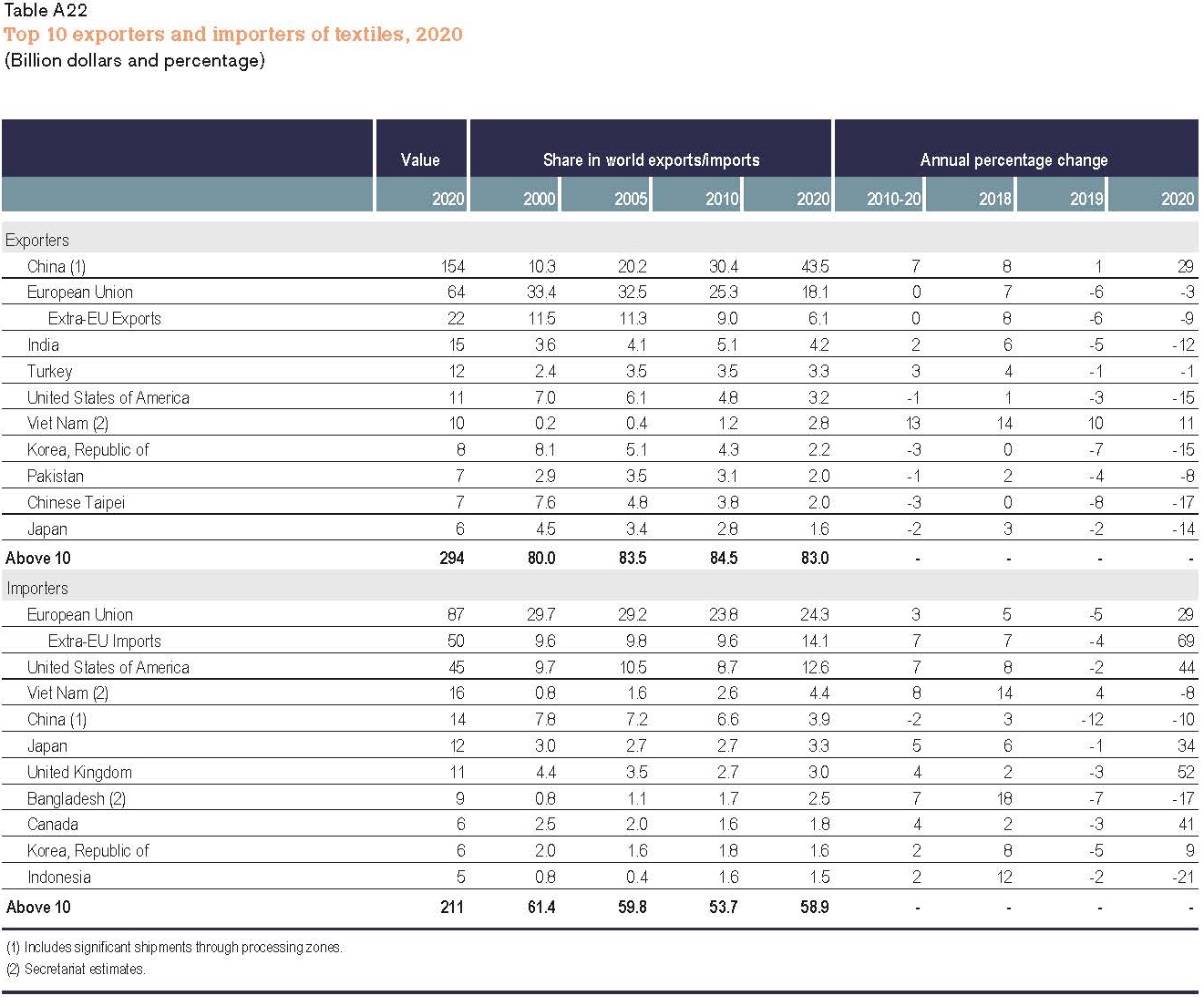
China, the European Union (EU), and India remained the world’s three largest textile exporters in 2020. Together, these top three accounted for 65.8% of the world’s textile exports in 2020, similar to 66.9% before the pandemic (2018-2019).
Notably, China and Vietnam enjoyed a substantial increase in their textile exports in 2020, up 28.9% and 10.7% from a year ago, respectively. The complete textile and apparel supply chain and considerable production capability allow these two countries to switch clothing production to PPE manufacturing quickly. In particular, Vietnam exceeded South Korea and ranked the world’s sixth-largest textile exporter in 2020 ($10 bn of exports), the first time in history.
