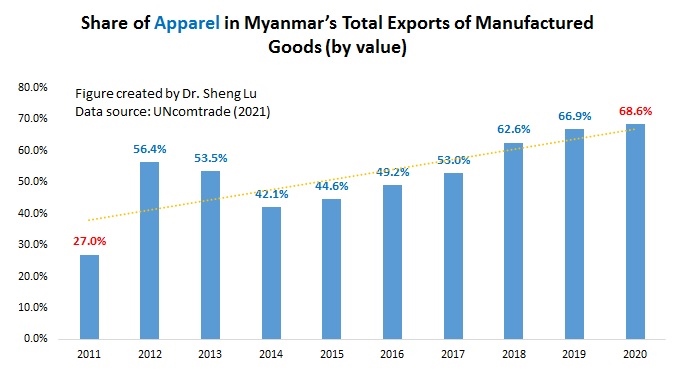
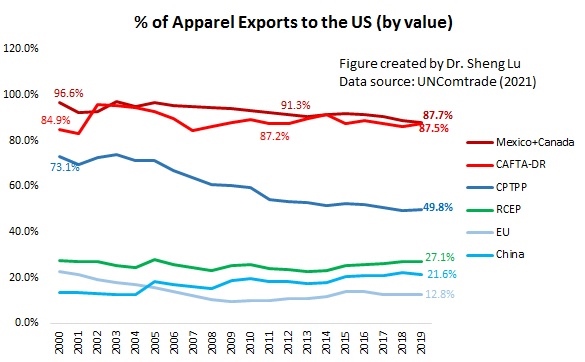
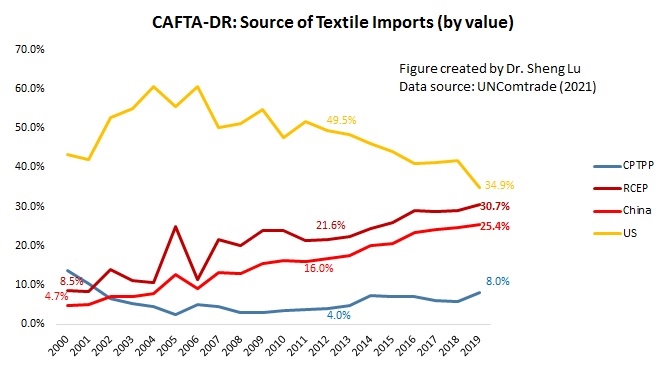
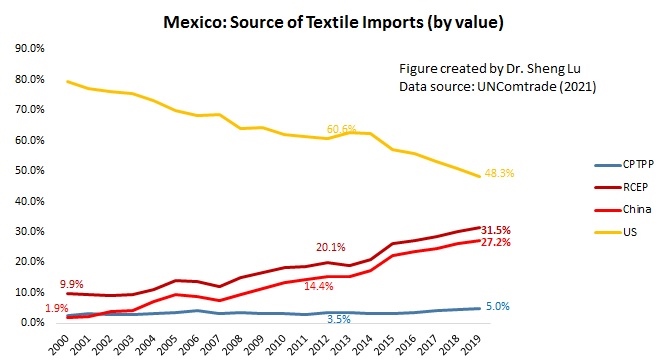
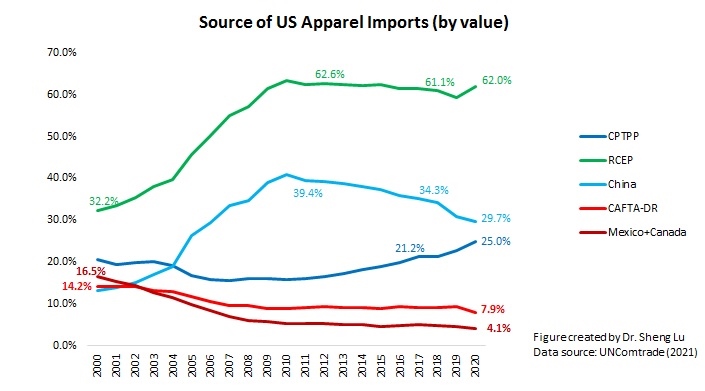
The textile and apparel industry plays a significant role in Myanmar’s economy, particularly the export sector. Data from UNComtrade shows that textile and apparel accounted for nearly 69% of Myanmar’s total exports of manufactured goods in 2020, a substantial increase from only 27% in 2011. Data from the International Labor Organization (ILO) also indicates that the textile and industry (ISIC 17 & 18) employed more than 1.1 million workers in Myanmar in 2019, up from 0.69 million in 2015. Most garment workers in Myanmar are women today (around 87%).
Since the United States lifted the import ban on Myanmar and the EU reinstated the Everything But Arms (EBA) trade preferences in 2013, Myanmar was one of the most popular emerging apparel sourcing bases among fashion companies. From 2020 to July 2021, some of the top fashion brands that carry “Made in Myanmar” apparel items include United Colors of Benetton, Next, Only, H&M, Guess, and Jack & Jones.
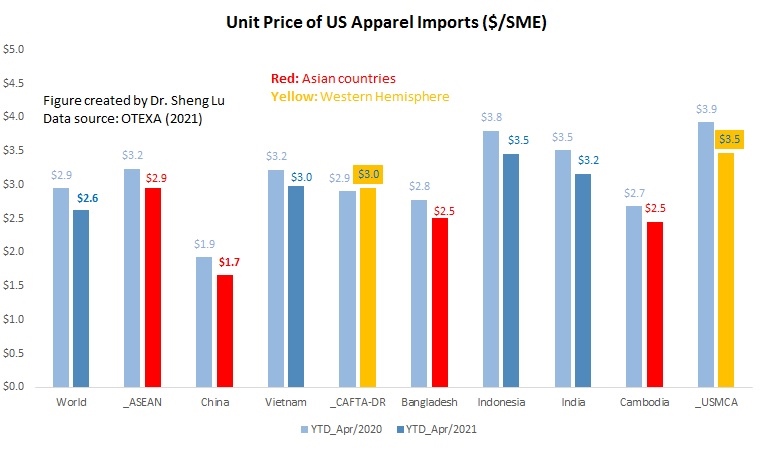
Thanks to foreign investment (note: nearly half of Myanmar’s garment factories are foreign-owned), Myanmar specializes in making relatively higher-quality functional/technical clothing (i.e., outwear like jackets and coats. Here is an example). This is different from many other apparel-exporting countries like Bangladesh, Vietnam, and Cambodia, mostly exporting low-cost tops and bottoms.