The United States dropped one place and ranked the world’s fifth-largest textile exporter in 2020 (was 4th from 2015 to 2019), accounting for 3.2% of the shares (was 4.4% in 2019). Production disruptions at the beginning of the pandemic and the shift toward PPE production for domestic consumption were the two primary contributing factors behind the decline in U.S. textile exports. Due to the regional trade patterns, around 67% of U.S. textile exports went to the Western Hemisphere in 2020, including 46% for members of the U.S.-Mexico-Canada Trade Agreement (USMCA) and another 17.2% for members of the Dominican Republic-Central America Free Trade Agreement (CAFTA-DR).
Pattern #3: Fashion companies’ efforts to diversify apparel sourcing from China somehow slowed during the pandemic.
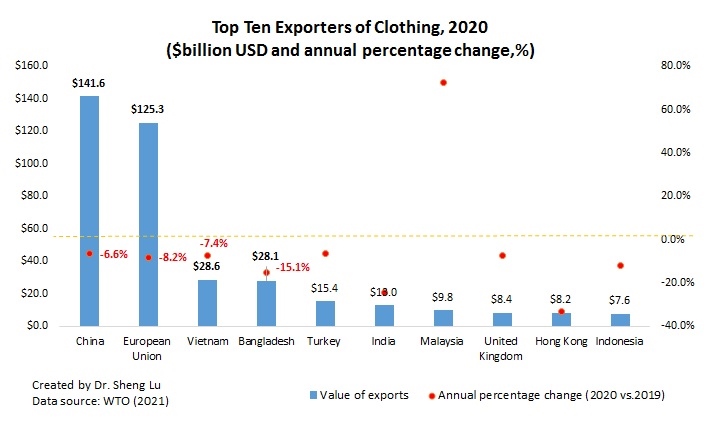
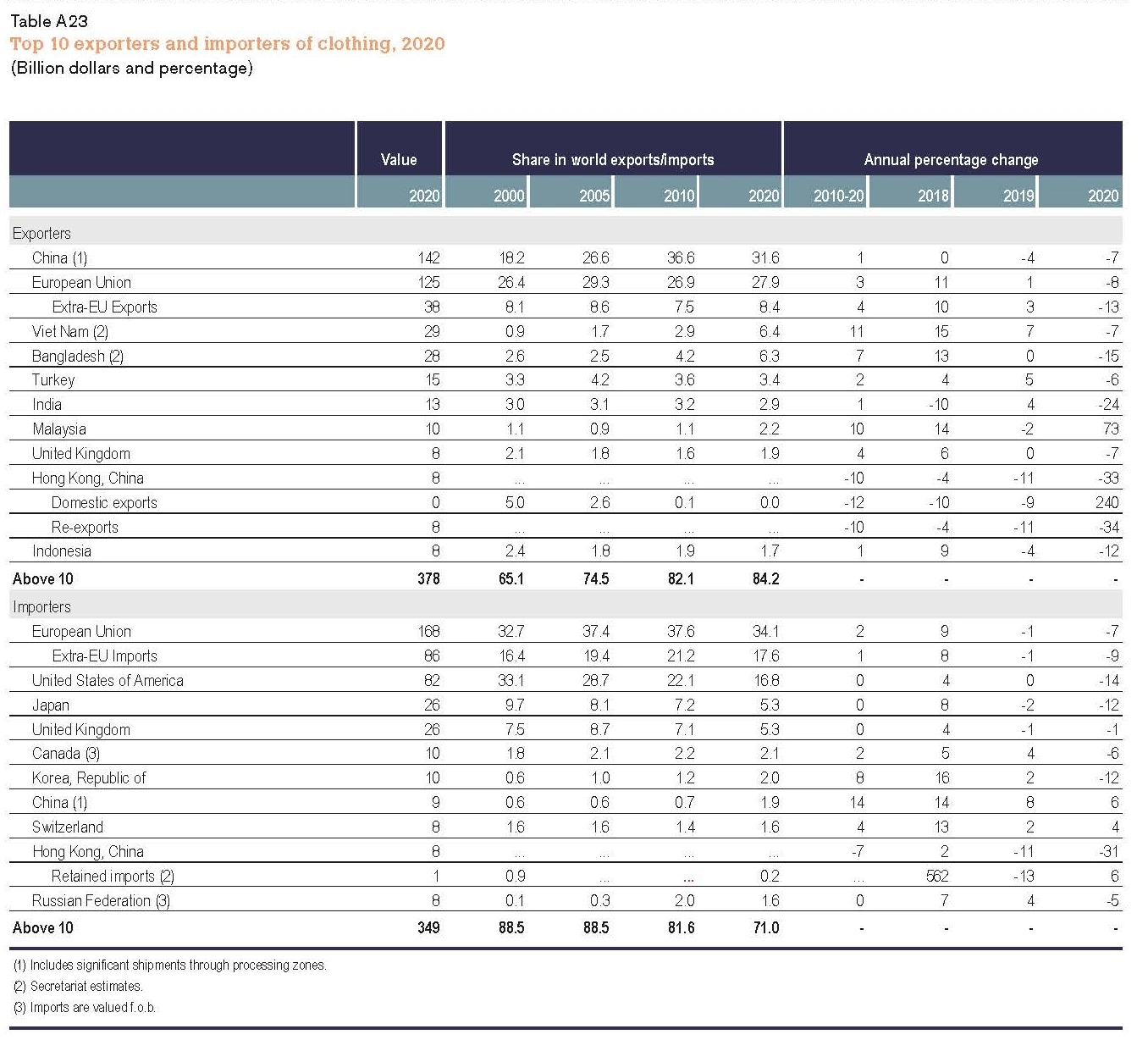
China, the European Union, Vietnam, and Bangladesh unshakably remained the world’s four largest apparel exporters in 2020. Altogether, these top four accounted for 72.2% of the world market shares in 2020, higher than 71.4% in 2019.