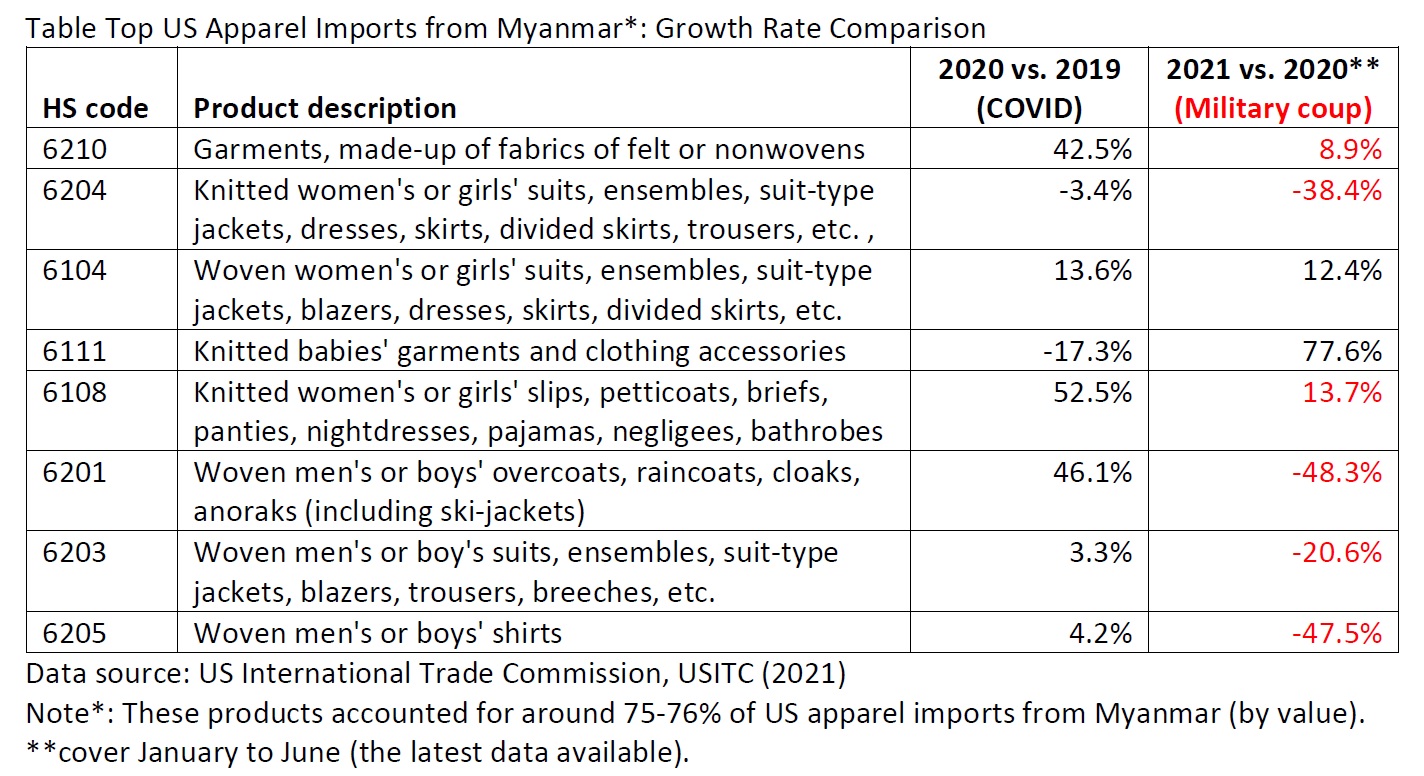
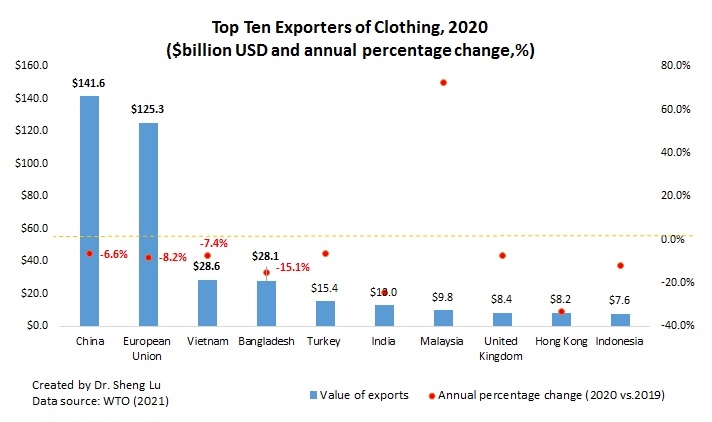
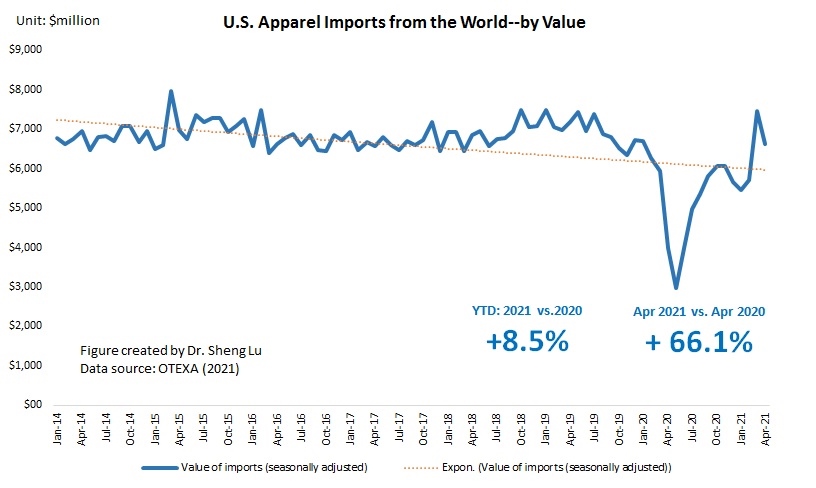
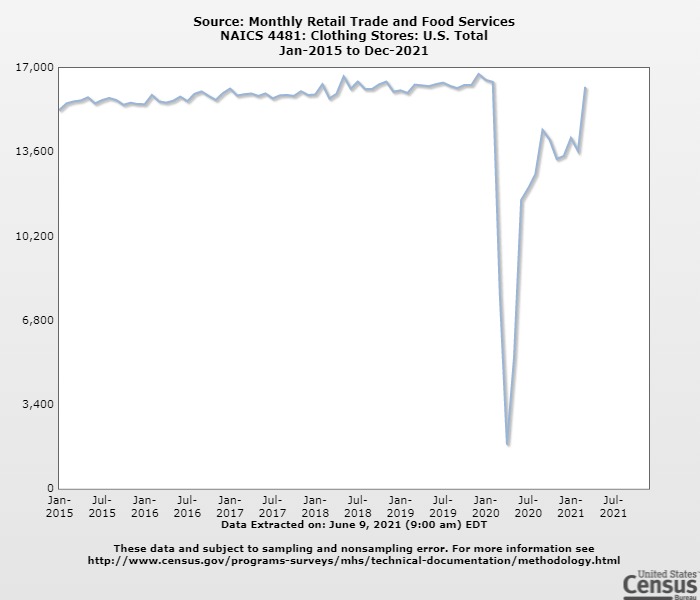
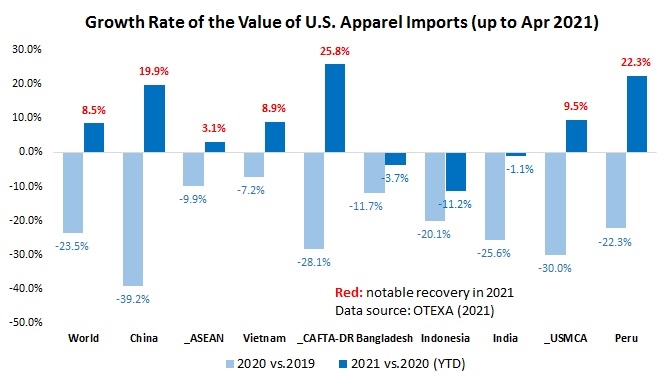
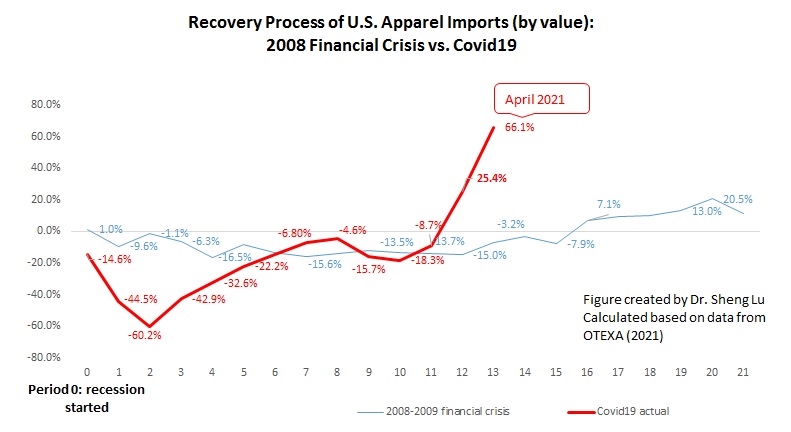
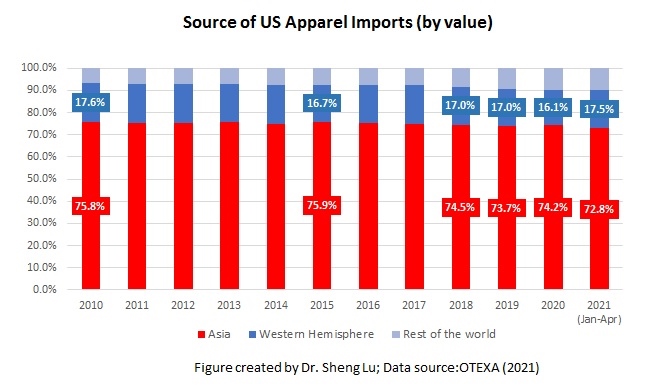
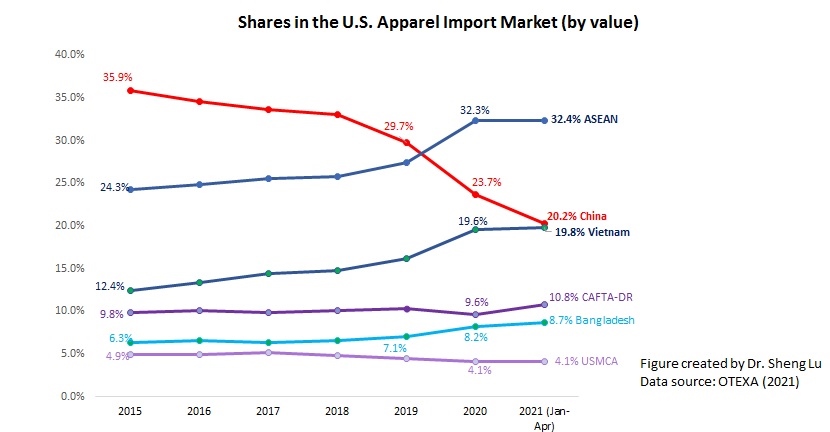
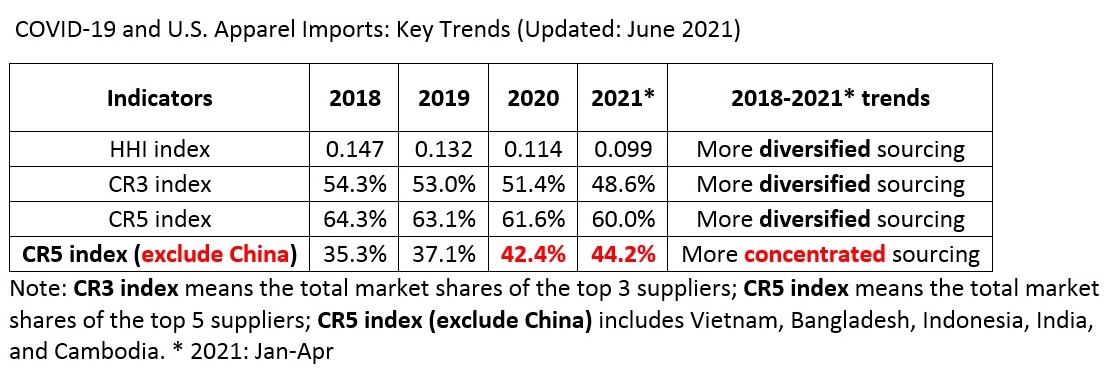
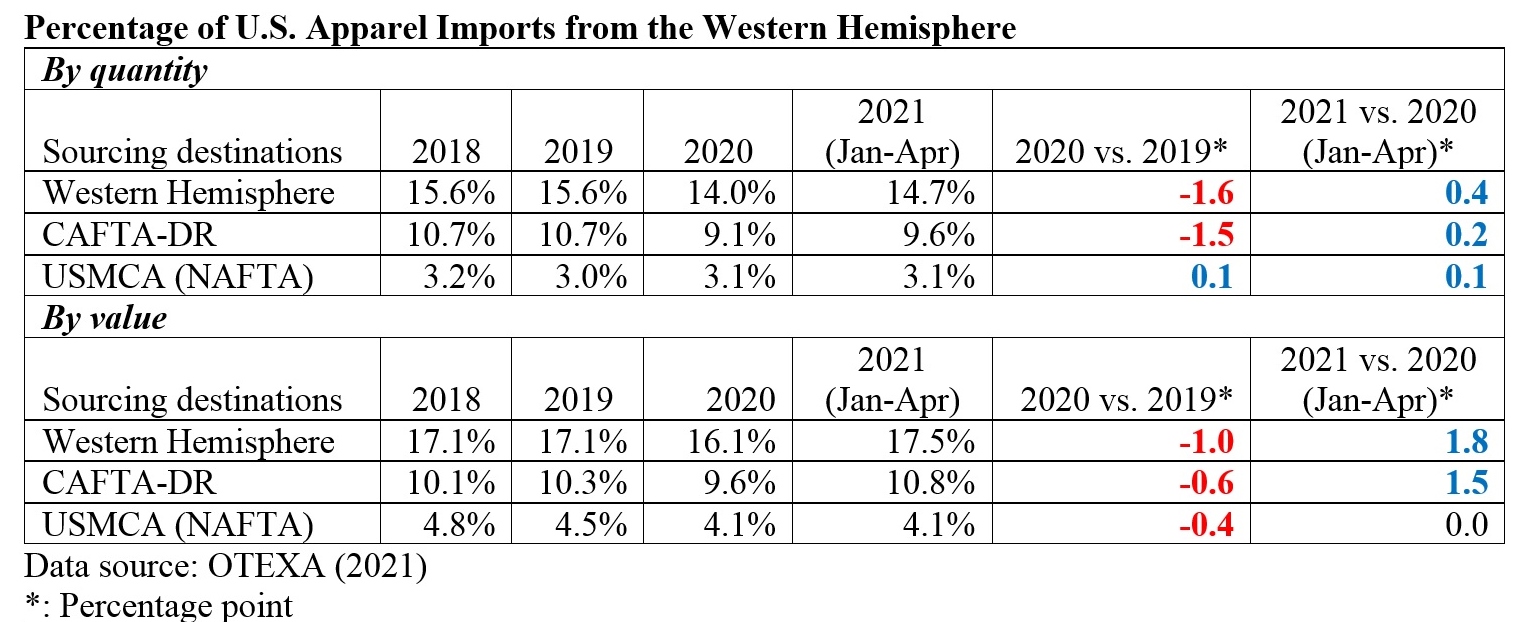
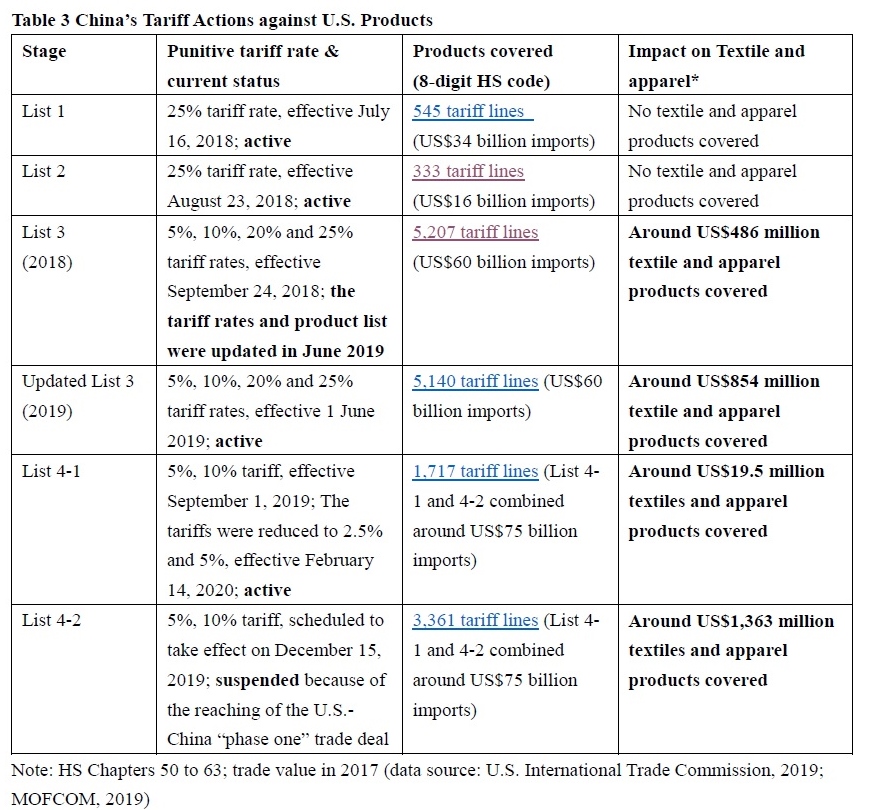
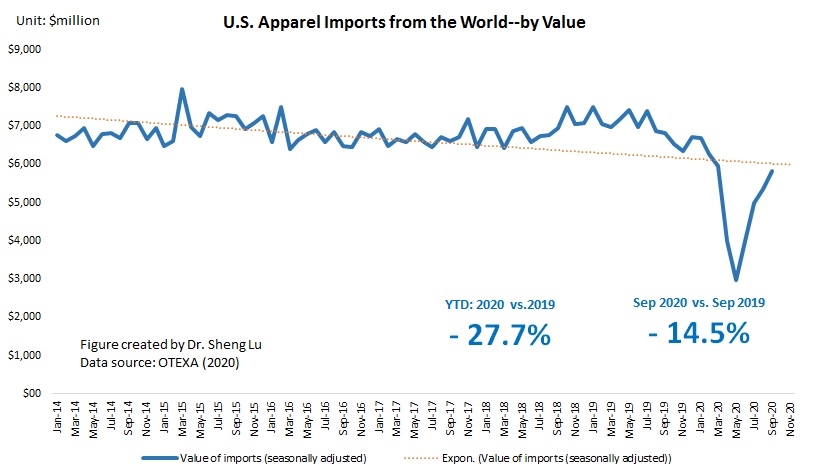
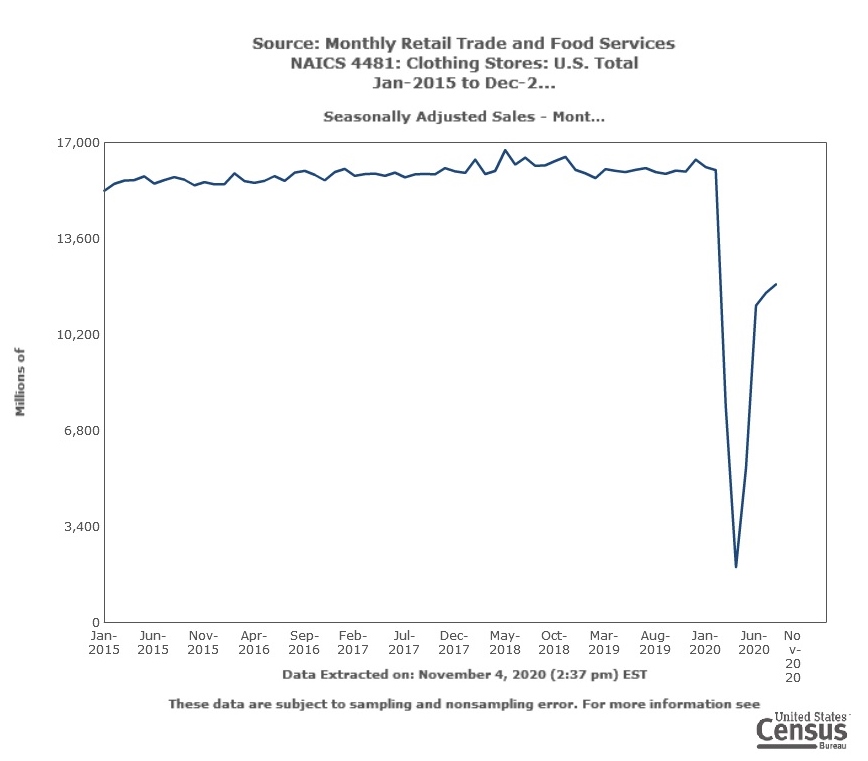
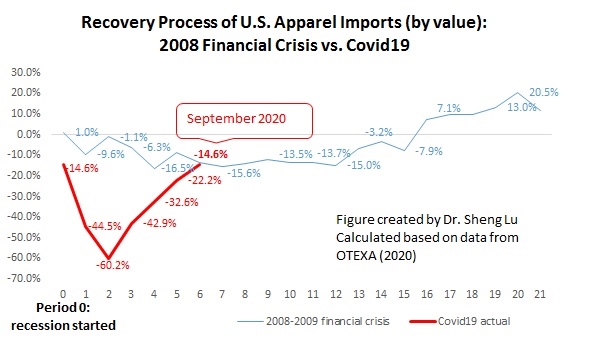
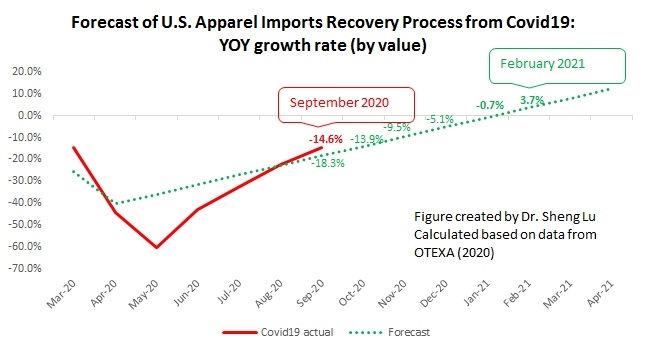
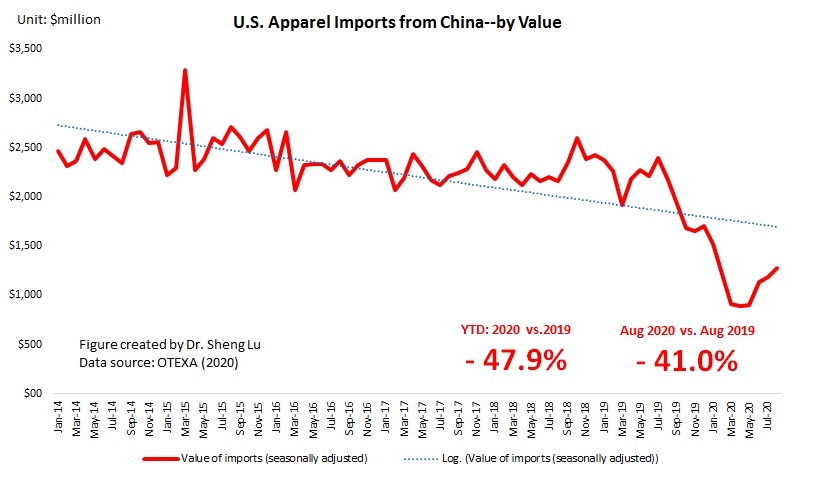
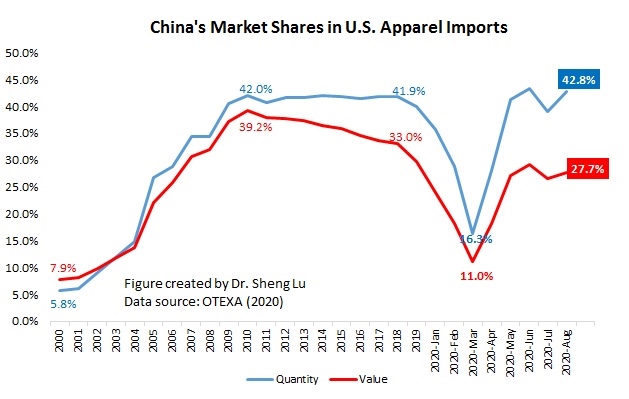
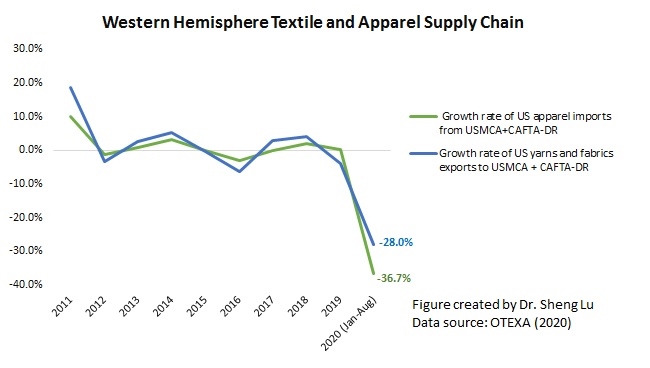
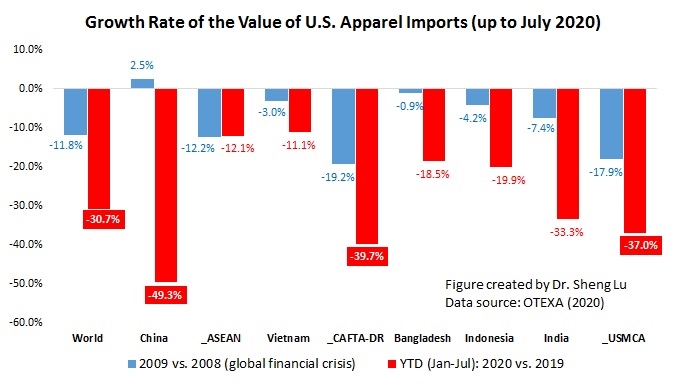