Notably, while China steadily accounted for declining shares in the world’s total apparel exports since 2015, its market shares rebounded to 31.6% in 2020 from 30.7% in 2019. We can observe a similar pattern in Canada (up from 36.2% to 41.2%) and the EU (31.2% to 31.3%), two of the world’s leading apparel import markets. Even in the U.S. market, where Chinese goods face adverse impacts of the tariff war, the market shares of “Made in China” only marginally decreased from 30.8% in 2019 to 29.8% in 2020, compared with a more significant drop before the pandemic (i.e., fell from 34.4% 2018 to 30.8% in 2019).
Several factors could explain the resilience of China’s apparel exports: 1) fashion brands and retailers’ particular sourcing criteria match China’s competitiveness during the pandemic (e.g., flexibility, agility, and total landed sourcing cost). 2) China has one of the world’s most complete textile and apparel supply chains, allowing garment factories to access textile raw material and accessories locally. 3) Compared with many other apparel exporting countries, China suffered a shorter COVID lockdown period and resumed apparel production earlier and more quickly. Most Chinese textile and apparel factories started to reopen in April 2020, and they resumed an overall 90%-95% operational capacity rate by July 2020.
Nonetheless, fashion companies are NOT reversing their long-term strategies to reduce “China exposure” for apparel sourcing. On the contrary, non-economic factors, particularly the concerns about forced labor in China’s Xinjiang region, push most western fashion brands and retailers to develop apparel sourcing capacities beyond China. Meanwhile, no single country has yet and will likely become the “Next China” because of capacity limits. Instead, from 2015 to 2020, China’s lost market shares in the world apparel exports (around 7.8 percentage points) were picked up jointly by its competitors in Asia, including ASEAN members (up 4.4 percentage points), Bangladesh (up 1.3 percentage points), and Pakistan (up 0.3 percentage point). Such a trend is most likely to continue in the post-COVID world.
Pattern #4: Developed economies led textile PPE imports during the pandemic, whereas the developing countries imported fewer textiles as their apparel exports dropped.
On the one hand, the value of textile imports by developed economies, including EU members, the United States, Japan, and Canada, surged by more than 30 percent in 2020, driven mainly by their demand for PPE. The result also reveals the significant contribution of international trade in supporting the supply and distribution of textile PPE globally. On the other hand, the developing countries engaged in apparel production and export drove the import demand for textile raw materials like yarns and fabrics. However, most of these developing countries’ textile imports fell in 2020, corresponding to their decreased apparel exports during the pandemic.
Pattern #5: Despite COVID-19, the world apparel import market continues to diversify. The import demand increasingly comes from emerging economies with a booming middle class.
Affected by consumers’ purchasing power (often measured by GDP per capita) and the size of the population, the European Union, the United States, and Japan remained the world’s three largest apparel importers in 2020, a stable pattern that has lasted for decades. While these top three still absorbed 56.2% of the world’s apparel imports in 2020, it was a new record low in the past ten years (was 58.1% in 2019 and 61.5% in 2018), and much lower than 84% back in 2005.
Behind the numbers, it is not the case that consumers in the EU, the United States, and Japan necessarily purchase less clothing over the years. Instead, several emerging economies have become fast-growing apparel-consuming markets with robust import demand. For example, despite COVID-19, China’s apparel imports totaled $9.5bn in 2020, up 6.5% from 2019. From 2010 to 2020, China’s apparel imports enjoyed a nearly 15% annual growth, compared with only 0.56% of the traditional top three. Around 30% of China’s apparel imports today are luxury items made in the EU.
By Sheng Lu
Further reading: Lu, S. (2021). World textiles and apparel trade amidst a pandemic – statistical review 2021. Just-Style.
Appendix

18 thoughts on “WTO Reports World Textiles and Apparel Trade in 2020”