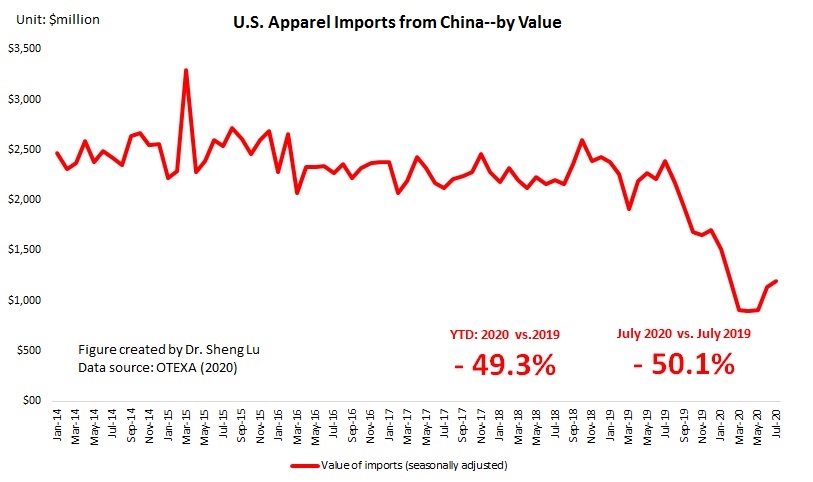
However, the latest trade data shows that Myanmar’s military coup that broke out in early 2021 had hurt the country’s apparel exports significantly. According to the US International Trade Commission (USITC), even though the total US apparel imports enjoyed a robust recovery in the first half of 2021 (up nearly 27%), the value of US apparel (HTS chapters 61 and 62) imports from Myanmar dropped by 0.4%. Almost ALL Myanmar’s top apparel exports to the US suffered a substantial decline or much slower growth in 2021 than the trend BEFORE the military coup (see the Table above). As US fashion companies switch sourcing orders from Myanmar to other suppliers, Myanmar’s market shares fell from 0.5% in 2020 to only 0.3% in the first half of 2021.
Highly consistent with the trade data, according to the 2021 Fashion Industry Benchmarking Study, many surveyed US fashion companies expressed concerns about the military coup in Myanmar and the rising labor and social compliance risks when sourcing from the country. Some respondents explicitly say they are leaving because of the current situation. “(We) have terminated sourcing from Myanmar due to instability.” says one respondent. Another adds, “We had orders in Myanmar that have already been moved to Cambodia. We are unlikely to place orders until the current situation is resolved.”
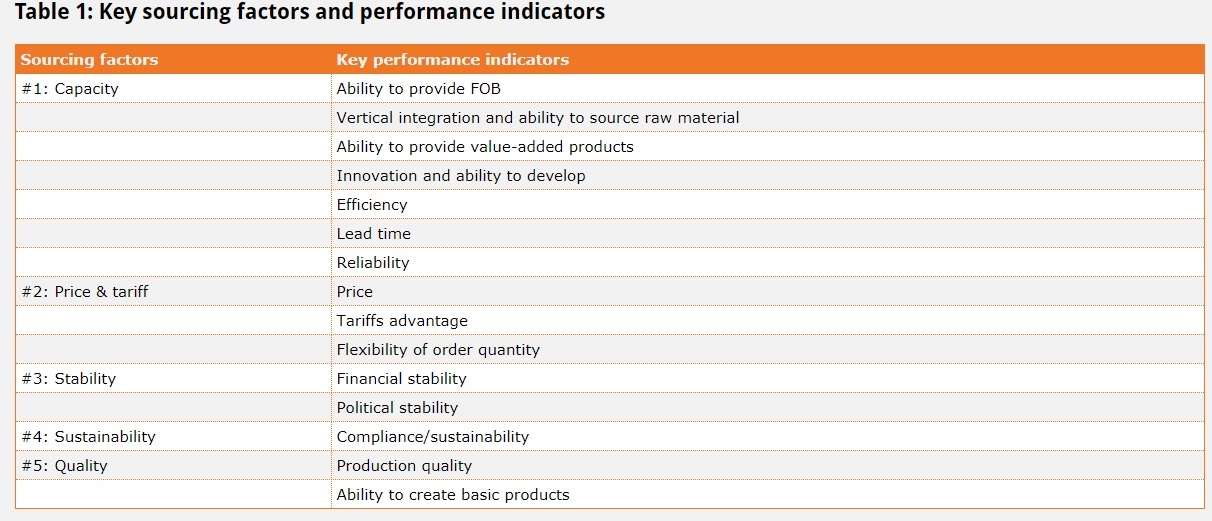
In another recent study, we find that apparel sourcing is not merely about “competing on price.” Instead, fashion companies give substantial weight to the factors of “political stability” and “financial stability” in their sourcing decisions today. In other words, the reputation risks matter for sourcing.
Unfortunately, the situation could get worse. The international community, including the US and the EU, is considering new sanctions against Myanmar, including suspending Myanmmar’s trade-preference program eligibility.
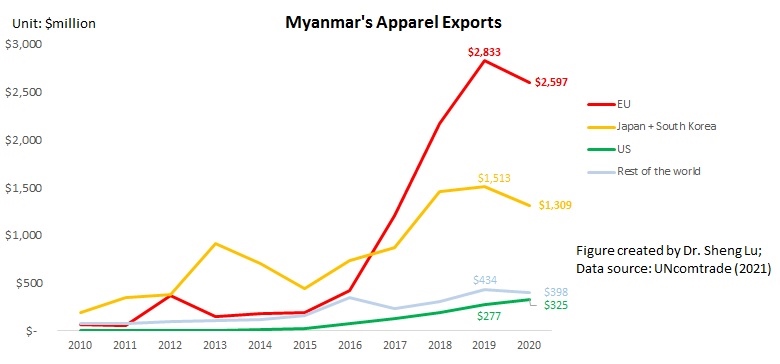
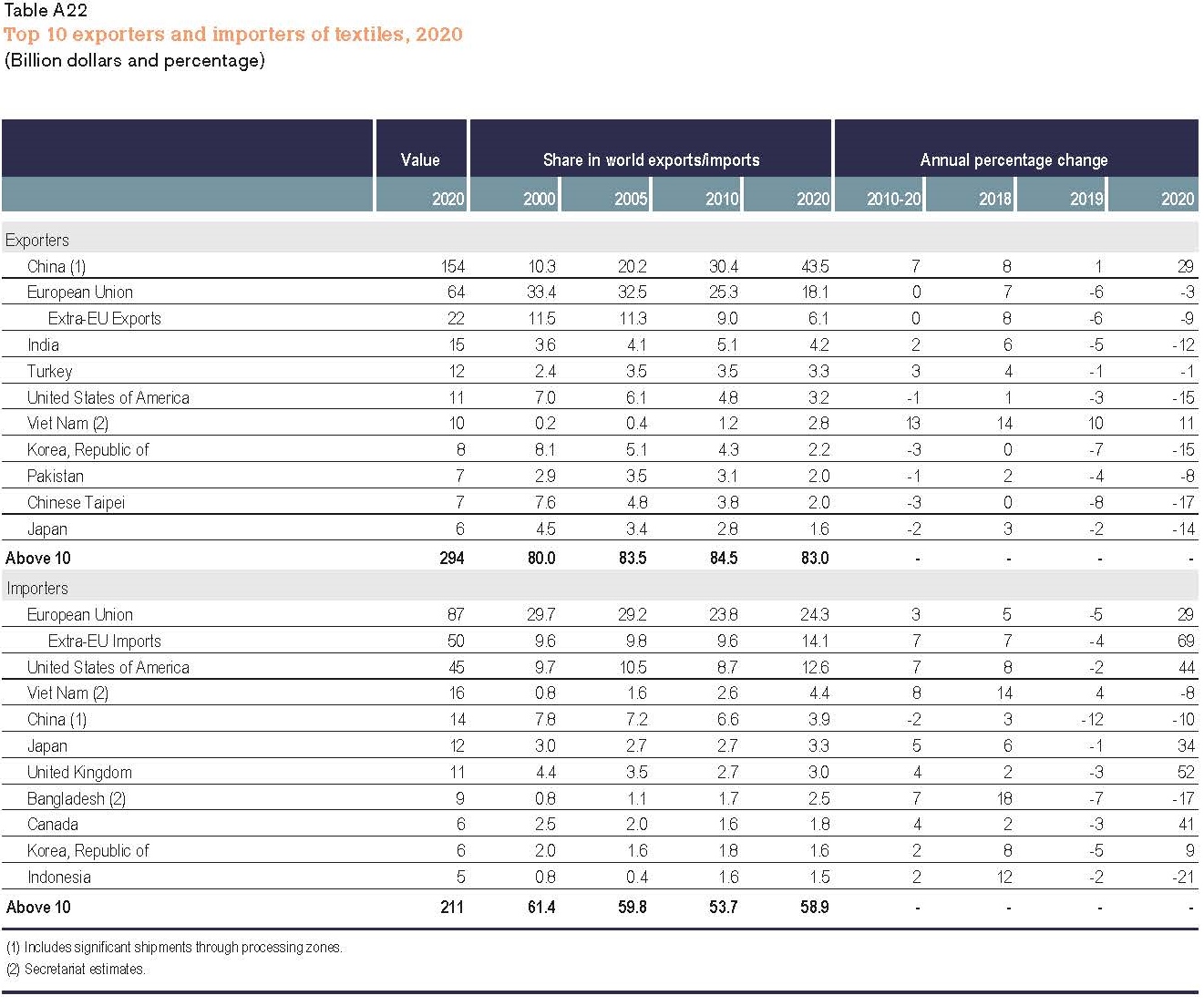
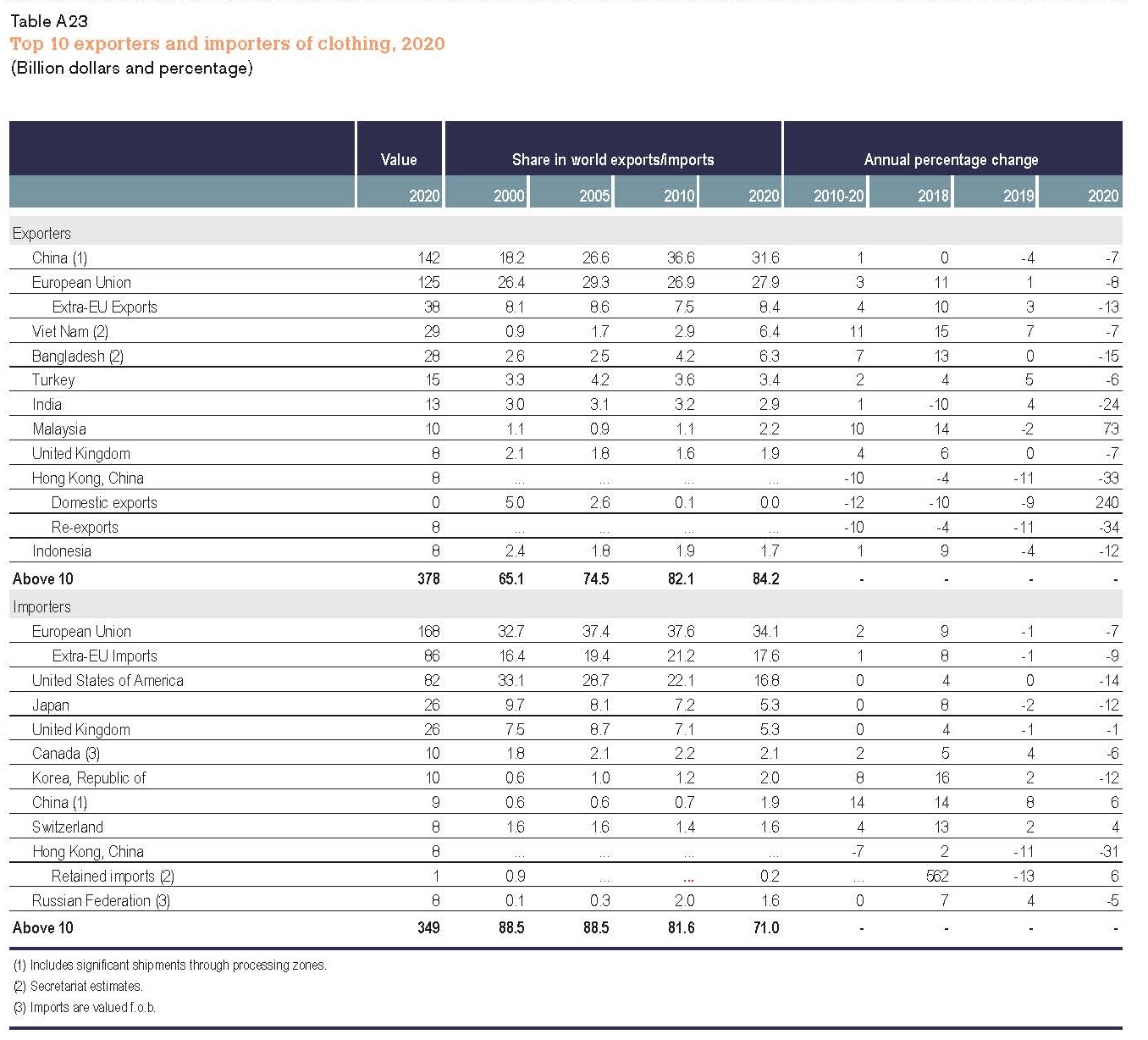
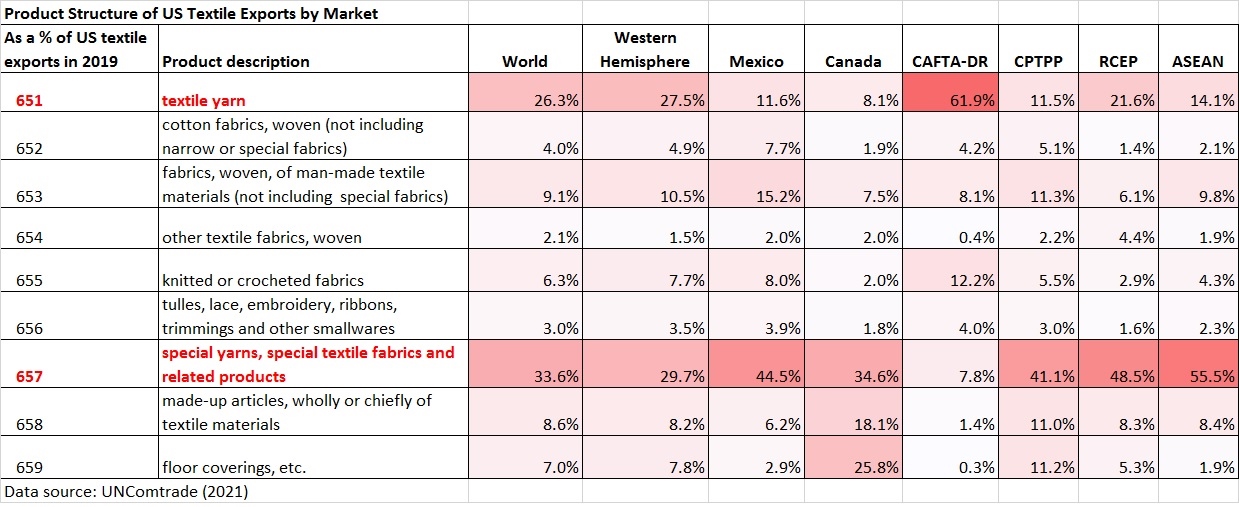
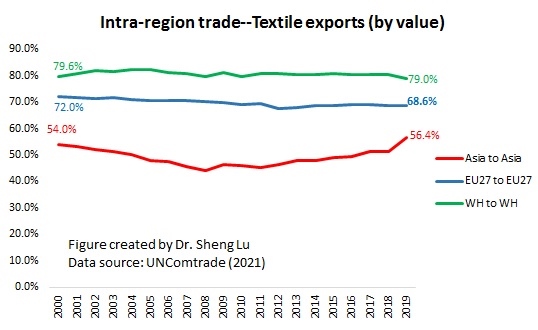
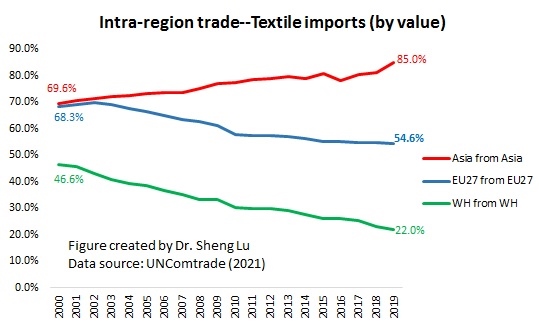
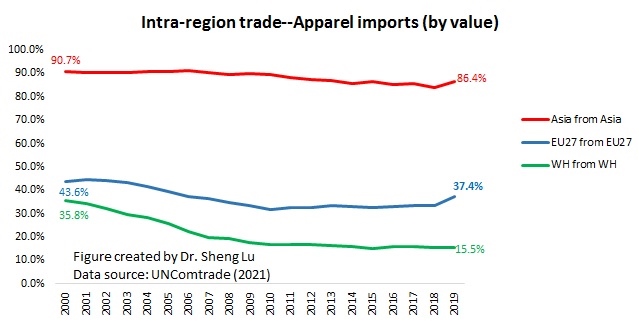
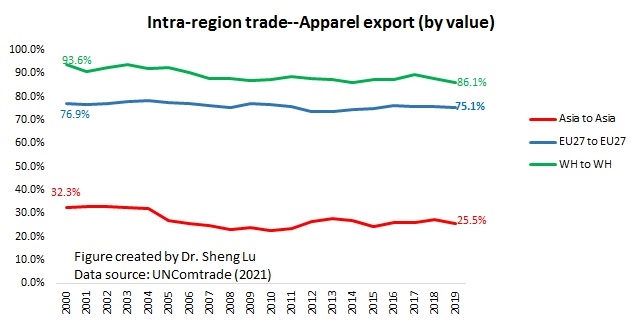
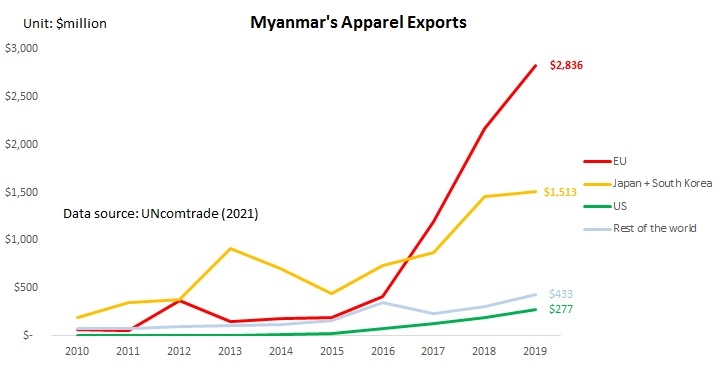
Designated as a “least developed country” (LDC) by the World Trade Organization, Myanmar’s apparel exports enjoy duty-free market access in the EU, Japan, and South Korea. These countries also, in general, offer very liberal “single transformation” (or commonly known as cut and sew) rules of origin for qualifying apparel made in Myanmar. This explains why Myanmar’s apparel exports mostly go to the EU (56%), Japan, and South Korea (around 30%).
The United States is another important export market for Myanmar, accounting for 7% of the country’s total apparel exports in 2020. As a beneficiary of the US Generalized System of Preferences (GSP) program, Myanmar’s luggage exports enjoy duty-free benefits in the US market. However, the US GSP program excludes textile and apparel products, meaning Myanmar’s apparel exports to the US still are subject to the regular Most-Favored-Nation (MFN) tariff rate at around 14.3% on average in 2020.
The Office of the US Trade Representative (USTR) already hinted that even if US Congress renews the GSP program, which expired on 31 December 2020, the US government likely will suspend Myanmar’s GSP eligibility because of the military coup in the country. Likewise, in February 2021, the European Union suspended its support for development projects in Myanmar to avoid providing financial assistance to the military after the coup. Should Myanmar lose the EU’s Everything But Arms (EBA) program eligibility, its export-oriented garment sector and millions of garment workers could be among the biggest losers.
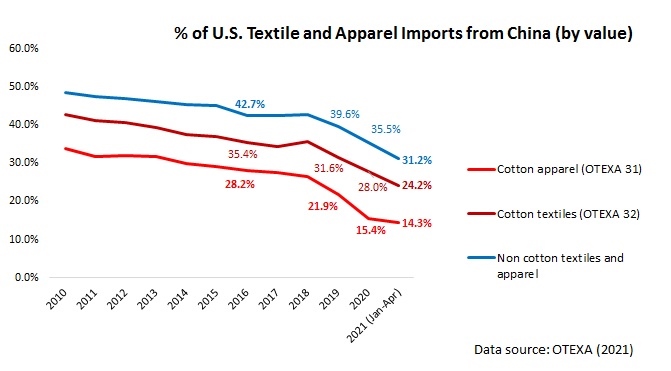
Further, given Myanmar’s highly concentrated apparel export markets and the pandemic, it will be challenging for Myanmar’s garment producers to find alternative apparel export markets in a relatively short period. For example, although China is recognized as one of the world’s largest and fastest-growing emerging import markets, only 1.4% of Myanmar’s apparel exports went to China in 2020.
by Sheng Lu
Further reading: Lu, Sheng (2021). A snapshot of the Myanmar apparel and exports industry in 2021. Just-Style.